File
advertisement

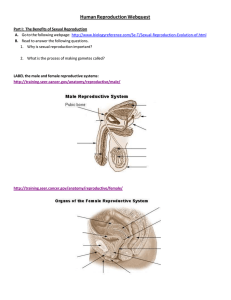
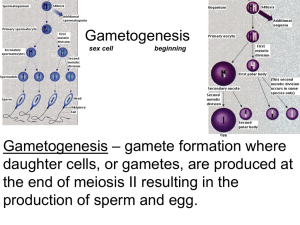
Reproductive System Ch 19 General Functions of reproductive system. Produce and nurture sex cells Gametes Sperm Eggs Transport them to sites of fertilization. Meiosis - Overview Creates sex cells with half the number of chromosomes as normal cells. Haploid Two divisions Males: Spermatogenesis Females: Oogenesis 46 46-46 23-23 23 23-23 23 23 23 Meiosis - Sperm Meiosis - Egg Locate and describe the general functions of each part of the male reproductive system testes epididymis scrotum bulbourethral gland prostate gland seminal vesicle ductus deferens urethra corpus cavernosum corpus spongiosum penis glans penis Outline the process of spermatogenesis. spermatogenesis – formation of sperm Spermatogenic cells (spermatogonia) formed in the testes (46 chromosomes) At puberty when testosterone production resumes... Form primary spermatocytes Meiosis takes place First division makes secondary spermatocytes Second division makes spermatids (23 chromosomes) Outline the process of spermatogenesis. When spermatids reach the epididymis, they are nonmotile. By the time they are pushed through the epididymis, they have matured into sperm cells and can move independently. Describe semen production and exit from the body. Production takes place in four parts: Testes – sperm Seminal vesicles Prostate gland Bulbourethral glands Exits by ejaculation through the penis. Vocabulary spermatogenesis spermatogonia spermatid Explain how hormones control the activities of the male reproductive organs… GnRH – released in hypothalamus Pituitary gland– secretes gonadotropins In males, these are androgens LH (leutinizing hormone) FSH (follicle-stimulating hormone) Testosterone …and the development of male secondary sex characteristics Body hair Lower voice Thickening of skin Increased muscular growth Thickening/strengthening of bones More about hormones There’s a negative feedback system that controls the amount of testosterone released. Locate and describe the general functions of each part of the female reproductive system Ovaries Uterine tube Uterus Cervix Vagina Clitoris Endometrium Myometrium Perimetrium Outline the process of oogenesis. What is oogenesis? Primordial follicles are formed during fetal development. These are also calle primary oocytes. At puberty, primary oocytes continue meiosis. Cytoplam is distributed unevenly, so only one secondary oocyte is formed. Meiosis - Egg Outline the process of oogenesis. Secondary oocyte is released from the ovary – Ovulation Uterine tubes – fertilization IF it’s fertilized, it will go through Meiosis II and become a zygote. Only have about a day! Uterus – receives embryo and sustains development Three layers Endometrium Myometrium Perimetrium Vagina – birthing purposes and receives sperm Explain how hormones control the activities of the female reproductive organs... Puberty – FSH is released and ovaries enlarge LH triggers ovulation. Two main types of female hormones – estrogens and progesterones. Ovaries are the major source of estrogens. They stimulate enlargement of vagina, uterus, uterine tubes, and ovaries. They develop secondary sex characteristics. ...and the development of the female secondary sex characteristics. Development of breasts and ductile system of mammary glands Increased deposition of adipose tissue generall, and specifically in the breasts, thighs, and buttocks. Increased blood vessels in skin. Females also have a low androgen concentration that stimulates hair growth in pubic and axillary regions. Vocabulary Spermatogenesis Spermatid Spermatogonia Oogenesis Oocyte Ovulation Androgen Testosterone Estrogen Progesterone Describe the major events of the reproductive cycle. FSH and LH released from pituitary gland. FSH causes follicle to become primary oocyte. Follicular cells secrete estrogen causing endometrium to thicken. More LH from pituitary gland stimulates ovulation. More estrogen and progesterone is released – waiting for fertilization. Describe the major events of the reproductive cycle. If fertilization does not occur, estrogen and progesterone stop – causes endometrium to quit building. Uterine lining disintegrates and sloughs off. Cylce repeats with LH and FSH being released from pituitary.