Cell Membranes
advertisement

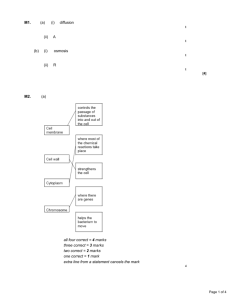
The cell membrane’s purpose is to control what goes in and what goes out of a cell The cell membrane also provides protection and support The Lipid Bilayer The cell membrane is made up primarily of two sheets of lipids called the lipid bilayer In addition to lipids, some carbohydrates and proteins are embedded in the bilayer. Because of these embedded molecules we refer to the lipid bilayer as a fluid mosaic. Concentration How does a cell membrane control what enters and exits a cell? The concentration of the liquids on either side of the membrane is the key. Concentration is the measure of the amount of “stuff” (solutes) in any given amount of a solvent. Concentration = mass of solute / volume of solvent. 8 grams of an salt in 2 liter of water gives us a concentration of 4 g/L. Which of these is more concentrated for sugar? 2 gallon of iced tea with one spoonful of sugar 3 gallons of iced tea with two spoonfuls of sugar Which of these is more concentrated for sugar? 3 gallons of iced tea with two spoonfuls of sugar Diffusion http://www.uh.edu/phar2362/animations/simple_diff usion.html Diffusion Diffusion is the random spreading out of molecules In diffusion molecules move from areas of high to areas of low concentration The cell membrane is only permeable to some substances. It is selectively permeable. Diffusion can only occur across a cell membrane if that membrane is permeable to the solute in question. Osmosis Cell membranes usually permeable to water, so a special kind of diffusion called osmosis can occur. Osmosis is diffusion of water. Osmosis moves water from high concentration of water to low concentrations of water. Concentration of Water If a water solution is highly concentrated for a solute, it has a low concentration of water. Which of these is more concentrated for iced tea? 2 gallon of iced tea with one spoonful of sugar 3 gallons of iced tea with two spoonfuls of sugar Which of these is more concentrated for iced tea? 2 gallon of iced tea with one spoonful of sugar Where will salt move? Where will water move? Transport When substances move across a cell membrane we call it transport There are 2 types of transport Passive Active Passive Transport No energy Moves from high to low concentration Facilitated Diffusion Special protein channels allow substances to pass through a membrane High to low concentration Active Transport Uses energy Requires transport protein Low concentration to high concentration Tonicity Hypotonic Solution – concentration is lower Tonicity Isotonic Solution – concentration is equal Tonicity Hypertonic Solution – concentration is higher Why can’t we drink sea water? Salt water is hypertonic to our cells Water intoxication Drinking extremely large amounts of water in a short time period can lead to death Our cells are hypotonic to pure water