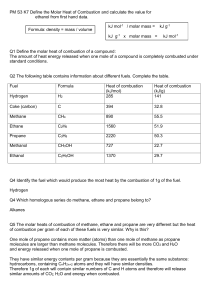
Thermochemistry Review: SCH4U Test Prep
advertisement
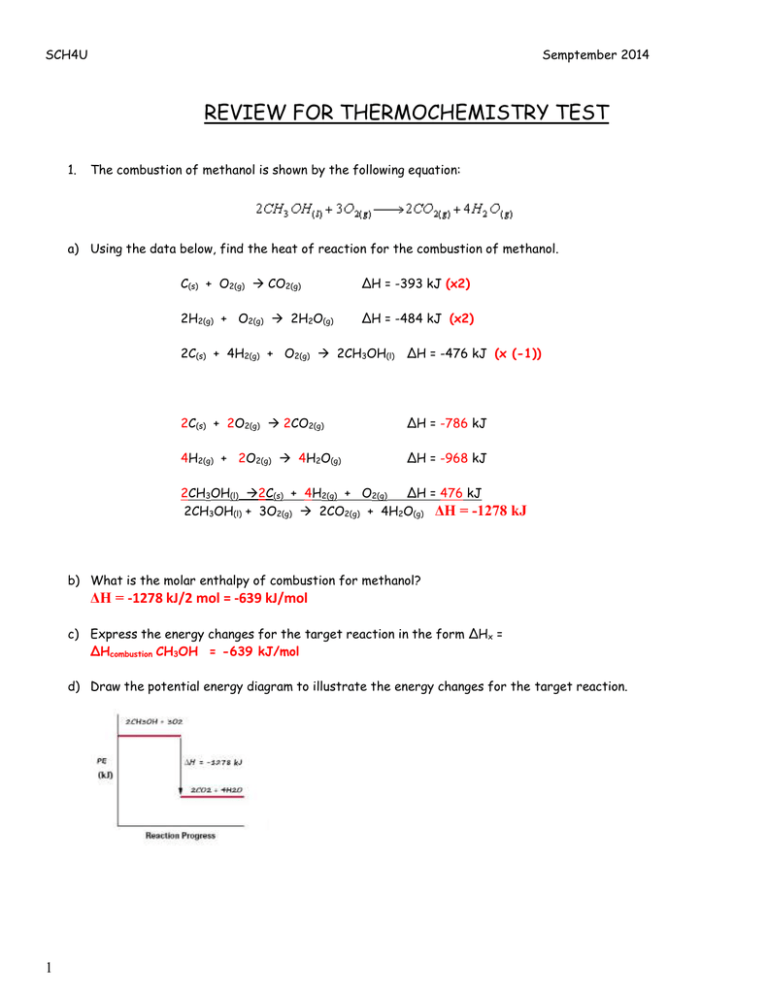
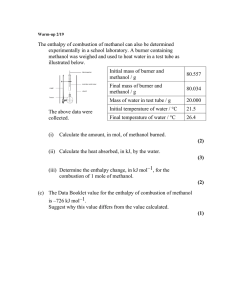
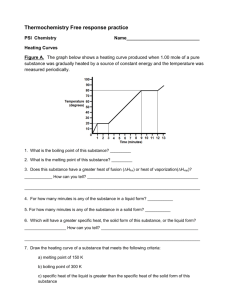
SCH4U Semptember 2014 REVIEW FOR THERMOCHEMISTRY TEST 1. The combustion of methanol is shown by the following equation: a) Using the data below, find the heat of reaction for the combustion of methanol. C(s) + O2(g) CO2(g) ΔH = -393 kJ (x2) 2H2(g) + O2(g) 2H2O(g) ΔH = -484 kJ (x2) 2C(s) + 4H2(g) + O2(g) 2CH3OH(l) ΔH = -476 kJ (x (-1)) 2C(s) + 2O2(g) 2CO2(g) ΔH = -786 kJ 4H2(g) + 2O2(g) 4H2O(g) ΔH = -968 kJ 2CH3OH(l) 2C(s) + 4H2(g) + O2(g) ΔH = 476 kJ 2CH3OH(l) + 3O2(g) 2CO2(g) + 4H2O(g) ΔH = -1278 kJ b) What is the molar enthalpy of combustion for methanol? ΔH = -1278 kJ/2 mol = -639 kJ/mol c) Express the energy changes for the target reaction in the form ΔHx = ΔHcombustion CH3OH = -639 kJ/mol d) Draw the potential energy diagram to illustrate the energy changes for the target reaction. 1 e) Write the target reaction that includes the heat term in the equation. 2CH3OH + 3O2 2CO2 + 4H2O + 1278 kJ f) What mass of water could be heated from 20.00 C to 35.00 C by the burning of 10.0 g of methanol that is held in a calorimeter with a heat capacity of 2.9 kJ/ oC? qmethanol = qH2O + qcalorimeter nΔH = mcΔT + CΔT (0.312)(639000) = m(4.18)(15.0) + 2900(15.0) m = 2480 g n = 10.0/32.04 =0.312 mol lΔHl = 639 kJ/mol = 639000 J/mol Ccal = 2.9 kJ/oC = 2900 J/oC g) Will entropy increase or decrease in the combustion of methanol? Will ΔS be positive or negative? Entropy will increase because there will be an increase from 3 to 6 moles of gas. ΔS will be positive. h) Calculate the change in entropy for the combustion of methanol. ΔS = [2(214) + 4(189)] – [2(127) + 3(205)] = 315 J i) Consider your values of ΔH and ΔS. Will the combustion of methanol always be spontaneous? Explain. ΔH is negative (i.e.the products are more stable than the reactants) and ΔS is positive (i.e. the products are more randomly organized than the reactants). Both of these conditions favour a reaction occurring therefore the combustion of methanol will always be spontaneous. j) Calculate the change in Gibb’s free energy for the combustion of methanol at 100 oC. Is the reaction spontaneous or non-spontaneous at this temperature? Explain your choice. ΔG = ΔH –TΔS ΔS = 315 J = 0.315 kJ = -1278 – (373)(0.315) T = 273K + 100 = 373 K = -1395 KJ ΔG is negative therefore the reaction is spontaneous. 2 2. Consider the reaction: NH4Cl(s) NH3(g) + HCl(g) What are the temperature requirements for the above reaction to work? ΔH = [(-46) + (-92)] – [(-314)] = 176 kJ ΔS = [193 + 187] – [96] = 284 J = 0.284 kJ For the reaction to work, ΔG must be negative OR ΔH –TΔS < 0 176 – T(0.284) <0 -0.284T< -176 T> 619 K * remember to change the direction of the inequality when dividing by a negative value Therefore the reaction will only work when the temperature is greater than 619.7 K or greater than 346.7 oC. 3. The molar enthalpy of combustion of butane is -2871 kJ/mol. What is the molar enthalpy of formation of butane? HINT: first write out the balanced equation for the combustion reaction. 2C4H10(g) + 13O2(g) 8CO2(g) + 10H2O(l) ΔH = -5742 kJ ΔH = [8(ΔHf CO2 ) + 10(ΔHf H2O )] – [2 ΔHf C4H10 + 13ΔHf O2] -5742 = [8(-393) + 10(-286)] – [2 ΔHf C4H10 + 13(0)] 2 ΔHf C4H10 = -262 ΔHf C4H10 = -131 kJ 4. a) Draw the heating curve for methanol, given: enthalpy of fusion = 3.2 kJ/mol; enthalpy of vaporization = 35.3 kJ/mol; heat capacity of liquid methanol = 2.5 J/g∙ oC; heat capacity gaseous methanol 1.6 J/g∙oC ; the melting point of methanol = -97.6oC; boiling point of methanol = 64.7oC. 3 b) What amount of energy would be required to raise a 10.0 g sample of methanol from 0oC to 100oC. From 0oC to 64.7oC: (liquid) Q = mcΔT = (10.0 g)(2.5 J/goC)(64.7-0) = 1620 J Boiling: 10.0 g = 10.0/32.04 = 0.3121 mol Q = (0.3121 mol)(35.3 kJ/mol) = 11.02 kJ = 11020 J From 64.7oC to 100oC: (gas) Q = mcΔT = (10.0 g)(1.6 J/goC)(100-64.7) = 565 J Therefore the amount of energy to raise 10.0 g of methanol from 0oC to 100oC = 1620 + 11020 + 565 = 13.2 kJ NOTE: You will be expected to create the formulas for any of the hydrocarbons we studied in class as well as create their combustion reactions. NOTE: You will be expected to understand the activities and labs from this unit. Similar questions will be on the test. 4