Chapter 12
advertisement

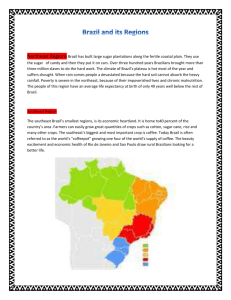
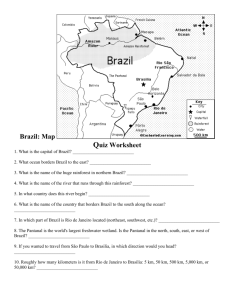
Chapter 12 Brazil AGENDA 3.16.15 ON 1. PDN 2. Finish Chap. 12 Sec 1 CHAPTERS 11 and 12 3. Review Standard: 7.3.8.A THURSDAY MARCH 19, Explain the human characteristics of places 4. Chap. 9-10 Test back 2015 5. Go over tests of places and regions using economic activities . 7.2.8.A Explain the characteristics of places Beginning Objective: and regions. Identify existing environmental and Anchor: CC8.5.6-8.D: Determine the economic challenges in the Northeast. meaning of words as they are used in text. TEST Introduction to Brazil • Biggest country in S. America. • Two major types of landforms – Plains – Plateaus • Behind coastal plains is a huge interior plateau. As it drops sharply to the plains, it forms an escarpment. – A steep cliff between two level areas at different heights. Northeast Region • Bulges into the Atlantic • Portuguese built sugar plantations along fertile coastal plain. • Brazil became the world’s major producer of sugar. Northeast Region Continued… • Over 3 million enslaved Africans were brought to Brazil, from 1500-1800s, to work on plantations. • Folktales, food and religion of the Northeast still reflect this African heritage. Northeast Region Continued… • Inland from the Northeast's coastal plains lies the sertao, or interior plain. – Tropical wet and dry climate, often bakes through a year or more of drought. – When it does rain, the hard soil cannot absorb rain. Northeast Region Continued… • Severe Poverty – Yearly income about 1/3 of what someone might make in the Southeast Region of Brazil. • Impoverished lives and malnutrition leads to ??? OBJECTIVE REVIEW • What are some environmental challenges in the Northeast region? • What is the economic challenge in the Northeast region? NEW OBJECTIVE • Students will describe the effects of urbanization on the southeast region. Southeast Region • Brazil’s smallest region is its economic heartland. • 11% of countries area = 40% of population. • Humid subtropical climate + fertile soil means farmers can grow cash crops like cotton, sugar cane, rice and cacao. • Southeast’s biggest and most important crop is coffee. Southeast Region Continued… • Today, Brazil is often referred to as the world’s “coffeepot,” growing one fourth of the world’s supply. • Great agriculture but most live near the cities of Sao Paulo and Rio de Janeiro. Southeast Region continued… • Beauty, excitement and economic health of Rio and Sao Paulo draw rural Brazilians looking for a better life. • Undereducated and lacking experience many find no jobs or settle for low pay. • Most end up living in slum communities called favelas. Brazilian Culture • Despite poverty, Rio de Janeiro is known around the world for Carnival. – 4 days preceding Lent (40 day period of fasting). – Samba – Brazil’s national dance. Objective Review • What are the effects of urbanization on the southeast region? NEW OBJECTIVE • Students will be able to explain why the government has encouraged economic development in the Brazilian Highlands. Brazilian Highlands Brazilian Highlands Continued… • North of the southeast region. • Interior area of hills on the country’s central plateau. • Brasilia, country’s capital, is located here. Brazilian Highlands Continued… • Rio de Janeiro = former capital, too crowded. • In 1956, hoping to boost development of the interior and to draw people away from the coastal cities, the government decided to build a new capital city, 600 miles inland. OBJECTIVE REVIEW • Why did the Brazilian government encourage economic development in the Highlands? NEW OBJECTIVE • List the main characteristics of the Amazon River basin ecosystem. Amazon River Region • Largest and least explored region of Brazil is the Amazon River Basin. • Growing season never ends. (80 deg.) • Amazon rain forest is home to thousands of species of plants and animals. The Amazon Indians • Only 10% of Brazilians live in the Amazon Basin, including about 200,000 Indians from 180 different tribes (Down from 2-5 million). • Govt. provides – Reservations • Comes with opponents who argue that reservations actually contribute to the disappearance of language, customs and religion. – Compensation OBJECTIVE REVIEW • What are some characteristics of the Amazon River basin ecosystem? Chapter 12 Section 1 Review • What is one environmental challenge of northeast Brazil? • What is one economic challenge of northeast Brazil? • What are the effects of urbanization on southeast Brazil? • Why has the government encouraged economic development in the Brazilian Highlands? • What are some characteristics of the Amazon River basin ecosystem? Chapter 12, Section 2 • Brazil’s Quest for Economic Growth AGENDA: 1. PDN 2. Amazon River Movie 3. FINISH CHAPTER 12 NOTES 4. Ticket out the door review Standard: 7.3.8.A: Explain the human characteristics of places and regions using the following criteria: Economic activities Anchor: CC8.5.6-8.D: Determine the meaning of words as they are used in text. CHAPTER 11 and 12 TEST ON THURSDAY MARCH 19, 2015!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! !!!!!! BEGINNING OBJECTIVE: Students will, identify the economic challenges urban and rural poor in Brazil face. Introduction • Brazil is a country of extremes. – Huge country – Rich in natural resources – Extreme poverty Introduction Continued… • Brazil today, is no longer a society of only rich and poor. • Industry growth and manufacturing has helped create a middle class. • Cities have grown, doctors, teachers and government workers have moved in to fill the need of growing population. Economic Challenges • Urban favelas • Many parents cannot feed or house their children, much less provide them with schooling. • Hungry and/or homeless children live on the streets seeking menial jobs or begging for coins with which to buy food. Economic Challenges Continued… • Conditions in agriculture contribute to poverty. • A handful of wealthy families own the profitable plantations or large commercial farms. Economic Growth • Industry accounts for more than 1/3 of Brazil’s GDP. • One major step was the successful development of a new alcohol-based fuel called gasohol. – Mix of gasoline and ethanol. Environmental Changes • Deforestation, or the permanent removal of woodland, threatens vast numbers of plant and animal species of the Amazon. • The Amazon basin contains some 1,300 plants that can be used in the treatment of a variety of illnesses. • Military and police combine forces to seize illegally logged timber. Environmental Changes • The government also encourages ecotourism, or tourism that encourages environmental awareness and has little effect on the ecosystem.