Normal & Abnormal Radiography
advertisement

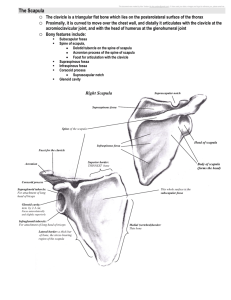
Chapter- 3 Student must recall structural features / landmarks in different images of Shoulder joint & Upper Limb. Student must Distinguish between different landmarks / parts of structures in different images of Shoulder & Elbow joint. Student must Distinguish between normal and abnormal X Ray images of Shoulder & Elbow joint. Student must Analyse the pathological findings of different images of Shoulder & Elbow joint. Normal Shoulder AP view with external rotation AP view with internal rotation Axillary view v AC vvgreater/less GH joint,joint, glenoid er acromion, tuberosity fossa clavicle GH joint, glenoid Fossa AC joint, acromion, clavicle greater/less er tuberosity greater/lesser tuberosity scapula, spine of scapula, Coracoid process • GH joint • glenoid Fossa • • • • • • AC joint Acromion, clavicle greater/lesser tuberosity scapula, spine of scapula, Coracoid process Axillary View Taken with arm abducted Cassette is placed on the superior aspect of the shoulder Arm is abducted enough to allow the radiographic beam to pass between the Chest & Arm GH joint, Humeral head, Glenoid Greater tubercle Acromion Clavicle coracoid Acromion Supraspinatus Glenoid fossa Subscapularis Humerus Clavicle Hill-Sachs lesion- Notched defect of flattening of humeral head Glenoid fossa & labrum (low intensity) Long head of biceps Subscapularis Humeral head Infraspinatus, subscapularis Scapula, spine of scapula, coracoid process Clavicle Humerus, greater /lesser tubercle, long head of biceps Anterior dislocation of the humeral had toward coracoid process Marked overlap of the humeral head of the glenoid Axillary View Note: humeral head is not in the Glenoid fossa AP with internal rotation Note: small & false “joint space” as the humeral head sits behind the glenoid fossa Lateral View – Scapular fracture on the lateral border Lateral View Oblique fracture of the Shaft of Humerus AP View - Mild displaced fracture Tear of RC are associated with intermediate signal on T1 images Increased signal on T2-weighted images May have fluid in the subdeltoid & subacromial bursae Retraction of supraspinatus tendon with atrophy of the muscles Impingement: 40 y/o male was dx with shoulder impingement MRI shows fluid in the subacromial bursa Arthroscopic finding: 2 cm supraspinatus tear 60 y/o with shoulder pain T2 oblique coronal image Increased signal in the RC tendon. An effusion is also seen in the joint spaces & subdeltoid bursae. --------ROTATOR CUFF TEAR 48 y/o paraplegic who fell T1 – weighted coronal image Focal area of increased signal in the supraspinatus tendon Tendon is also swollen with fluid in the subacromial bursae & in the joint space- ROTATOR CUFF TEAR- Case-1 48 y/o paraplegic who fell Spin density coronal image Focal area of increased s ignal in the supraspinatus tendon Tendon is also swollen with fluid in the subacromial bursae & in the joint space – ROTATOR CUFF TEAR – CASE-2 Radius : head/shaft Humeroradial & humerulnar Joint Humerus: Olecranon fossa, medial/lateral epicondyle, capitulum trochlea Ulna: olecranon, coronoid process, shaft