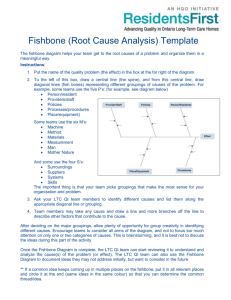
Root Cause Analysis - freesixsigmasite.com
advertisement

Root Cause Analysis • Analyze • Kaizen Facilitation Objectives • Learn and be able to apply a fishbone diagram • Utilize “Why” analysis technique to uncover causes 2 2 “Why” Analysis • Question asking technique used to explore the cause and effect relationships underlying a particular problem • Four to five iterations of asking why is generally sufficient to get to a root cause, but may go more • EXAMPLE: The vehicle will not start (problem statement) • Why? – The battery is dead • Why? – The alternator is not working • Why? – The alternator belt is broken • Why? – The belt was beyond its useful life • Why? – The vehicle was not maintained per the recommended schedule 3 Tips For Successfully Using “Why” Analysis • Root cause of the vehicle example appears to be the lack of scheduled maintenance… this is a process that can be improved • You know when you have gotten to the cause when the answer points to a process that is not working or does not exist • The root cause generally is not time, money, or manpower • Processes fail, not people or money, so ask the question “Why did the process fail?” 4 What is a Fishbone Diagram? • The Fishbone diagram (or Ishikawa Diagram) is used to identify possible causes for an effect • Causes are grouped into major categories to identify the sources of variation through the 6M’s • • • • • • 5 Manpower Machines Materials Methods Measurements Mother nature [environment] Fishbone Diagram - Example Materials Stuck Cones Damaged containers Methods Yard Planning Unrealistic Deadlines Incorrect Stow Plans Manpower New Driver Untrained Driver Driver in Bad Mood POOR CRANE PRODUCTION CAUSES Condition of Crane Broke cell guides Type of Crane Machines 6 EFFECT Additional long travels Physical Terminal Layout High winds Mother Nature Service Overdue Operating with Defect Measurements Why Use a Fishbone? • Groups potential causes for defects into logical categories • Helps teams work together to get to root cause • Highlights where additional data gathering needs to occur 7 Step 1: Determine the Problem/Issue • To construct a fishbone: • Start with stating the problem in the form of a question, such as “Why is crane production low?” • Agree on the problem (effect) and place it in a box at the “head” of the fishbone Why is Crane production low? 8 Step 2: Establish the Categories • Determine which categories you will use to find causes and draw the lines (bones) • Feel free to modify the categories for your project and subject matter • Most common categories called 6 M’s: • Manpower • Machines • Materials • Methods • Measurements • Mother nature [environment] 9 Machines • The Machines category groups root causes related to tools or equipment • Examples of questions to be asked: • • • • • Was the correct tool/tooling used? Does it meet production requirements Is the machine properly maintained? Was the equipment used within its capabilities and limitations? Are all controls clearly labeled and/or color-coded or differentiated? Machines 10 Y Methods • The Method category groups root causes related to how the work is done • Examples of questions to be asked: • Are the work instructions clearly written & complete? • Are mistake-proofing devices/techniques employed? • How many “if necessary” and “approximately” phrases are found in this process? Y • Are features of the process critical to safety clearly spelled out? Methods • Is the work standard upgraded and to the current revision? 11 Materials • The Materials category groups root causes related to parts, supplies, forms or information needed to execute the process • Examples of questions to be asked: • • • • Is all needed information available and accurate? Was the material substituted? Was the material defective? Was the raw material the wrong type for the job? • Was the material handled properly (stored, dispensed, used & disposed)? 12 Materials Y Measurements • The Measurement category groups root causes related to the measurement and measuring of a process activity or output • Examples of questions to be asked: • • • • • 13 Is there a metric issue? Is there a valid measurement system? Is the data good enough? Is data readily available? Does the measuring gage have proper measurement resolution? Measurements Y Manpower • The Manpower category groups root causes related to people, staffing and organizational structure • Examples of questions to be asked: • • • • • Was the proper training to perform the task administered to the person? Was too much judgment required to perform the task? Were guidelines for judgment available? Is fatigue a contributing factor? Manpower How much experience does the individual have in performing this task? Y 14 Mother Nature (Environment) • The Mother Nature category groups root causes related to the work environment, market conditions, and regulatory issues • Examples of questions to be asked: • • • • Is the workplace safe and suitable/ comfortable? Are outside regulations impacting the business? Is the process affected by temperature changes over the course of a day? Are associates distracted by noise, Y uncomfortable temperatures, fluorescent lighting, etc.? Mother Nature 15 Step 3: Brainstorm Causes • For each category, brainstorm possible root causes of the problem that may be related to the problem/ issue • For each cause identified, continue to ask “why does that happen?” and attach that information as another line (bone) of the category branch 16 Step 4: Review the Diagram • The diagram should now show all of the possible causes of the problem that you can think of • Prioritize the key causes identified on the fishbone • Agree on which of these possible causes are actually contributing 17 Summary 1. Identify the problem or issue • • Draw horizontal line across center of page Write problem at fish head 2. Establish the categories • • Use the 6M’s: Manpower, Machine, Method, Measurement, Material, Mother Nature (Environment) - or choose your own Draw lines (bones) and the labels 3. Brainstorm/ record ideas onto fishbone • Create sub-branches as needed 4. Review completed diagram and set focus • 18 Score / Vote or Rank as appropriate to group thoughts, or prioritize the issues by data analysis (most frequently occurring) or cost impact on the process or risk of failure/ work stoppage, etc. Exercise: Create a Fishbone Diagram • With your team, construct a detailed Cause and Effect Diagram on the process / example presented • Identify and label categories • Examine using the “why” analysis • Brainstorm as many inputs as possible with each branch and/ or sub-branch 19 Review • Learn and be able to capture thoughts using a fishbone diagram • Learn to apply “Why” analysis technique to uncover root causes 20 Why Analysis Example 21 Why Analysis Example 22 Why Analysis Example 23 Why Analysis Example 24 Why Analysis Example 25 Why Analysis Example 26 Fishbone Example 27 Fishbone Example 28