Advanced development of the arts.
advertisement

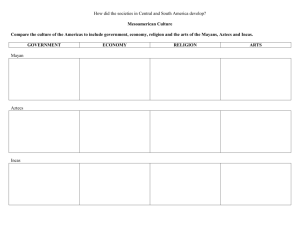
Central American Civilizations Lesson 1.6 SSWH 8 – The student will demonstrate an understanding of the development of societies in Central and South America (a) Explain the rise and fall of the Olmecs, Mayan, Aztecs, and Inca empires. (b) Compare the cultures of the Americas: including government, economy, religion, and the arts of the Mayans, Aztecs, and Incas Major Central American Cultures • OLMEC ca. 1200-300 bce • TEOTIHUACAN flourished 100-650 ce • MAYAN – Preclassic 2000 bce-100 ce – Classic 100 -900 ce – Postclassic 900 ce-1500 ce • AZTEC 1350-1519 ce SSWH 8 – The student will demonstrate an understanding of the development of societies in Central and South America (a) Explain the rise and fall of the Olmecs, Mayan, Aztecs, and Inca empires. (b) Compare the cultures of the Americas: including government, economy, religion, and the arts of the Mayans, Aztecs, and Incas Part 1: Olmec and Mayan Theme: The connection between agriculture, religion, and society Lsn 1.6 Quick Vocab • bloodletting rituals, cocoa, maize, Maya, Mayan calendar, Mayan decline, Olmec, Popol Vuh, Temple of the Giant Jaguar, Tikal Olmecs and Mayans Olmecs • Earliest known ceremonial centers is near modern day Veracruz around 1200 B.C. – Served as the nerve center for the first complex society of the Americas, the Olmecs • “Olmec” was not what the people called themselves – It means “rubber people” and comes from the rubber trees that flourish in the region SSWH 8 – The student will demonstrate an understanding of the development of societies in Central and South America (a) Explain the rise and fall of the Olmecs, Mayan, Aztecs, and Inca empires. (b) Compare the cultures of the Americas: including government, economy, religion, and the arts of the Mayans, Aztecs, and Incas Characteristics of Olmec Civilization • Intensive agricultural techniques – Area received abundant rainfall so extensive irrigation systems were unnecessary – The Olmecs built elaborate drainage systems • Specialization of labor – Jade craftsmen • Cities – Built around ceremonial centers • A social hierarchy – Society was probably authoritarian – Common subjects provided labor and tribute to the elite Characteristics of Olmec Civilization • Organized religion and education – Ceremonial centers, priests, temples, altars, and human sacrifice • Development of economic exchange – Imported jade and obsidian and exported small jade, basalt, and ceramic works of art • Development of new technologies – Excellent astronomers and mathematicians who developed a calendar • Advanced development of the arts. (This can include writing.) – Created colossal human heads sculpted from basalt rock SSWH 8 – The student will demonstrate an understanding of the development of societies in Central and South America (a) Explain the rise and fall of the Olmecs, Mayan, Aztecs, and Inca empires. (b) Compare the cultures of the Americas: including government, economy, religion, and the arts of the Mayans, Aztecs, and Incas Olmec Head at La Venta Decline of the Olmec • Olmecs systematically destroyed their ceremonial centers and then deserted the sites – Statues were broken and buried, monuments defaced, and capitals burned • No one knows why! • but some speculate reasons involving civil conflicts or doubts about the effectiveness or legitimacy of the ruling classes SSWH 8 – The student will demonstrate an understanding of the development of societies in Central and South America (a) Explain the rise and fall of the Olmecs, Mayan, Aztecs, and Inca empires. (b) Compare the cultures of the Americas: including government, economy, religion, and the arts of the Mayans, Aztecs, and Incas Mayans • Began to develop around 300 A.D. in what is now southern Mexico, Guatemala, Belize, Honduras, and El Salvador • Known as “The People of the Jaguar” SSWH 8 – The student will demonstrate an understanding of the development of societies in Central and South America (a) Explain the rise and fall of the Olmecs, Mayan, Aztecs, and Inca empires. (b) Compare the cultures of the Americas: including government, economy, religion, and the arts of the Mayans, Aztecs, and Incas Olmec Influence on the Mayans • Maize • Ceremonial centers with temple pyramids • Calendar based on the Olmec one • Ball games • Rituals involving human sacrifice SSWH 8 – The student will demonstrate an understanding of the development of societies in Central and South America (a) Explain the rise and fall of the Olmecs, Mayan, Aztecs, and Inca empires. (b) Compare the cultures of the Americas: including government, economy, religion, and the arts of the Mayans, Aztecs, and Incas Characteristics of a Civilization • • • • • • Intensive agricultural techniques Specialization of labor Cities A social hierarchy Organized religion and education Development of complex forms of economic exchange • Development of new technologies • Advanced development of the arts. (This can include writing.) SSWH 8 – The student will demonstrate an understanding of the development of societies in Central and South America (a) Explain the rise and fall of the Olmecs, Mayan, Aztecs, and Inca empires. (b) Compare the cultures of the Americas: including government, economy, religion, and the arts of the Mayans, Aztecs, and Incas Agriculture Maize Cacao Agriculture • Soil in Mesoamerican lowlands was thin and quickly lost fertility – Mayans built terraces to retain the silt and therefore greatly improved agricultural production Cacao tree • Raised maize, cotton, and cacao SSWH 8 – The student will demonstrate an understanding of the development of societies in Central and South America (a) Explain the rise and fall of the Olmecs, Mayan, Aztecs, and Inca empires. (b) Compare the cultures of the Americas: including government, economy, religion, and the arts of the Mayans, Aztecs, and Incas Specialization Specialization • • • • Astronomers Mathematicians Warriors Architects and sculptors • Potters • Tool manufacturers • Textile makers SSWH 8 – The student will demonstrate an understanding of the development of societies in Central and South America (a) Explain the rise and fall of the Olmecs, Mayan, Aztecs, and Inca empires. (b) Compare the cultures of the Americas: including government, economy, religion, and the arts of the Mayans, Aztecs, and Incas Cities Cities: Tikal • the Maya built more than eight large ceremonial centers – All had pyramids, palaces, and temples • Some of the larger ones attracted dense populations and evolved into genuine cities – The most important was Tikal SSWH 8 – The student will demonstrate an understanding of the development of societies in Central and South America (a) Explain the rise and fall of the Olmecs, Mayan, Aztecs, and Inca empires. (b) Compare the cultures of the Americas: including government, economy, religion, and the arts of the Mayans, Aztecs, and Incas Tikal: Temple of the Jaguar • 154 feet high • Served as funerary pyramid for Lord Cacao, Maya ruler of the late 6th and early 7th centuries SSWH 8 – The student will demonstrate an understanding of the development of societies in Central and South America (a) Explain the rise and fall of the Olmecs, Mayan, Aztecs, and Inca empires. (b) Compare the cultures of the Americas: including government, economy, religion, and the arts of the Mayans, Aztecs, and Incas Social Hierarchy A Mayan Warrior A Mayan Priest Social Hierarchy • King and ruling family • Priests • Hereditary nobility (from which came the merchant class) • Warriors • Professionals and artisans • Peasants • Slaves SSWH 8 – The student will demonstrate an understanding of the development of societies in Central and South America (a) Explain the rise and fall of the Olmecs, Mayan, Aztecs, and Inca empires. (b) Compare the cultures of the Americas: including government, economy, religion, and the arts of the Mayans, Aztecs, and Incas Religion and Education Human Sacrifice and Bloodletting Ritual Religion: Bloodletting Rituals • Mayans believed the shedding of human blood would prompt the gods to send rain to water the maize • Bloodletting involved both war captives and Mayan royals Mayan queen holds a bowl filled with strips of paper used to collect blood. Economic Exchange Mayan symbol for movement Economic Exchange • Traveling merchants served as traders and ambassadors to neighboring lands and allied people • Traded mainly in exotic and luxury goods such as • rare animal skins, • cacao beans, and • finely crafted works of art • Cacao used as money SSWH 8 – The student will demonstrate an understanding of the development of societies in Central and South America (a) Explain the rise and fall of the Olmecs, Mayan, Aztecs, and Inca empires. (b) Compare the cultures of the Americas: including government, economy, religion, and the arts of the Mayans, Aztecs, and Incas New Technologies Mayan Calendar Observatory at El Caracol SSWH 8 – The student will demonstrate an understanding of the development of societies in Central and South America (a) Explain the rise and fall of the Olmecs, Mayan, Aztecs, and Inca empires. (b) Compare the cultures of the Americas: including government, economy, religion, and the arts of the Mayans, Aztecs, and Incas New Technologies • Excelled in astronomy and mathematics – Could plot planetary cycles – Invented the concept of zero and used a symbol to represent zero – By combining astronomy and mathematics, calculated the length of the solar year at 365.242 days Mayan numerical system SSWH 8 – The student will demonstrate an understanding of the development of societies in Central and South America (a) Explain the rise and fall of the Olmecs, Mayan, Aztecs, and Inca empires. (b) Compare the cultures of the Americas: including government, economy, religion, and the arts of the Mayans, Aztecs, and Incas New Technologies: Calendar • Mayan priests developed the most elaborate calendar of the ancient Americas • Interwove two kinds of year – A solar year of 365 days governed the agricultural cycle – A ritual year of 260 days governed daily affairs by organizing time into twenty “months” of thirteen days each What is interesting about this calendar? SSWH 8 – The student will demonstrate an understanding of the development of societies in Central and South America (a) Explain the rise and fall of the Olmecs, Mayan, Aztecs, and Inca empires. (b) Compare the cultures of the Americas: including government, economy, religion, and the arts of the Mayans, Aztecs, and Incas Art and Writing Mayan writing Mayan Decline • By about 800, most Mayan populations had begun to desert their cities – Full scale decline followed everywhere but in the northern Yucatan • Possible causes include • foreign invasion, • internal dissension and civil war, • failure of the water control system leading to agricultural disaster, • ecological problems caused by destruction of the forests, • epidemic diseases, • and natural disasters SSWH 8 – The student will demonstrate an understanding of the development of societies in Central and South America (a) Explain the rise and fall of the Olmecs, Mayan, Aztecs, and Inca empires. (b) Compare the cultures of the Americas: including government, economy, religion, and the arts of the Mayans, Aztecs, and Incas Characteristics of a Civilization • • • • • • Intensive agricultural techniques Specialization of labor Cities A social hierarchy Organized religion and education Development of complex forms of economic exchange • Development of new technologies • Advanced development of the arts. (This can include writing.) Aztecs • Aztecs came into the Valley of Mexico during the 12th and 13th century A.D., and rose to be the greatest power in the Americas by the time the Spaniards arrived, in the 16th century. • According to myth, Huitzilopochtli told Tenoch to lead his people to a place of refuge on a swampy island in Lake Texcoco. When they reached their destination, they were to look for an eagle perched on a cactus. • At that location, they were to build their city and honor Huitzilopochtli with human sacrifices. The city they built was called Tenochtitlán: the city of Tenoch. SSWH 8 – The student will demonstrate an understanding of the development of societies in Central and South America (a) Explain the rise and fall of the Olmecs, Mayan, Aztecs, and Inca empires. (b) Compare the cultures of the Americas: including government, economy, religion, and the arts of the Mayans, Aztecs, and Incas Aztec Calendar Stone Agriculture • Because their capital was in a swamp they had to make adjustments. They made Chnampias (floating fruit and vegetable gardens) – Important to them were • • • • Sweet potato Maize Tomatoes Cacao (Chocolate ) SSWH 8 – The student will demonstrate an understanding of the development of societies in Central and South America (a) Explain the rise and fall of the Olmecs, Mayan, Aztecs, and Inca empires. (b) Compare the cultures of the Americas: including government, economy, religion, and the arts of the Mayans, Aztecs, and Incas Specialization of Labor • Just like the other cultures. People had the chance to specialize into one craft. – – – – – – – – – Farmers Priests Warriors Mathematicians Warriors Architects and sculptors Potters Tool manufacturers Textile makers Cities • Most famous and largest was the capital of the empire. Tenochtitlan. Sometimes referred to as the Venice of the West SSWH 8 – The student will demonstrate an understanding of the development of societies in Central and South America (a) Explain the rise and fall of the Olmecs, Mayan, Aztecs, and Inca empires. (b) Compare the cultures of the Americas: including government, economy, religion, and the arts of the Mayans, Aztecs, and Incas Social Hierarchy • • • • • • King Priests Nobles Warriors Commoners Slaves SSWH 8 – The student will demonstrate an understanding of the development of societies in Central and South America (a) Explain the rise and fall of the Olmecs, Mayan, Aztecs, and Inca empires. (b) Compare the cultures of the Americas: including government, economy, religion, and the arts of the Mayans, Aztecs, and Incas Organized Religion and Education • Believed in 1000’s of gods and goddesses • Emperors were the direct link of Gods on Earth • Sacrifice and bloodletting were a part of their religious belief. • Temples and Pyramids were often gateways to speaking with the gods SSWH 8 – The student will demonstrate an understanding of the development of societies in Central and South America (a) Explain the rise and fall of the Olmecs, Mayan, Aztecs, and Inca empires. (b) Compare the cultures of the Americas: including government, economy, religion, and the arts of the Mayans, Aztecs, and Incas Economic Exchange • Economy was based on trade/barter • Cacao beans were often used at a form of money (i.e. 30 beans = a rabbit and about 600= selling your kid) • Quachtli- type of cotton cloth that was highly valued. SSWH 8 – The student will demonstrate an understanding of the development of societies in Central and South America (a) Explain the rise and fall of the Olmecs, Mayan, Aztecs, and Inca empires. (b) Compare the cultures of the Americas: including government, economy, religion, and the arts of the Mayans, Aztecs, and Incas New Technologies • Prime Example is the capital itself. SSWH 8 – The student will demonstrate an understanding of the development of societies in Central and South America (a) Explain the rise and fall of the Olmecs, Mayan, Aztecs, and Inca empires. (b) Compare the cultures of the Americas: including government, economy, religion, and the arts of the Mayans, Aztecs, and Incas Technologies • Others were – Weapons – Calendar – Astronomy – Mathematics – Agricultural (Canapés) – Dugout Canoes SSWH 8 – The student will demonstrate an understanding of the development of societies in Central and South America (a) Explain the rise and fall of the Olmecs, Mayan, Aztecs, and Inca empires. (b) Compare the cultures of the Americas: including government, economy, religion, and the arts of the Mayans, Aztecs, and Incas Development of the Arts • Mostly a form of religious expression and was a way to pay tribute to the gods. • Most art in the Aztec empire was in the form of – Sculpture, pottery, or pictographs. SSWH 8 – The student will demonstrate an understanding of the development of societies in Central and South America (a) Explain the rise and fall of the Olmecs, Mayan, Aztecs, and Inca empires. (b) Compare the cultures of the Americas: including government, economy, religion, and the arts of the Mayans, Aztecs, and Incas Quick Vocab • Cuzco, Inca roads, quipu, terrace farming SSWH 8 – The student will demonstrate an understanding of the development of societies in Central and South America (a) Explain the rise and fall of the Olmecs, Mayan, Aztecs, and Inca empires. (b) Compare the cultures of the Americas: including government, economy, religion, and the arts of the Mayans, Aztecs, and Incas Inca Inca • By the 13th Century, the Inca had established domination over the regional states in Andean South America • In 1438, Pachacuti launched a series of military campaigns that greatly expanded Inca authority – Success bred success and the Inca empire expanded • By the late 15th Century, the Inca empire covered more than 2,500 miles, embracing almost all of modern Peru, most of Ecuador, much of Bolivia, and parts of Chile and Argentina Characteristics of a Civilization • • • • • • Intensive agricultural techniques Specialization of labor Cities A social hierarchy Organized religion and education Development of complex forms of economic exchange • Development of new technologies • Advanced development of the arts. (This can include writing.) Agriculture Llamas SSWH 8 – The student will demonstrate an understanding of the development of societies in Central and South America (a) Explain the rise and fall of the Olmecs, Mayan, Aztecs, and Inca empires. (b) Compare the cultures of the Americas: including government, economy, religion, and the arts of the Mayans, Aztecs, and Incas Agriculture • Intensive agricultural techniques – Inca empire spanned many types of environments and required terraces to make farmland out of the mountainous terrain – Chief crop was the potato – Herded llamas and alpacas for meat, wool, hides, and dung (used as fuel) SSWH 8 – The student will demonstrate an understanding of the development of societies in Central and South America (a) Explain the rise and fall of the Olmecs, Mayan, Aztecs, and Inca empires. (b) Compare the cultures of the Americas: including government, economy, religion, and the arts of the Mayans, Aztecs, and Incas Specialization of Labor Inca textile fragment Specialization of Labor • Large class of bureaucrats to support centralized government • Much fewer skilled craftsmen – Some potters, textile workers, and tool makers – Inca designated different specialties for captured people to meet the society’s needs SSWH 8 – The student will demonstrate an understanding of the development of societies in Central and South America (a) Explain the rise and fall of the Olmecs, Mayan, Aztecs, and Inca empires. (b) Compare the cultures of the Americas: including government, economy, religion, and the arts of the Mayans, Aztecs, and Incas Cities Cities: Cuzco • Inca capital at Cuzco served as the administrative, religious, and ceremonial center of the empire • May have supported 300,000 residents SSWH 8 – The student will demonstrate an understanding of the development of societies in Central and South America (a) Explain the rise and fall of the Olmecs, Mayan, Aztecs, and Inca empires. (b) Compare the cultures of the Americas: including government, economy, religion, and the arts of the Mayans, Aztecs, and Incas Social Hierarchy SSWH 8 – The student will demonstrate an understanding of the development of societies in Central and South America (a) Explain the rise and fall of the Olmecs, Mayan, Aztecs, and Inca empires. (b) Compare the cultures of the Americas: including government, economy, religion, and the arts of the Mayans, Aztecs, and Incas Social Hierarchy • • • • • Rulers Aristocrats Priests Bureaucrats Peasant cultivators of common birth SSWH 8 – The student will demonstrate an understanding of the development of societies in Central and South America (a) Explain the rise and fall of the Olmecs, Mayan, Aztecs, and Inca empires. (b) Compare the cultures of the Americas: including government, economy, religion, and the arts of the Mayans, Aztecs, and Incas Social Hierarchy • Chief ruler was king and was an absolute and infallible ruler • Dead rulers retained their prestige even after death – Remains were – Were seen as intermediaries with the gods SSWH 8 – The student will demonstrate an understanding of the development of societies in Central and South America (a) Explain the rise and fall of the Olmecs, Mayan, Aztecs, and Inca empires. (b) Compare the cultures of the Americas: including government, economy, religion, and the arts of the Mayans, Aztecs, and Incas Social Hierarchy • Priests often came from royal and aristocratic families – They lived celibate and ascetic lives – Influenced Inca society by education and religious rituals • Large class of bureaucrats to support centralized government – Bureaucrats often were drawn from the loyal ranks of conquered people SSWH 8 – The student will demonstrate an understanding of the development of societies in Central and South America (a) Explain the rise and fall of the Olmecs, Mayan, Aztecs, and Inca empires. (b) Compare the cultures of the Americas: including government, economy, religion, and the arts of the Mayans, Aztecs, and Incas Social Hierarchy • Peasants worked lands allocated to them – Surplus supported the ruling, aristocratic, and priestly classes as well as providing public relief in times of famine or to widows SSWH 8 – The student will demonstrate an understanding of the development of societies in Central and South America (a) Explain the rise and fall of the Olmecs, Mayan, Aztecs, and Inca empires. (b) Compare the cultures of the Americas: including government, economy, religion, and the arts of the Mayans, Aztecs, and Incas Religion and Education Inti Raymi, the feast of the sun Religion and Education • Main god was Inti, god of the sun • Sacrificed agricultural produce or animals rather than humans • Believed in life after death where an individual received rewards or punishments based on the quality of his earthly life SSWH 8 – The student will demonstrate an understanding of the development of societies in Central and South America (a) Explain the rise and fall of the Olmecs, Mayan, Aztecs, and Inca empires. (b) Compare the cultures of the Americas: including government, economy, religion, and the arts of the Mayans, Aztecs, and Incas Economic Exchange Inca gold Economic Exchange • Inca society did not produce large classes of merchants or skilled artisans • Locally they bartered among themselves • Long distance trade was supervised by the central government using the excellent Inca roads SSWH 8 – The student will demonstrate an understanding of the development of societies in Central and South America (a) Explain the rise and fall of the Olmecs, Mayan, Aztecs, and Inca empires. (b) Compare the cultures of the Americas: including government, economy, religion, and the arts of the Mayans, Aztecs, and Incas Economic Exchange • Gold, the Inca’s most valuable commodity, proved to be their undoing when Spanish conquistadors destroyed much of the empire in the early 1500s in search of gold • The Spanish melted down almost all the gold so few works of art remain Arrival of Francisco Pizarro in South America SSWH 8 – The student will demonstrate an understanding of the development of societies in Central and South America (a) Explain the rise and fall of the Olmecs, Mayan, Aztecs, and Inca empires. (b) Compare the cultures of the Americas: including government, economy, religion, and the arts of the Mayans, Aztecs, and Incas New Technologies Major Roads of the Inca Empire • New Technologies: Roads Allowed the Inca government to: – maintain centralized control – move military forces quickly, transport food supplies where needed, – tying the widespread territories together • Rest stations were built a day’s walk apart • Runners were positioned at convenient intervals to deliver government messages SSWH 8 – The student will demonstrate an understanding of the development of societies in Central and South America (a) Explain the rise and fall of the Olmecs, Mayan, Aztecs, and Inca empires. (b) Compare the cultures of the Americas: including government, economy, religion, and the arts of the Mayans, Aztecs, and Incas Art and Writing Quipu (khipu) Art and Writing • The Inca had no writing • Instead they kept records using a quipu – A array of small cords of various colors and lengths, all suspended from a thick cord – By tying knots in the small cords, Inca could record statistical information 586 on a quipu SSWH 8 – The student will demonstrate an understanding of the development of societies in Central and South America (a) Explain the rise and fall of the Olmecs, Mayan, Aztecs, and Inca empires. (b) Compare the cultures of the Americas: including government, economy, religion, and the arts of the Mayans, Aztecs, and Incas