MODULE 1 TAKING A HEALTH HISTORY Format Components
advertisement
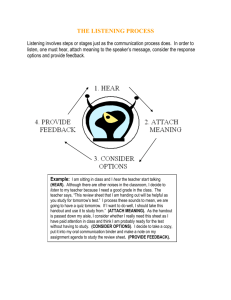
MODULE 1 TAKING A HEALTH HISTORY Format Components Module Description and Content Goals: Given topics on health care taking and collecting subjective data; texts that are varied and of a specialized and medical nature, which include information presented from dialogues and other sources (e.g. photographs, drawings, reference text /research information), the participant will use English with 70 % accuracy to: 1. Review and use idioms people regularly use to report when they are feeling sick. (Words and Expressions to Know). 2. Identify and demonstrate proper note-taking techniques; take notes of a health history. (Listening) 3. Identify and use some common medical abbreviations used in the recording of health histories. (Writing) 4. Listen for main ideas and details. (Listening) 5. Identify health history terms. (Speaking) 6. Review how to form questions properly. (Grammar) 7. Conduct an interview between a patient and a doctor taking a health history. (Speaking) 8. Identify the importance of giving patients enough time for responses, using open-ended questions and avoiding leading questions (Communication Tip) 9. Identify techniques of effective communication between health care workers and patients. (Reading) Estimated Completion Time: This is a self-paced module designed to be completed in an average amount of time. The specific time required for completion will vary from student to student based on their individual skills and learning environment. As an average, this module takes three to five hours to complete. Prerequisite Knowledge and Skills: ESOL Intermediate level courses Resources Inventory: Student Handouts: H1:1; H1:2; H1:3; H1:4; H1:5; H1:6; H1:7 CD with Module 1 listening activities The Sound Recorder Program Instructions (for students who work independently and need to record themselves) Module 1 Answer Key Fundamentals of English Grammar by Betty Azar , Chapter 5 Asking Questions (optional) Longman Advanced American Dictionary or Oxford Dictionary of American Dictionary Module components with specific instructions and Learning Activity Plan Specific instructions: 1. It is best to work on this module in pairs and with a tutor. However, since detailed explanations of all the activities and new concepts are provided in the student handout, students can successfully master the material on their own. 2. If the SPEAKING exercises are not done in the presence of a tutor, they should be recorded in the lab, using the Sound Recorder Program (instructions are attached) for further assessment by a tutor. 3. If you are working on the module on your own, compare your answers with those provided in the Module Answer Key after completing each exercise. Learning Activity Plans: Learning Activity # 1 Content Goal # 1: Review and use idioms people regularly use to report when they are feeling sick. (Words and Expressions to Know) Handout 1:1 A-B Words and Expressions to Know Words and Expressions to Know handouts list vocabulary words and expressions for each module. Most of these words are widely used in the medical field. Each word will appear in the dialogues or readings that follow the list. Warm Up - Look at the title of Module 1 and the picture on the cover page. Ask the students to predict what they will study in this module and have them brainstorm as many words associated with the picture and the title as they can. H 1:1 A - Read the phrases and sentences and ask the students to repeat them after you. Explain that the words in the left-hand column of the chart will appear in the recording they are going to hear. Have the students write what they think each one means in the second column. Discuss the correct definitions after they are done. H 1:1 B – The students work on this exercise individually and then compare their answers with their partner. If there is no partner, the students should check their answers with their tutor or look in the Module 1 Answer Key. Learning Activity # 2: Content Goal # 2 : Identify and demonstrate proper note-taking techniques; take notes of a health history (Listening) Handout 1:2 A H 1:2 A – Tell students that to be able to remember what their client tells them, it’s a good idea to take notes. Ask them if they can share some tips on how to take notes efficiently and remember the info from the speech they have just heard. Write their suggestions on the board. Have the students read the tips in H 1:2. Which ones are new to you? Tell them that these techniques will help them not only take notes of their patients’ answers, but also will be useful for taking notes of the lectures at the nursing school. Share with the students the following commonly used symbols: + = ≠ ≈ < > @ & plus, and equal, is is not, does not equal is approximately equal is less than is more than at and male ↑ ↓ “ ? ! $ → ← an increase/a rise/an improvement in smth. a decrease/a fall/a reduction/a deterioration in smth. the same as the word above question this is an important point dollar causes/results in/becomes/makes is caused by/is the result of/is made from female Learning Activity # 3 Content Goal # 3: Identify and use some common medical abbreviations used in the recording of health histories. Handout 1:2 B-C (Writing) H 1:2 B – Have the students read the abbreviations in the chart and ask them if they have already used any of them. Which ones are new? Do you have any questions? What’s the Latin for “every”? Go over all the abbreviations with q. Ask them if they know what b, t and q in bid, tid and qid stand for (the first letter of the Latin numbers – bi-, tres, quarto) H 1:2 C - Ask the students to cover Part B of H1:2 and complete the matching exercise without looking at the table with the abbreviations. Learning Activity # 4 Content Goal # 4: Listen for main ideas and details. Handout 1:3 A-B (Listening) CD - EX. H1:3 A and H1:3 B Listening: Tell the students that in the next three modules they are going to go through the stages of taking a health history. Although it is presented here as a doctor taking a history, it could easily be adapted so that it could be used by other health care professionals. H 1:3 A – Listening for Main Ideas -Read aloud the instructions for H 1:3 A. Remind the students that the goal of this exercise is to listen for main ideas. Ask them to look at the picture in this handout. Explain to them that this picture illustrates what is happening in the recording they are about to hear. Have the students read the case history components. Prompt them to ask questions if they don’t understand these terms. Play the CD and have the students fill in the blanks. Play it again if the students had trouble catching all the information. Then go over the answers together. Did you use any abbreviations? Students who work on their own should consult the Module 1 Answer Key. H 1:3 B – Tell the students that in this listening exercise they will hear questions that are frequently asked while taking a health history. Those questions are omitted in their handout. Ask the students to fill in as many of them as they can on their first listening. Offer to discuss any questions they have at that point. Play the recording again and have them repeat what the speaker says after each pause. Ask them to compare their answers with their partners and then with the answer key. Then read the dialogue in pairs. Learning Activity # 5 Content Goal # 5: Identify health history terms. (Speaking) Handouts 1:3 C H 1:3 C – Elicit from the students all the health history components. Tell them that the complete health history is modified when necessary. For example, it was shortened in the interview between Dr. Howell and Ms. Sandler. Ask the students to answer the question in H 1:3 C individually and then compare their answers with their partners. They may have to read the dialogue again to see which health history components are missing. Learning Activity # 6 Content Goal # 6: Review how to form questions properly. (Grammar) Handouts 1:4 A-B H 1:4 A – Tell the students that this is just a review. – This material should be familiar to them from the ESOL High Beginning and Intermediate level courses. Have them read the grammar explanation in the handout and then do Exercise B. If the students have problems forming questions in English, encourage them to study Chapter 5 of Fundamentals of English Grammar by Betty Azar. Tell them that his whole chapter is dedicated to the interrogative sentences, and it provides plenty of practice for forming various kinds of questions. Learning Activity # 7 Content Goal # 7: Conduct an interview between a patient and a doctor taking a health history. (Writing, Speaking) Handout 1:5 A-D H1:5 A – Have the students study the notes and figure out the abbreviations. Answer any questions they may have about the four case summaries. H1:5 B - Give each student a different case and ask him or her to write the questions. Refer them to the dialogue in this module for help with these questions. Ask those who completed this exercise first to write their questions on the board. Discuss their answers together. Go over any problematic areas. H 1:5 C – When the students have enough practice and are comfortable writing health history questions, have them do Activity C. This is a communicative activity that reinforces all the language points introduced in this tutorial. It winds up the oral work in this module. This kind of activity can be organized in two ways: Whole group activity: One student chooses a case and comes to the front of the group. The other students ask questions. Pair activity: Form pairs for this role play. Tell the members of each pair to change roles for each case. Walk around the class and give help as needed. This is a fluency activity. Therefore, so don’t interrupt the students but rather record any problems you hear and elicit the most common ones after they are done interviewing each other. H 1:5 D – The students may have difficulty with this activity. Be prepared to explain to them each diagnose and why you arrived at this decision. Learning Activity # 8 Content Goal # 8: Identify the importance of giving patients enough time for responses, using open-ended questions and avoiding leading questions. (Communication Tip) Handout 1:6 A-B H 1:6 A – Have the students read Communication Tip 1. Make sure they understand the difference between open-ended and close-ended questions before they do the next activity. Tell the students that there are only three open-ended questions in the exercise that follows Communication Tip 1. Ask them to find them. Then have them work on the rest of the questions individually. When they are done, ask them to compare their answers with their partners. Going over the questions with a partner may provide a meaningful conversation and further practice their speaking skills. H 1:6 B – The students may already know the answer to this question. However, if not, have them listen to the dialogue again. Learning Activity # 9 Content Goal # 9: Identify techniques of effective communication between health care workers and patients. (Reading) Handout 1:7 H 1:7 – Reading Pose the pre-reading questions. Have two columns on the board: What health care workers can do… and What patients can do… Write down the best and most interesting answers on the board. Then have the students read the article and ask them to go to the board and add other techniques of effective communication that they have learned from this reading. Ask them to explain the title of the article (Doctors are from Venus; Patients are from Mars). Then have them read the post-reading questions and answer them in pairs. Call on individual students to give the correct answer. Ask them to them explain their answers. Learning Outcomes Assessment is attached.