Plant Nutrition
advertisement

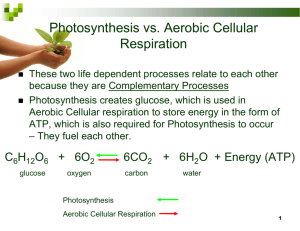
UNIT 5: Photosynthesis and Respiration BIG IDEA: Energy is produced and released by making and breaking chemical bonds Think About It: • With your partner, come up with a list of activities that you do that requires energy • What gives us energy? Energy • Directly or indirectly , all energy in living things comes from the sun Obtaining Energy • Autotrophs • Organisms that are capable of making food (energy) from simple inorganic substances • EX: green plants, algae Two Types of Autotrophs • 1. Photoautotrophs: use carbon dioxide and light energy to drive reactions needed to make food Next type… • 2. Chemoautotrophs: utilize inorganic chemicals for the energy to drive food making reactions Obtaining Energy • Heterotrophs • Organisms that cannot make their own food (energy) and must depend on other plants or animals as food source (energy) • Examples: Humans, dogs, cats Photosynthesis • Process of capturing energy of sunlight and transforming it into chemical energy • CO2 + H2O----glucose + O2 Photosynthesis • Two stages – Light reactions- light energy is converted into chemical energy of two intermediate molecules – Calvin cycle-Organic molecules are formed from CO2 Photosynthesis • Sunlight, sometimes called white light, is a form of energy that travels in waves • Wavelength: the distance between the crest of one wave and the crest of the next wave Visible Light Spectrum • • • • • • Depends on wavelength Blue: 380 (nm) Green: 500 (nm) Yellow 560 (nm) Light red: 600 (nm) Darker red: 750 (nm) Photosynthesis • Pigments: absorb light • EX: a red object absorbs all the visible colors of the spectrum except red which is reflected and gives the object the red color Types of Photosynthetic Pigments a. Chlorophylls: absorb red and blue light, appear green b. Carotenes: absorb blue, appear orange c. Xanthophylls: appear yellow, may not be used to absorb light The color of an egg yolk is from the xanthophyll carotenoids lutein and zeaxanthin • The color of an egg yolk is from the xanthophyll carotenoids lutein and zeaxanthin CHLOROPLAST • Site of Photosynthesis PARTS OF THE CHLOROPLAST Inner and outer membrane Thylakoids Grana Stroma Parts of the Chloroplast • Thylakoid- Membrane of the thylakoid contains photosynthetic pigments; flattened sacs • Site of the light reactions Parts of the Chloroplast • Grana- Stacks of thylakoids • Stroma-Region b/t grana – Site of the light independent reactions Photosynthesis Reactions • Light Dependent Reactions-energy from light makes the reaction happen • Light Independent Reactions- Doesn’t need the energy from light to make the reaction happen but they do need products of the light reaction to proceed. Steps in Light Dependent Light Dependent Reactions- In the Chloroplast • Pigments in the photosynthetic membranes absorb light (pigments are located in Photosystem I & II • When the light hits the chlorophyll in Photosystem II the electrons become excited and jump up. • The electrons are captured by the electron transport chain. • We need to replace the electrons that are lost so we steal some from water . This breaks the water molecule apart forming H+ and O • As we transport electrons down the chain we use their energy to produce ATP • The electrons now go to Photosystem I and it loses electrons to NADP+ to make it NADPH. The final products of the light reaction • At the end of the light reaction we have made 1. NADPH 2. ATP 3. O2 Reactants used during the light reaction • Water • Also used sunlight Light independent reaction ( Calvin Cycle) • A. Use CO2 , ATP, NADPH • B. Uses products from light reaction (Light is not necessary for this reaction) • C. Location stroma Steps in Light Independent Reaction: • 6 CO2 reacts with the sugar, ribulose phophate (RuBP)sugar called phosphoglycerate (PGA) • PGA12 phosphoglyceraldehyde (PGAL) • NADPH and ATP from light reaction provide energy for this step Steps in Light Independent Reaction (con’t) • PGAL does 2 things: a. Makes more RuBP to continue cycle (requires 10 PGAL to do this) b. Form 1 glucose (requires 2 PGAL) Concept Map Section 8-3 Photosynthesis includes Lightdependent reactions use Energy from sunlight Calvin cycle Thylakoid membranes to produce ATP NADPH takes place in take place in Stroma of O2 Chloroplasts uses ATP NADPH to produce High-energy sugars Figure 8-7 Photosynthesis: An Overview Section 8-3 Light CO2 Chloroplast Chloroplast NADP+ ADP + P LightDependent Reactions Calvin Cycle ATP NADPH O2 Sugars Factors Affecting Photosynthesis • a. b. c. d. Four main types: Light intensity Temperature Water Mineral availability Cellular Respiration • Release of the energy stored in food • Occurs in the inside of the cells of both autotrophs and heterotrophs Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) • Energy released during cellular respiration is stored as ATP • Consists of adenine, ribose and three phosphates How is energy stored in ATP? • Energy is stored in the bonds. Once a bond breaks (causing ATP to lose a phosphate group), there is a release of energy. Release of Energy Adenosine diphosphate or (ADP) • Two phosphate groups, adenine, and ribose • Where would the energy be in ADP Two Types of Cellular Respiration Aerobic Respiration: • Occurs in presence of oxygen • Occurs in the mitochondria • Produces about 36 ATP Second Type of Cellular Respiration Anaerobic Respiration: • Occurs without oxygen • Occurs in the cytoplasm • Produces 2 ATP Which type of cellular respiration is more efficient? • Aerobic because it produces more ATP (more energy) Two types of Anaerobic Respiration: • 1. Alcoholic Fermentation: yeast produces alcohol • 2. Lactic Acid Fermentation: muscles produces lactic acid when they don’t have enough oxygen What is the equation for cellular respiration? GLUCOSE+ 6O26 CO2 + 6 H2O + Energy (36 ATP) What is the relationship between photosynthesis and cellular respiration? • Opposite reactions • Let’s write the two reactions to see