Trading States of Africa
advertisement
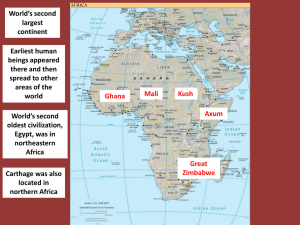
What are some of the methods scientists use to learn about the history and culture of early civilizations? What do you remember from last year when we studied Africa? Sahara Desert Mediterranean Atlantic Ocean Strait of Gibraltar Red Sea The Physical geography of Sub-Saharan Africa strongly influenced the growth of human societies. Sub Saharan Africa is a plateau Congo, Niger, Zambezi Rivers are blocked by rapids Because of the rivers, made trade and communication hard, but blocked them from invasion. Sahara Desert covers about one-fourth of the African continent Sahara desert use to be fertile, and well watered. Changes in wind and weather patterns caused the area to become dry Shael- southern edge of the desert is a region known as “shore” Rainfall is sparse and uncertain, also sometimes harsh droughts (may last years) Farming difficult throughout the region. South of Shael vast stretches of dry grasslands (Savannas) few trees and thorny bushes. Farming techniques began to spread in Africa about 3000BC Savanna farmers; grains, sorghum, millet and rice. Savanna meets the desert people herded cattle. Rainfall is greater farther south, some places in central and western Africa receive more than 100 inches of rainfall Tropical rain forest's are found in this area Jungles- dense tangles of plants grow wherever there is sunlight. Hot, wet climate of the rain forests provides breeding grounds for insects, some carry deadly diseases. Malaria, yellow fever, carried by mosquitoes South of the rain forest: more deserts The Kalahari Desert and the Namib Desert Range from the center of southern Africa westward to the Atlantic coast. Natural Features Lake Victoria is one of the worlds largest lakes. Great Rift Valley What different kinds of landforms, climates and features are in Sub-Saharan Africa? Linguists- scientists who study languages, have used computers to compare modern African words Bantu-family of closely related African languages “the cradle land” of Bantu lies in west central , present border of Nigeria and Cameroon. Oral traditions- poems, songs and stories passed by word of mouth from generations to another. Often hold moral lessons, griots Griots- were highly trained speakers and entertainers who memorized the oral tradition of their village. Cultural exchange: between Africa and Asia Scholars looked at musical instruments, language, plants. Question: what evidence is there of cultural exchange between early Africa and Asia? Life in Africa: Africans lived in small, independent farming, herding or fishing villages. Women important both family and economically Women primarily farmers, Sub-Saharan Africa were matrilineal People traced their ancestors and inherited property through their mothers rather than fathers. Religion : sprits populated the world, lived in everything Elders in villages, community leaders What are some political units of a village, Write down ideas and give a brief description of them. I will call on you… Study for quiz Thursday and read chapter 8 (all of it) Kush: Trade important, cities thrived on trading; Gold, ivory, ebony and ostrich feathers Kush became a kingdom, capital Napata Close economic and cultural ties with Egypt, 1520 BC Egypt’s New Kingdom brought Nubia and Kush under their control Kush conquered Upper Egypt and a Kush dynasty ruled and unified Egypt 50 years. 671 BC the Assyrians armed with iron weapons invaded Kush, weakening the kingdom. Kush lost trade routes Aksum: Ethiopian Highlands south of Kush Important trade routes stretching from the Red Sea into Egypt. Kush declined and Aksum used this to their advantage. Imported glass, metal ornaments and pottery, wine and olive oil 350 AD King Ezana of Aksum conquered Kush Collected taxes on trade goods Converted to Christianity made it the official religion of Aksum Aksum: Christianity in this region laid the foundations of the Ethiopian Church. Aksum major center of long-distance trade through coastal East Africa. Decline of Aksum: environmental, problems (erosion, caused by excessive land use and the destruction of forests made land less productive) Persians, gained control over much of the Red Sea trade, in 700 Ad. Rise of Islamic Arab power led to new economic and political competition with Aksum. Declined as a commercial and political power. East Africa and Great Zimbabwe: City-states emerged Trade routes linked all shores of the Indian Ocean, Africans exported gold, ivory, hides and tortoise shells. Imported porcelain and weapons, sold slaves Islamic religion from Arabia to northeasters Africa spurred trade. merchant, families and adventurers to Africa came to make money. People from Indonesia settled on Madagascar. Swahili states: Swahili- developed in East Africa, spoke Swahili a Bantu language with Arabic and Persian influences. Swahilis were linked by language and trade. Kilwa became a leading port (trade) Found massive trade centers and large mosque. Great Zimbabwe: Demand of gold increased in 900 AD. Kingdoms competed for control over both mining and shipping gold. Shona- were a people who migrated onto the plateau of what is today Zimbabwe. Took control over local people and the gold they mined and traded. Believed to have gained great wealth and power. Great Zimbabwe the largest and most important of these fortresses. Center of the Shona state. Great Zimbabwe: Unknown reasons Great Zimbabwe declined in the 1400s AD Population grew too fast, outpaced dwindling supplies of food and water. West Africa: Ghana, Mali and Songhai. Lay between Lake Chad and the Atlantic Ocean The Wealth and strength of these kingdoms depended on control of the trade routes across the Sahara. Gold mined south of the Sahel , traded for salt mined in the desert. West Africa: Lay between Lake Chad and the Atlantic Ocean and included the kingdoms of Ghana, Mali and Songhai Wealth and strength of these kingdoms depended on control of the trade routes across the Sahara. At the desert’s southern edge commerce developed, gold mined south of the Shael. Salt was mined in the desert. Monarchs ruled the West African kingdoms, Ghana: Earliest of the kingdoms Established by the Soninke people sometime after 300 AD Lived in western Sahel, northwest –day nation of Ghana Ghanaian kings were powerful and wealthy from the gold Most powerful rulers was Tunka Manin- ruled in 1067 AD Commanded the army Began to decline- Berbers invaded from the North , lose control of the salt trade, neighboring Malinke overthrew Ghana Mali: Mali followed the fall of Ghana, came into power in the area that had been Ghana Great Ruler, Mansa Musa 1300 AD supported education, the arts and public building. Under his rule the city of Timbuktu became a leading center of learning. Large Universities attracted scholars from Egypt and Arabia. Musa famous for his historic pilgrimage to Mecca Islamic holy place in Arabia Mali: Rival members of the royal court fought for leadership of the empire. Weakened central authority within Mali. Kingdom kept control of the desert trade routes until 1400 AD 1468 AD rebel leader Sonni Ali captured Timbuktu and built up the kingdom of Songhai. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=RveLuguI tPI