2.1 Observable Properties of Matter
advertisement

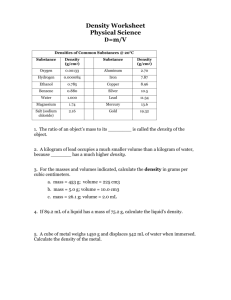
2.1 Observable Properties of Matter Ms. Wells, Science Property Types • Physical: properties that can be observed without changing the IDENTITY of the matter • Chemical: property of a substance that changes it into a NEW substance (changes the identity of the substance) Examples of Physical Properties • Volume, mass, color, texture, shape and density • Great example: • Stretching a rubber band may change its color and shape, but its still made of rubber and is still a rubber band! More about Density • Density = amount of matter (mass) in a certain amount of space (volume) • Density is constant (does not change for one substance) • Different substances = different densities U.S. Population Density Calculating Density (D) • Formula: D = m / V • Mass (m) = kilograms (kg) or grams (g) • Volume (V) = cubic centimeters (cm3) • Sooo…. Units for density are g/ cm3 • Said “grams per cubic centimeters” The Clay Example: Density = Constant • You have a 200g piece of clay with volume of 100 cm3 • V = 200g/100 cm3 • V = 2 g/cm3 • If you break it in half, you have 2 pieces of clay that are 100g and 50 cm3 each • V = 100g/50cm3 • V = 2 g/cm3 • SAME DENSITY! Examples of Chemical Properties and Changes • Describe how substances form into new substances • Examples: rusting, combustibility (burning), tarnishing, sometimes cooking, etc. • Chemical REACTIONS = Chemical Changes Physical Changes • Any change that does not change the actual substance itself • Changes in states of matter are physical (melting ice, etc.) • Other examples: • Breaking an object • Wool on a sheep or a wool sweater is still wool Signs of a Chemical Change • Odor – new smell (rotting meat, burning smell) • Temperature change – log goes from wood to ash, feel the heat! • Color change – not always chemical, but often • New solids from liquids (called precipitates) – clams make shells by mixing seawater substances and substances in their bodies Pictures of Chemical Changes • Precipitates forming (new solids from different liquid substances) Pictures of Chemical Changes • Water and salt of sweat reacts with oils and substances on your skin = body odor THE END OF 2.1 Properties of Matter in Matter and Energy