Warranties_review_ver010712
advertisement

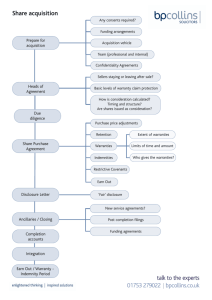
Warranties Review Questions 1. a. b. c. d. The person who becomes secondarily liable for another’s debt or performance is called the: Guarantee Warrantor Guarantor Warrantee 1. a. b. c. d. The person who becomes secondarily liable for another’s debt or performance is called the: Guarantee Warrantor Guarantor Warrantee 2. An affirmation of fact or promise made by the seller to the buyer that relates to the goods and becomes a part of the basis of the bargain creates….. a. An implied warranty b. A full warranty c. An express warranty 2. An affirmation of fact or promise made by the seller to the buyer that relates to the goods and becomes a part of the basis of the bargain creates….. a. An implied warranty b. A full warranty c. An express warranty 3. A warranty is a promise that a. A proposition that certain facts are truly as they are represented to be and that they will remain so. b. A party will undertake collaterally to answer for the payment of another’s debt 3. A warranty is a promise that a. A proposition that certain facts are truly as they are represented to be and that they will remain so. b. A party will undertake collaterally to answer for the payment of another’s debt 4. All of the following are reasons that construction warranties are required EXCEPT: a. To protect the owner against faults, defects, or failures, in spite of technical compliance with the terms of the contract. b. To provide a remedy to the owner for non conformance with the contract after completion and acceptance of construction. c. To give the owner recourse against additional parties who are not in a direct contractual relationship with the owner. d. To stop the manufacturer’s responsibility at the end of the correction period. 4. All of the following are reasons that construction warranties are required EXCEPT: a. To protect the owner against faults, defects, or failures, in spite of technical compliance with the terms of the contract. b. To provide a remedy to the owner for non conformance with the contract after completion and acceptance of construction. c. To give the owner recourse against additional parties who are not in a direct contractual relationship with the owner. d. To stop the manufacturer’s responsibility at the end of the correction period. 5. a. b. c. d. A written warranty that fails to meet one or more of the minimum standards for a “full warranty” is…. An express warranty A warranty of title An implied warranty A limited warranty 5. a. b. c. d. A written warranty that fails to meet one or more of the minimum standards for a “full warranty” is…. An express warranty A warranty of title An implied warranty A limited warranty 6. “Terms and Conditions” refers to: a. The requirements that apply to maintaining valid warranties. b. The general conditions and supplementary conditions. c. The contract between the owner and the contractor d. Insurance settlements. 6. “Terms and Conditions” refers to: a. The requirements that apply to maintaining valid warranties. b. The general conditions and supplementary conditions. c. The contract between the owner and the contractor d. Insurance settlements. 7. a. As a result of the widely held misconception that a contractor’s responsibility for defective work lasts only for one-year guaranty period: The Supplementary Conditions should state that the period lasts a specific additional amount of time. b. EJDC and AIA have changed their documents to say correction period instead guaranty period. c. The owner accepts any repairs after the date d. The courts relieve the contractor of his responsibility. 7. a. As a result of the widely held misconception that a contractor’s responsibility for defective work lasts only for one-year guaranty period: The Supplementary Conditions should state that the period last a specific additional amount of time. b. EJDC and AIA have changed their documents to say correction period instead guaranty period. c. The owner accepts any repairs after the date d. The courts relieve the contractor of his responsibility. 8. When the General Conditions state that the Contractor shall correct any work to be found defective within one year after the date of substantial completion; a. The specific warranties on the project are nullified after the date b. The Contractor is responsible for no other work to be done after that date. c. The Contractor may still have to perform corrections when evidence is presented to overcome the presumption that they are the responsibility of the owner d. The architect is responsible for corrections that he did not catch during the final punch list. 8. When the General Conditions state that the Contractor shall correct any work to be found defective within one year after the date of substantial completion; a. The specific warranties on the project are nullified after the date b. The Contractor is responsible for no other work to be done after that date. c. The Contractor may still have to perform corrections when evidence is presented to overcome the presumption that they are the responsibility of the owner d. The architect is responsible for corrections that he did not catch during the final punch list. 9. According to the UCC (Uniform Commercial Code) a full warranty includes: a. Full refund of the cost of the product or replacement of the product. b. Labor to repair or replace the product c. Consequential or incidental damages due to failure of the product d. All of the above 9. According to the UCC (Uniform Commercial Code) a full warranty includes: a. Full refund of the cost of the product or replacement of the product. b. Labor to repair or replace the product c. Consequential or incidental damages due to failure of the product d. All of the above 10. All of the following are true about extended warranties EXCEPT: a. b. c. d. They are usually written from the manufacturer’s point of view They usually prorate the product for the years of service it has already performed Usually exclude consequential damage to any building components other than the warranted product itself Most manufacturers find the risks inconsequential and do not limit performance. 10. All of the following are true about extended warranties EXCEPT: a. b. c. d. They are usually written from the manufacturer’s point of view They usually prorate the product for the years of service it has already performed Usually exclude consequential damage to any building components other than the warranted product itself Most manufacturers find the risks inconsequential and do not limit performance. Answers 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. c c a d a a b c d d