Unit 3
advertisement

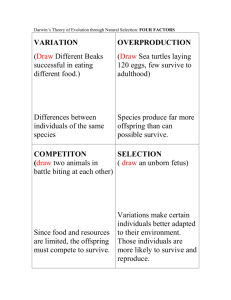
Unit 3 Public Relations Qin Yuhua The Department of Foreign Languages and Literature of Hetao College PART I Text-Related Information Public Relations: Relations with the general public as through publicity, specifically, those functions of a corporation, organization, government department, etc. that acquaint the general public with its activities, purposes, policies, and accomplishments so as to improve its public image and create favorable public opinion for itself. Public Opinion: The opinion of a majority of people generally, especially as a force in determining social, political or economic action. Public Relations Officer/Worker (PRO): A person employed within a corporate or institutional framework or in a public relations counseling firm to promote good public relations. PART II WARM-UP Before reading the passage, think about the questions. 1.What is the usual abbreviation for public relations? 2. Why do some companies have public relations people? PART III Outline Para. 1 The importance of winning public support and trust. Paras. 2–3 The main concerns of public relations: a. winning public confidence and goodwill; b. giving the public the necessary information about a company; c. telling the public about a company’s activities, plans or ideas; d. being on good terms with the public, whether large or small. Paras. 4–8 Activities of public relations: a. the guidelines for PR work: The thoughtfulness about other people’s beliefs, interests, and feelings is the key factor in gaining the confidence of the public. b. the ways to set up a public image: 1) making speeches; 2) distributing pamphlets and booklets; 3) producing motion-picture films; 4) undertaking public service projects; 5) hiring independent public relations firms. PART IV LANGUAGE POINT 1. ... they said that a “decent respect” ... why they were freeing themselves of British rule. — ... in their opinion, what people in general thought about had to be given a proper consideration and therefore it was absolutely necessary for the American colonies to let the people both at home and abroad know the reasons for their effort to gain independence from Britain. 2. Negation can be achieved by using the following expressions or words: none of + noun, neither of + noun, no + noun, nothing, none, nobody, neither, never, nowhere, nor, neither ... nor e.g. None of us were present when the accident took place. No one is allowed to drive along that road from May to July. 3. Partial negation can be achieved by using the following structures: every ... not = not every, both ... not = not both, all ... not = not all, each ... not = not each e.g. Everyone cannot answer all the questions. Not every child wants to become a film star. It is also possible to use words like always, much, many, often to realize partial negation: e.g. We can see that failure is not always an evil. Not many of things are of use in the form in which they are found. 4. affect: v. to cause some result or change in; influence e.g. The tax increases have affected us all. This is an important decision that will affect the future of the company. Stock market cannot avoid being affected by the macro-economic policies. cf. effect: n./v. 1) used as a noun e.g. us. Government policy will not have any effect on The advertising campaign didn’t have much effect on sales. 2) used as a verb, it is very formal and means “to bring about, usually according to one’s wishes” e.g. He was able to effect certain changes in government policy. The main pleasure Hillary derives from her success is the ability to effect change for the better. 5. There is not just one big public ... to survive and grow. Only a few organizations, such as a national government, are so large that all the public has some opinion about their actions. e.g. He was so weak that he could hardly stand up. There was so much smoke that they couldn’t see across the hallway. Everything happened so quickly I hadn’t time to think 6. survive: v. 1) to continue to exist, especially in a difficult or unpleasant situation e.g. The organization cannot survive unless we make some major changes. Only three buildings survived the earthquake. 2) to continue to live, especially after coming close to death e.g. The doctor says it’s a miracle that he survived. Just eight passengers survived the plane crash. 3) to manage to deal with something difficult or unpleasant e.g. I don’t know how I ever survived high school. Don’t worry about Molly – she’ll survive. cf. She survived her own daughter by ten years. (to remain alive after someone has died) Insurance statistics show that most wives survive their husbands. 7. be on good/bad terms with: to get along well with; have a friendly relationship/bad relationship with e.g. Mr. Smith was no longer on good terms with his brother. It is quite easy for a teacher like him to be on good terms with his students. cf. He left on bad terms with team owner Mark Cuban, but respected and beloved by most others It is difficult to keep on good terms with such a man. 8. so as to: in order to e.g. He raised his voice so as to be heard by everyone. We went along silently on tiptoe so as not to disturb anyone. We will continue to contact those departments, so as to keep you updated with the arrangements and facilitate your interview. The function of the press is to present ideas so as to keep citizens informed. I’m going to make an early start so as not to get stuck in the traffic. 9. take ... into account: to consider or include particular facts or details when making a judgment or decision e.g. There are four points to take into account here. The teachers promised to take into account the wishes of the parents before making any changes. His final exam results were not very good, but we must take his long illness into account. take account of e.g. We should also take account of difficulties. These figures do not take account of changes in the rate of inflation. This kind of approach does not take full account of differences between models. take... into consideration e.g. The following are some factors taken into consideration. I always take fuel consumption into consideration when buying a car. Your teacher will take your recent illness into consideration when marking your exams. 10. as if/though: used to describe how a situation seems to be e.g. It looks as if/though it is going to rain. You look as if/though you’re going to cry. A subjunctive mood is often used in the clause introduced by “as if” or “as though”. e.g. She treats me as if I was/were a stranger. She treated me as though I were/had been a stranger. 11. care about: to be worried, anxious, or concerned (about); mind e.g. He cares about nothing but money. Henry is such a man who never cares about what people think. cf. care for: means “like” in questions and negative sentences. e.g. Would you care for a drink? He doesn’t really care for his occupation. I don’t much care for chocolate. 12. be made up of: to consist of; be composed of e.g. The United Kingdom is made up of Great Britain and Northern Ireland. The family is made up of Jane, her husband and three children. 13. reveal: v. to make known (something previously unknown or secret) e.g. She promised not to reveal his secret. 泄露 His letters reveal a different side of his personality. 显示 The company has just revealed its plans for the coming year, including the opening of new offices in Paris. 展示 I can now reveal that the new chairperson of the department is to be Bill Handsome. 透露 cf. conceal: v. to keep from being known e.g. I tried to conceal my surprise when she told me her age. The doctor decided that he could not conceal the truth from the old man any longer. 14. club: n. a society of people with a special interest, usually a sport or entertainment union: n. an association of people who see themselves as uniting for a particular purpose circle: n. a group of people associated in an informal way because of common interests chamber: n. a group of persons organized for purposes of trade institution: n. a large society or organization, usually set up to do something for others PART V Reading Skills: Comparison and Contrast Practice 1 Read the paragraph and answer the questions that follow. The reading process is similar to the writing process. Both are a form of communication by using the written words. The job of the writer, however, is to convey his or her message in a clear manner. The job of the reader, on the other hand, is to extract from the written page as accurately as possible the information being communicated. PART VI E-C Translation Skills 反正译:英语从反面表达,汉语从正面表达 反正译是用变换语气的方法把原文的否定 式译成汉语的肯定式。翻译时恰当地运用这 一方法可 以使译文自然流畅。英语中的 “not ... until” 结构和双重否定结构常用这种 方法来翻译。另外,“no less than”、“no more than”、“nothing but”、“cannot ... too” 等含有否定词语的结构也常用反正译的方法 来表达。 例如: 1.Metals do not melt until heated to a definite temperature. 金属要加热到一定温度才会熔化。 2.He doesn’t do it for nothing. 他这样做是有道理的。 3.There is no rule but has exceptions. 凡规则总有例 外。 4.Never too old to learn. 活到老,学到老。 5.She is no less diligent than her sister. 她和她姐姐一 样用功。 6.I have no more than ten dollars in my pocket. 我口袋里最多只有十美元。 7. Early computers did nothing but compute: adding, subtracting, multiplying, and dividing. 早期的计算机只能做加减乘除运算。 8.The experiment couldn’t be more successful. 这次实验很成功。 9.We cannot be too careful in doing experiments. 我们做实验越仔细越好。 常用结构译法介绍 so as to:“so as + 动词不定式” 通常表 示目的,一般放在句末,且多用于口语。其 语气比单独用动词不定式强,比in order to 弱,意思是“为的是”。该结构有时也表示 结果,翻译时要灵活处理。一般可译为“为 (了)”、“要”、“以(便)”、“使得” 或“结果”、“以至”等。 例如: 1. He tried to shout so as to be heard all along the street. 他竭力叫喊,使得全街都能听见。(目的) 2. He was afraid of making any noise so as to be heard by the baby. 他怕弄出声来让孩子听见。(结果) PART VII 借条与收据 (I.O.U. and Receipt Forms) 借据和收条是指通常我们借用或接受款项或物 品时打的条据。英文的写法一般包括时间、正 文、署名等几个部分。 今借到外语系录音机一台。 July 2, 2008 Borrowed from the Foreign Languages Department a tape recorder. Li Ming 2. 今借到王玲小姐人民币陆千元整,言明一 年内归还,年息5厘,此据。 July 2, 2008 To Miss Wang Ling, I.O.U. six hundred yuan (RMB) to be paid back within one year from this date with interest at 9% per annum. Li Ming THANK YOU!