An Age of Exploration
advertisement

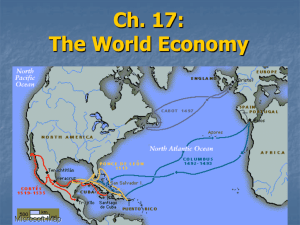
1400-1800 I. Europeans Explore the East for “God, Gold, and Glory” A. Europeans Seek New Trade Routes 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. New desire for contact with Asia develops in Europe in early 1400s Main reason for exploration is to gain wealth Contact during the Crusades spurs demand for Asian goods Muslims and Italians control trade Other European nations want to bypass these powers Europeans Explore the East B. The Spread of Christianity 1. Desire to spread Christianity also spurs exploration 2. Portuguese explorer Bartolomeu Dias wants to serve God and king C. Technology Makes Exploration Possible 1. In 1400s, the caravel makes it possible to sail against the wind (triangular sails) 2. Astrolabe makes navigation easier 3. Magnetic compass improves direction II. Portugal and Spain A. The Portuguese Explore Africa 1. Prince Henry, the son of Portugal’s king, supports exploration 2. In 1419, he founds navigation school on coast of Portugal 3. By 1460, Portuguese have trading posts along west coast of Africa B. 1. 2. 3. Portuguese Sailors Reach Asia In 1488, Dias sails around southern tip of Africa In 1498, Vasco da Gama sails to India In 1499, da Gama returns to Portugal with valuable cargo Europeans Explore the East C. A Rival Power 1. In 1492, Christopher Columbus sails for Spain 2. Convinces Spanish to support plan to reach Asia by sailing west 3. Reaches Americas instead 4. Opens Americas to exploration and colonization 5. In 1493, pope divides these lands between Spain and Portugal 6. Agreement formalized by Treaty of Tordesillas in 1494 III. Trading Empires in the Indian Ocean A. Portugal’s Trading Empire 1. In 1509, Portugal defeats Muslims, takes over Indian Ocean trade 2. In 1510, Portugal captures Goa, port city in western India 3. In 1511, Portugal seizes Malacca, on Malay Peninsula 4. These gains break Muslim-Italian hold on Asian trade B. Other Nations Challenge the Portuguese 1. English and Dutch begin moving into Asia in 17th century 2. Dutch have more ships (20,000) than any other nation in 1600 IV. Other Explorers Take to the Seas A. Claims in the New World 1. Pedro Alvares Cabral claims Brazil for Portugal in 1500 2. Amerigo Vespucci identifies South America as new continent in 1501 3. In 1507, German mapmaker names the continent America 4. Vasco Nunez de Balboa reaches the Pacific Ocean 5. Juan Ponce de Leon claims Florida for Spain in 1513 6. In 1540s, Francisco Coronado explores Southwest, finds little gold B. Circumnavigation of the Earth 1. Ferdinand Magellan leaves to sail around the world in 1519 2. Magellan is killed, but some of his men return to Spain in 1522 V. Spanish Conquests A. Conquistadors 1. In 1519, Hernando Cortes – Spanish Adventurer – lands in Mexico 2. He and others become known as conquistadors – Spanish conquerors B. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Cortes and Pizarro Cortes and 600 men reach Aztec capital of Tenochtitlan By 1521, they conquer Aztec empire Conquest aided by superior weapons, Native American allies European diseases wipe out large numbers of Aztecs Spanish conqueror Francisco Pizarro leads force to Peru in 1532 Pizarro kills Atahualpa – Inca ruler – and defeats the Inca VI. Competing Claims in North America A. Explorers Establish New France 1. Samuel de Champlain founds New France (Canada) and Quebec 2. Main activity of the colony is the fur trade B. The English Arrive in North America 1. King James permits investors to start North American colony 2. In 1607, colonists founded Jamestown – English settlement in Virginia 3. Early years very difficult; many die, but settlement takes hold C. The Dutch Found New Netherland 1. In 1609 Henry Hudson explores waterways for Dutch 2. Dutch claim land, found New Netherland – now Albany and New York 3. Dutch focus on fur trade; welcome settlers from other lands D. Colonizing the Caribbean 1. European nations also start colonies in Caribbean 2. Large cotton, sugar plantations worked by enslaved Africans VII. The Atlantic Slave Trade A. The Causes of African Slavery 1. Slavery has existed in Africa for centuries 2. Spread of Islam produces more slavery in Africa 3. Need work workers in Americas raises demand for enslaved Africans 4. Atlantic slave trade – forced movement of many Africans to Americas B. A Forced Journey 1. Triangular trade – trade network linking Europe, Africa, Americas 2. One trade route – (1) manufactured goods move from Europe to Africa, then (2) people move from Africa to Americas, then (3) sugar, coffee, tobacco move from Americas to Europe 3. Voyage of enslaved Africans to Americas known as the middle passage 4. As many as 20% of Africans die on these journeys VIII. The Columbian Exchange A. Definition 1. Columbian Exchange – global transfer of food, plants, animals 2. Corn, potatoes from Americas become crops in Eastern Hemisphere 3. New animals, plants introduced by Europeans take hold in Americas 4. European diseases kill millions of Native Americans B. Global Trade 1. Wealth from Americas, growth of trade changes business in Europe 2. New economic system – capitalism – based on private property, profit 3. Increase in business leads to inflation – rising prices – in Europe 4. Joint-stock company lets investors share risk, profits of business 5. These companies help fund colonies in America Columbian Exchange (cont.) C. The Growth of Mercantilism 1. Policy of mercantilism emphasizes national wealth as a source of power 2. One way for a nation to increase wealth: gather gold, silver 3. Favorable balance of trade when nation sells more goods than it buys 4. Colonies provide raw materials that home country uses to make goods 5. Economic changes spur growth of towns, rise of merchant class 6. Still, most people are poor and live in rural areas