ESS 005
advertisement

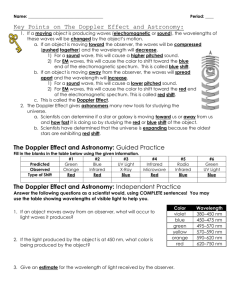
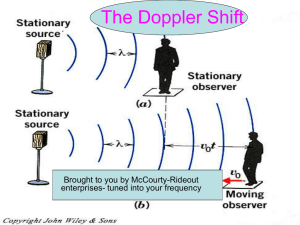
The Launch Pad Friday, 8/27/10 Which of the following provide compelling evidence for the Big Bang theory? A.The universe is expanding B.We can detect cosmic background radiation noise in all parts of space. C.Most galaxies are moving away from each other. D.All of the above are evidence. In ongoing observations of one of the universe's earliest, most distant cluster of galaxies using NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope, an international team of researchers led by Texas A&M's Dr. Kim-Vy Tran has discovered that a significant fraction of those ancient galaxies are still actively forming stars. Assignment Currently Open Pages Date of Notes on Website Date Issued Date Due Information Sheet N/A N/A 8/23 8/24 Class Procedures and Expectations 1-4 N/A 8/23 8/25 Einstein’s Theory of General Relativity Albert Einstein's theory of general relativity indicates that the universe (i.e., the space-time metric) was described by a metric tensor that was either expanding or shrinking (i.e., was not constant or invariant), this result coming from an evaluation of the field equations of the general theory. Friedmann derived the expanding-universe solution to general relativity field equations in 1922. Expansion of the Universe Diffuse cosmic background radiation (COBE spacecraft) Relative abundances of elements The end: Expansion forever or the Big Crunch? The Doppler Effect is the apparent change in frequency of waves (pitch) due to the motion of the source or observer. Note: The higher the frequency the higher the pitch. A great example is an ambulance’s siren coming toward you and then passing you. The pitch drops as the ambulance passes. The Doppler Effect • The Doppler Effect is the apparent change in wavelength of radiation caused by the relative motions of the source and observer. It is used to determine: direction of motion. increasing distance – wavelength is longer (“stretches.”) decreasing distance – makes wavelength shorter (“compresses.”) velocity – larger Doppler shifts indicate higher velocities. The Doppler Effect • So, the Doppler Effect is the change in the wavelength of light emitted by an object due to its motion. Movement away stretches the wavelength Longer wavelength Light appears redder Movement toward “squeezes” the wavelength Shorter wavelength Light shifted toward the blue Figure 23.2 The Doppler Shift • The amount of the Doppler shift indicates the rate of movement . •Large Doppler shift indicates a high velocity •Small Doppler shift indicates a lower velocity The Expanding Universe • Most galaxies exhibit a red Doppler shift , meaning they are moving away from us. • Far galaxies •Exhibit the greatest shift •Greater velocity • Discovered in 1929 by Edwin Hubble • Hubble’s Law – the recessional speed of galaxies is proportional to their distance • Accounts for red shifts • If a yellow star is stationary, the light waves it emits are neither bunched together nor stretched out; therefore, it appears yellow. • If the same yellow star is approaching rapidly, its light waves will be bunched together; therefore, it appears blue. • If the same yellow star is receding rapidly, its light waves will be stretched out; therefore, it appears red. • • When a star (or galaxy) is approaching us or receding from us, the light waves emitted as a particular color (e.g., yellow) are bunched together or stretched out. This shifts the object’s light (both the maximum and all spectral lines) toward the blue or red part of the spectrum.