Human Reproduction
advertisement

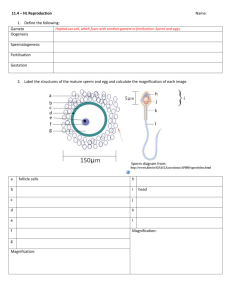
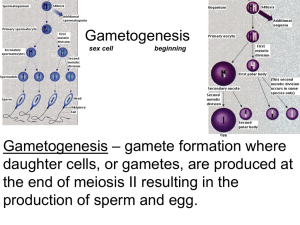
Human Reproduction Spermatogenesis Spermatogenesis • Sperm production begins during puberty and is stimulated by the release of hormones – Sperm production is controlled by the hypothalamus and ant. Pituitary through negative feedback Spermatogenesis •Hypothalamus releases gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH) which triggers ant. pit. To release FSH and LH •FSH triggers seminiferous tubules to produce sperm •LH triggers testosterone production by Leydig cells (interstitial cells) which increases sperm production Testosterone • Produced by interstitial cells in the Testes – Also responsible for Secondary sex chars. •Voice Deepens •Body Hair •Strengthening of muscles •Sex drive Hormonal control Spermatogenesis: The making of sperm • Seminiferous tubules in the testes are the site of sperm cell production – Lumen of tubules is lined with spermatogonia • 46 chromosomes • Undergo mitosis to form primary spermatocytes – primary spermatocytes undergo meiosis to produce secondary spermatocytes (46 Chromosomes *) and eventually spermatids (23 chromosomes) – One primary spermatocyte will eventually produce four sperm cells Spermatogenesis • Spermatogenesis occurs at the onset of puberty – Several hundred million produced/day – Formation of a mature sperm cell takes about 70 – 80 days • Sperm cells mature in the epididymis • Develop flagella and begin to swim within 4 days Spermatogenesis Mature Sperm Human Reproduction Oogenesis Oogenesis • All follicles are produced in the ovaries during the first during the 1st six months of fetal development – – – – Max. of 7 million produced 2 million left at birth 400,000 at onset on puberty Approx. 400-500 mature ova develop and are released during the reproductive years Oogenesis • Follicles consist of two types of cells: – Primary oocyte – Granulosa cells • Clusters of these cells are called primordial follicles – Granulosa provide nutrients, chemical signals, and protection for the developing follicle Oogenesis • 6-20 primary follicles begin to mature each month • Only one follicle fully matures and is released from one ovary each month during reproductive years Ovulation • The ovum is released out of the ovary and will move into the fallopian tube • Remaining follicular cells change and become the corpus luteum – Secretes progesterone and estrogen • If ovum remains unfertilized, corpus luteum degenerates and new cycle will begin Hormonal control • Cyclic process in females (continuous in males) • Hypothalamus secretes GnRH • Stimulates LH and FSH in ant. Pit. • Effects of LH and FSH on ovaries varies during the cycle The Ovarian Cycle • 28 days long, divided into 3 phases – Follicular phase (12 days) – Luteal phase (11 days) – Menstrual phase (approx. 5 days)