Glaciers
advertisement

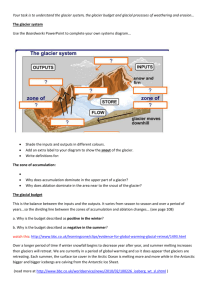
8.3 Glaciers Types of glaciers Alpine Small glaciers that form valleys Ice sheets Enormous glaciers that can cover entire continents Glacier Formation Describe the steps Firn: Thick, dense compacted snow Glacial ice: Firn compacts into glacial ice Advancing: A glacier growing faster than it is melting Retreating: A glacier melting (receding) at the leading edge faster than its growing. It’s NOT traveling backwards. Glacier Movements Plastic Flow Describe: Deep within, there is a huge amount of pressure due to weight of ice pressing down. 50 meters thick of ice creates enough pressure to cause ice to flow through the center of a glacier very slowly. Glacier Movements Basal Slip Describe: Water beneath glacier acts as a lubricant, so entire glacier can slide. This movement can cause a large crevasse (crack), to form. Rate of movement: Typically a few meters/ day, but can have faster surges. Glacial structures from erosion Striation Long scratch marks found in rocks due Describe: abrasion caused by rocks & gravel dragged by glacial movement. U-Shaped Valleys Describe: V-shaped valleys that are widened by glaciers. Glacial structures from erosion Horn peaks Describe: When several cirques converge, the part that is not cut out looks like a horn sticking out of the ground. Cirques Describe: Valleys that look like giant armchairs because they have 3 steep sides & one open side. Glacial structures from erosion Fjords Describe: Very steep inlets to the ocean. Roche moutonnees Landforms w/ 1 rough side & 1 side that has Describe: been abraded smooth. Glacial Drift Describe: The coarsely graded sediment deposited by glaciers Till Describe: Unsorted glacial sediment Structures Formed Glacial Erratics Describe: Big rocks deposited by a glacier into an area w/ a different type of rock. Morraines Describe: Piles of boulders, rocks, pebbles, & clay left behind by a glacier. Structures Formed Terminal Moraines Describe: form at the edge of glaciers. Drumlins Describe: Smooth, egg-shaped hills left behind by continental ice sheets. Stratified Drift Define: Deposits left by melted water coming off a glacier. Structures Formed: kettles Describe: When large blocks of ice get trapped under stratified drift, the ice melts and leaves large holes. Eskers Describe: Winding ridges of sand & gravel left behind by receding glaciers. Earth’s Orbit Effects: Change in Earth’s orbit around the sun cause slight temperature variations. Precession Effects: The tilt of Earth’s axis changes over time & can affect the amount of sunlight reaching different parts of earth. Current ice age theory Explain: Changes in the Earth’s axis of rotation can work together to alter the temperatures. This is thought to lead to the formation of large glaciers & put Earth into ice ages. Last ice age 2 million years ago, & peaked 20,000 years ago.