Temp. and Color: Blackbodies Radiation from a Heated Object
advertisement

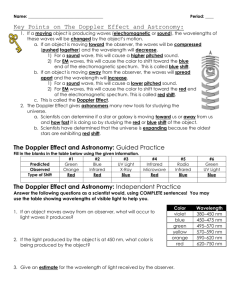
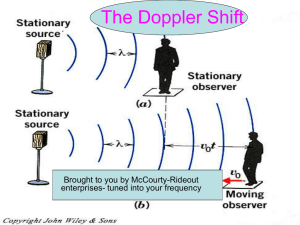
Temp. and Color: Blackbodies • A blackbody absorbs and re-emits all light that falls on it • Idealized objects – But still a good model for ______ Radiation from a Heated Object • Intensity vs. wavelength for three objects of different temperatures. • They don’t actually look black (misnomer) – Color depends on their temperature Radiation from a Heated Object • The curves are high in the middle and low at either end. – These objects emit most intensely at middle wavelengths. Radiation from a Heated Object • Wavelength of maximum intensity depends on __________. – The hotter the object, the ________ the wavelength of max. intensity Radiation from a Heated Object • The total ____ under each curve is proportional to the total _______ emitted. – Hotter object emits more total energy than cooler objects. Radiation from a Heated Object • Temperature determines the _____ of a glowing black body. – The hotter object emits more blue light than red, and thus looks blue. – The cooler object emits more ____ than ____, and consequently looks ____. 1 Temp. and Color: Blackbodies ______ Object _______ Object Blackbody Radiation Lecture Tutorial: page 57 • Work with a partner or two • Read directions and answer all questions carefully. Take time to understand it now! • Come to a consensus answer you all agree on before moving on to the next question. • If you get stuck, ask another group for help. • If you get really stuck, raise your hand and I will come around. Comparing Spectra • Peak at shorter wavelength = _______ temperature • Higher temperature = _____ in color • Larger _____ ____ under curve = higher total energy output 2 Example: Solar Spectrum What can we learn from light? • • • • Temperature Energy Chemical Composition Speed towards or away from us All from the ________! Hydrogen Lines Visible Hydrogen Spectrum Lines: _______ Series Lower E, Lower f, _____ λ Long λ = ____ E Visible! Higher E, Higher f, ______ λ Spectral Classification • Get spectral type from line features, predict ____________ • Subdivisions within each letter: 0-9 – 0 is _______, 9 is _______ – Sun is a G2 star (hotter than a G8 star) Short λ = ____ E Spectral Classification • O, B, A, F, G, K, M – “Oh Be A Fine Girl/Guy Kiss Me” – “Only Boring Astronomers Feel Good Knowing Mnemonics” • Subdivisions 0-9 – Sun is a G2 star – Predict temperature to 5% 3 Actual Spectrum from SDSS The Doppler Effect Intensity Balmer • How does light tell us the speed of a distant object? Lines Wavelength The Doppler Effect Doppler Effect • Definition: “The change in ________ of radiation due to relative radial motion between the source and the observer.” Real Life Example of Doppler Effect The change in the pitch of a siren on a police car, fire truck, or ambulance as it zooms past (sound waves) Doppler Effect • When something which is giving off light moves towards or away from you, the _______ of the emitted light is changed or shifted V=0 Star Light Wave Astronomers deal with the Doppler Effect of light waves 4 Doppler Effect • When the source of light is moving away from the observer the wavelength of the emitted light will increase. We call this a “_______”. Doppler Effect • When the source of light is moving towards the observer the wavelength of the emitted light will appear to decrease. We call this a “_______”. Doppler Effect • “Radial” means “along line of sight” • Doppler Effect happens only if the light source is moving _______ you or _____ _____ you. Direction of shift tells us direction of light source’s motion Doppler Effect V=0 Amount of shift tells us speed of source’s motion 5 Doppler Shifts • Redshift (to _______ wavelengths): The source is moving away from the observer • Blueshift (to _______ wavelengths): The source is moving towards the observer Δλ= ____________ λ0 = wavelength if source is ____ _______ V = velocity of source c = speed of light Doppler Effect Lecture Tutorial: Page 73 • Work with a partner or two • Read directions and answer all questions carefully. Take time to understand it now! • Come to a consensus answer you all agree on before moving on to the next question. • If you get stuck, ask another group for help. • If you get really stuck, raise your hand and I will come around. Chapter 6 Recap • Atoms, electron energy levels, absorbing & emitting light • Temperature & color • Types of spectra: absorption, emission, continuous • Spectral Classes: OBAFGKM • Doppler shift & speed 6