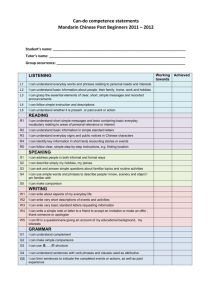
Vocabulary Activities in Writing Classes
advertisement
Integrating corpus-based vocabulary activities into an academic writing course TESOL 2005, San Antonio, Texas March 30, 2005 John Bunting Georgia State University jbunting@gsu.edu Ways to build upon vocabulary Meaning(s) The spoken form The written form Its frequency (compared with similar words) Its grammar Collocations Register (and any related changes in meaning) Association with other words/concepts Its overall positive/negative (or other) coloring? Its use in any specific textual position? What challenges exist? New ways of seeing Explaining value to students Learning new activity types Finding appropriate material Using new software Filtering out ‘noise’ Why integrate new techniques? Changing technology leads to • changes in expectations • greater student autonomy • access to a wider range of authentic texts • new ways to look at patterns in text What are the goals? Learn about words and phrases receptively & productively Begin to ‘notice’ patterns in text Develop strategies for approaching other words and phrases Academic Writing 0950 Last level before entering the university Content-based course – American History from early 1500s to mid 1700s Focus on writing for tests and classroom assignments Writing based on displaying knowledge of reading of college-level textbooks Assessment heavily weighted towards exams based on textbook readings The students/writers Primarily international students Almost all planning to study at either graduate or undergraduate level in the next semester Highly motivated Range of L1 and cultural backgrounds: • Spanish (Latin American), Korean, Chinese, Japanese, Nepalese, Vietnamese The timeline project Students construct a project creating a timeline that shows historical events and people from different countries, relating or contrasting them with events and people from US History Students gain some perspective on how historical events that shaped the US connected with the rest of the world (Snell, 2004) Timeline project – details Semester-long project Requires articles about related topics (narrow reading) The corpus-based activities are part of this project Initial steps Define and exemplify terminology: • • • • • Collocation KWIC Concordancing Register Corpus/corpora Show students ways to copy and save text files Create links to relevant websites Initial steps Building a corpus of studentselected texts In small groups, determine topics Assign tasks based on timeline project Included in tasks: select articles and read them Save articles as text files Send text files to teacher along with assignment Compile text files and use them for additional assignments Adding to the corpus Repeat the text-compiling process for each assignment Incorporate other tasks into each assignment Compile the texts into country-specific folders and one “complete” text Finding articles and saving them as text files IEP 0950 Writing from Reading Assignment #1 Finding articles about your timeline project, and saving text files Name:_____________________________ The assignment: Online, find two scholarly articles and two news articles on your topic. They need to be in readable form (either as text documents or html files). Read through them and write a one to two sentence summary of the article. Time period: ________________________ Country/culture: _____________________ Summary sentences: 1. 2. Please email me the text files for all articles as text attachments Finding concordance lines using an online concordancer The assignment: For your word, you will need to do the following for your word: Create a definition for the word List all its forms (noun, verb, etc. in a chart) Find 20 concordance lines from academic readings for the word, using Compleat Lexical Tutor Find one pattern about that word (this can be other words that go with it, or grammar patterns that seem common) based on the concordance lines that you find. Concordance lines - student results Trying to identify patterns from concordance lines T1: Pattern: Someone assumes that something happens [Clause] Example: People automatically assume that I'm in college. S1: Pattern: Something is processed into something Example: The material will be processed into plastic pellets. S2: Pattern: analysis of do/carry out/conduct an analysis Example: Further analysis of the data is needed. They were doing some type of statistical analysis Reviewing the AWL vocabulary Connecting articles to the AWL The assignment: Choose one of your texts to use in this website. Find and make a list of the AWL words from sublist 1 and 2. Choose two words from those that you think are very important and find then in the text. Copy the sentences from the text that includes those words. Write two more sentences (about the same country) that uses that word (or one of its word forms) Connecting articles to the AWL– Student work Examining word frequency in articles Look at the most frequent words in the articles chosen for all the timeline projects. Decide which words are function words, which are probably about specific countries (the US, China, etc.) and which might be considered ‘academic’ vocabulary. Students determine which words from the frequency list are function words or content words. They also determine which content words might be more strongly connected to one topic (country) or another Examining phrases in the corpus Choosing phrases in the corpus – student work Some useful phrases that students chose from the texts: • As well as the • by the end of • at the same time • at the end of • put an end to • in addition to the Creating phrases– student work Some phrases that students chose, not from the texts: • The outcome of the • The British government mentioned that • Between XXXX and XXXX • Influenced by World War II • The independence of Korea from Japan • A ‘long march’ led by Next steps Add/remove tasks based on student response Connect this to oral communication class, using MICASE Try working with scholarly articles in students’ fields of study (IEP or grad students) Have students use more sophisticated online programs for grammar/lexical patterns (WASP Bench) Bibliography Bunting, J. (2006). College Vocabulary 4. Boston: Houghton Mifflin. Schmitt, N. (2000). Vocabulary in language teaching. Cambridge, Cambridge University Press. Schmitt, N. and R. Carter (2000). "The Lexical Advantages of Narrow Reading for Second Language Learners." TESOL Journal 91: 4-9. Scott, M. (1999). Wordsmith Tools. Oxford, Oxford University Press: computer software. Underhill, A. (2002). MacMillan English dictionary for advanced learners of American English Workbook. Oxford: MacMillan. Websites Compleat Lexical Tutor (for frequency and vocabulary profiles) • Michigan Corpus of Academic Spoken English • http://www.lextutor.ca/ http://www.hti.umich.edu/m/micase WASP Bench: A Semi-Automatic Lexicographer's Workbench for Writing Word Sense Profiles • http://wasps.itri.bton.ac.uk/