Tissues - Uplift Education
advertisement

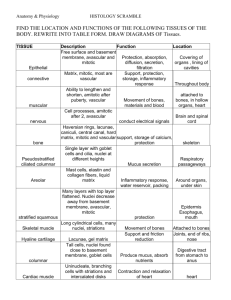
September 2-3, 2015 What are these? Tissues! Epithelial Tissue – lining, covering, & glandular Connective – protecting, supporting, and binding together Muscular – movement Nervous - control Epithelial tissues lines all body surfaces and cavities Functions: protection absorption filtration secretion Special features of epithelial tissue: Cells are tightly bound together Basal surface attached to basement membrane, apical surface is free. Avascular – no blood supply. Nutrition and gases diffuse from underlying connective tissue Excellent regenerative ability. Contain multi- and uni-potent stem cells. Turn & Talk: How does each special feature relate to the functions of epithelial tissue? - 2 min Basic Shapes Simple squamous epithelium A single layer of thin cells, specializing in rapid diffusion and filtration Found in: alveoli of lungs, walls of capillaries, kidney glomeruli, and serosae Simple squamous epithelium A single layer of thin cells, specializing in rapid diffusion and filtration Found in: alveoli of lungs, walls of capillaries, kidney glomeruli, and serosae Picture of alveoli of lungs. Simple cuboidal epithelium A single layer of cubeshaped cells Found in: glands, kidney tubules, ovaries Kidney tubules Simple columnar epithelium A single layer of tall shaped cells Often contain mucusproducing Goblet cells and / or cilia Found in: digestive tract (unciliated), bronchi (ciliated), and uterine tubes (ciliated) Small intestine Simple columnar epithelium A single layer of tall shaped cells Often contain mucusproducing Goblet cells and / or cilia Found in: digestive tract (unciliated), bronchi (ciliated), and uterine tubes (ciliated) Uterine tube Pseudostratified columnar epithelium A single layer of cells that differ in length. Often contain cilia and Goblet cells Found in: respiratory tract trachea Pseudostratified columnar epithelium A single layer of cells that differ in length. Often contain cilia and Goblet cells Found in: respiratory tract Notice that the nuclei appear at different levels. For our purposes: nuclei at different levels + cilia = pseudostratified columnar epithelia trachea Stratified Squamous Epithelium Multiple layers of epithelial tissue. Flattened and atrophied (‘dead’) at the apical edge; but can be rounder at basal edge. Apical edge sloughs off and is replaced. Function: protection from wear & tear Found in skin, mouth, esophagus Esophagus? Transitional epithelium Cells can change shape, allowing the tissue to stretch. Apical cells appear round when tissue is relaxed, and flat with tissue is stretched. Found in urinary tract. Ureter tube Transitional epithelium Cells can change shape, allowing the tissue to stretch. Apical cells appear round when tissue is relaxed, and flat with tissue is stretched. Found in urinary tract. Notice that the cells look rounded and irregular. Ureter tube Show with fingers: 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) Simple squamous Simple cuboidal Simple columnar Stratified squamous Transitional Show with fingers: 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) Simple squamous Simple cuboidal Simple columnar Stratified squamous Transitional Notice the cube-like shapes, and single layers separated by basement membrane Show with fingers: 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) Simple squamous Simple cuboidal Simple columnar Stratified squamous Transitional Show with fingers: 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) Simple squamous Simple cuboidal Simple columnar Stratified squamous Transitional Notice the many layers, and how the cells gradually become flatter Show with fingers: 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) Pseudostratified columnar Simple cuboidal Simple columnar Stratified squamous Transitional Show with fingers: 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) Pseudostratified columnar Simple cuboidal Simple columnar Stratified squamous Transitional Notice multiple layers, cells rounded and irregular Show with fingers: 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) Pseudostratified columnar Simple cuboidal Simple columnar Stratified squamous Transitional Show with fingers: 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) Pseudostratified columnar Simple cuboidal Simple columnar Stratified squamous Transitional Notice the nuclei at different levels, and the cilia Examine the following tissues under a microscope: Simple cuboidal (kidney tubule) Simple columnar (uterine tube?) Spend the time to do this right!! Stratified squamous (skin) Transitional (bladder?) Draw carefully and accurately. Use color. Compare to your Pseudostratified columnar (trachea?) textbook. As you observe these, create a histology guide by ASK FOR HELP IF YOU SURE IF& YOU ARE SEEING sketching each tissueAREN’T (USE COLOR LABEL IMPORTANT FEATURES). IT! Jotting down any notes that will help you identify the tissue in the You will getfuture to use these notes on a lab practical! Use your textbook to list both the FUNCTIONS and LOCATIONS of the tissues.