Ch14
advertisement

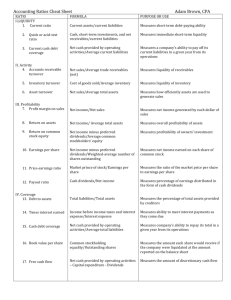
CHAPTER 14 Performance Measurement Sustainable Earnings • Likely level of future cash flows is generated by earnings • Sustainable earnings is net earnings adjusted for irregular items Irregular Items • Three types of irregular items are reported (all net of taxes) – Discontinued operations – Extraordinary items – Change in accounting principle Discontinued Operations • Disposal of a significant segment of a business • Report separately in statement of earnings – Earnings (loss) from continuing operations, and – Earnings (loss) from discontinued operations Discontinued Operations • Earnings (loss) from discontinued operations consists of: – Earnings (loss) from operations and – Gain (loss) on disposal of the segment • Both components are reported net of applicable taxes in a section entitled Discontinued Operations, which follows Earnings from Continuing Operations Extraordinary Items • Events and transactions that are: – Infrequent in occurrence – Unusual in nature – Not subject to management determination Change in Accounting Principle • Occurs when the principle used in the current year is different from the one used in the preceding year • Is permitted, when: – There has been a change in reporting circumstances, and – Management can show that the new principle is preferable to the old Comparative Analysis • Three types of comparisons: – Intracompany basis – Intercompany basis – Industry averages Comparative Analysis • Three tools: – Horizontal analysis – Vertical analysis – Ratio analysis Horizontal Analysis Change since base period Current year amount — Base year amount ——————————————————————— Base year amount ANY COMPANY INC. Assumed Net Sales (in thousands) 2005 $ 6,562.8 127% 2004 $ 6,295.4 121% 2003 2002 $ 6,190.6 $ 5,786.6 119% 112% 2001 $ 5,181.4 100% Vertical Analysis • Expresses each item in a financial statement as a percent of a base amount (total assets or net sales) ANY COMPANY, INC. Condensed Balance Sheets December 31 (in thousands) 2005 Assets Current assets Property, plant, and equipment Other assets Total assets Amount 2004 Percent Amount Percent $1,496.5 29.6% $1,467.7 30.1% 2,888.8 666.2 $5,051.5 57.2% 13.2% 100.0% 2,733.3 636.6 $4,837.6 56.9% 13.0% 100.0% Ratio Analysis Liquidity Ratios Measure short-term ability of the enterprise to pay its maturing obligations and to meet unexpected needs for cash Solvency Ratios Since 1892 Measure the ability of the enterprise to survive over a long period of time XYZ Co. Profitability Ratios Revenues - Expenses = Net Earnings Measure the earnings or operating success of an enterprise for a given period of time Liquidity Ratios • • • • • • • • Working capital Current ratio Cash current debt coverage Inventory turnover Days in inventory Receivables turnover Average collection period Acid-test (quick) ratio Working Capital • Measures short-term debt-paying ability Working Capital = Current Assets – Current Liabilities Current Ratio • Measures short-term debt-paying ability Current Ratio = Current Assets Current Liabilities Cash Current Debt Coverage • Measures short-term debt-paying ability (cash basis) Cash Current Debt Coverage = Cash Provided by Operating Activities Average Current Liabilities Inventory Turnover • Measures liquidity of inventory Inventory Turnover = Cost of Goods Sold Average Inventory Days in Inventory • Measures number of days inventory is on hand Days in Inventory = 365 Days Inventory Turnover Receivables Turnover • Measures liquidity of receivables Net Credit Sales Receivables Turnover = Average Gross Receivables Average Collection Period • Measures number of days receivables are outstanding Average Collection Period = 365 Days Receivables Turnover Acid-Test Ratio • Measures immediate short-term debt-paying ability Acid-Test Ratio = Cash + Short-Term Investments + Net Receivables Current Liabilities Solvency Ratios • • • • Debt to total assets Cash total debt coverage Times interest earned Free cash flow Debt to Total Assets Ratio • Measures % of total assets provided by creditors Debt to Total Assets = Total Liabilities Total Assets Cash Total Debt Coverage • Measures long-term debt-paying ability (cash basis) Cash Total Debt Coverage = Cash Provided by Operating Activities Average Total Liabilities Times Interest Earned • Measures ability to meet interest payments as they come due Times Interest Earned = Earnings Before Interest Expense and Income Tax Expense (EBIT) Interest Expense Free Cash Flow • Measures cash available for paying dividends or expanding operations Cash Capital Provided Expenditures by Operating Activities Dividends = Paid Free Cash Flow Profitability Ratios • • • • • • • • Earnings per share (EPS) Price-earnings (P-E) ratio Gross profit margin Profit margin Return on assets Asset turnover Return on common shareholders’ equity Payout ratio Earnings Per Share (EPS) • Measures net earnings earned on each common share Earnings Per Share = Earnings Available to Common Shareholders Average Number of Common Shares Price-Earnings (P-E) Ratio • Measures relationship between market price per share and earnings per share Share Price Price-Earnings Ratio = Earnings Per Share Gross Profit Margin • Measures margin between selling price and cost of goods sold Gross Profit Margin = Gross Profit Net Sales Profit Margin • Measures net earnings generated by each dollar of sales Profit Margin = Net Earnings Net Sales Return On Assets • Measures overall profitability of assets Return on Assets = Net Earnings Average Total Assets Asset Turnover • Measures how efficiently assets are used to generate sales Asset Turnover = Net Sales Average Total Assets Return on Common Shareholders’ Equity • Measures profitability of common shareholders’ investment Return on Common Shareholders’ Equity = Net Earnings – Preferred Dividends Average Common Shareholders’ Equity Payout Ratio • Measures % of earnings distributed in the form of cash dividends Cash Dividends Payout Ratio = Net Earnings Quality of Earnings • Increased importance today due to recent corporate scandals • Can be impacted by alternative accounting principles (variation and discretion in selection of GAAP) • Companies report pro forma earnings which are a non-GAAP earnings measure • Quality of earnings also affected by improper recognition of revenues and liabilities