The Behavior Intervention Plan
advertisement

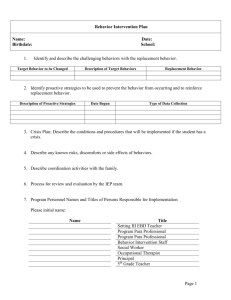
The Behavior Intervention Plan Function of the Behavior Attention o Like stage performers; they require an audience o I feel: irritated, annoyed o React by: scolding, coming to the rescue o When given attention, the behavior usually stops Escape o Any behavior whose purpose is to avoid or escape present or future circumstances o I feel: professional concern, frustration/anger, like giving up Self-Stimulation o Stimulating sensations produced by behaviors (loop talking, pulling hair out, etc) o I feel: embarrassed, irritated, professional concern Power/Control o They constantly challenge us through words and actions trying to prove they are in charge. Often power seeking students don’t act out until they’re assured of an audience. (attention) o I feel: angry, frustrated, fear of losing control of the situation or class Basic Guidelines All behavior is purposeful, learned and predictable. All behavior is maintained by reinforcement. It is more efficient for people to use existing behaviors. Changing behavior is a process, not a form. If you keep doing what you’re doing, you’ll keep getting what you’re getting Changing student behavior means changing your behavior FIRST! If the horse is dead … get off! (If your intervention doesn’t work, stop doing it!) Definition of a Behavior Intervention Plan: A BIP is an intervention plan with strategies to teach/replace skills students need in order to behave in a more appropriate manner. Interventions based upon control often fail to generalize and many times they serve only to suppress behavior. Why do a Behavior Intervention Plan? To identify proactive strategies to prevent rather than suppress undesirable behaviors To develop interventions that are logically related to functional categories. To teach replacement behaviors instead of suppressing behaviors through punishment. Step 1 – What we want the student to do… Learn an alternative socially acceptable behavior or new skill that serves the same function. Replacement behaviors: o Arguing – discusses appropriately o Out of seat – Purposeful, planned movement o Fighting – Use identified anger management techniques o Swearing – Use appropriate, socially acceptable language o Negative comments – Walks away from teasing and tries to find an adult o Incomplete assignments – Completes assignments with adaptations & modifications Skill Deficit: One the student cannot do or lacks the necessary information or skills to do. Performance Deficit: One the student is not motivated to do; has performed the skill previously or does it in some settings but does not generalize to other settings. Step 2 – What the teacher will do… Change the demands in the environment o Alter pace of instruction o Change the tasks o Insert easy activities along with difficult activities to increase probability of success o Change the peers o Change the materials o Alter adult’s behavior Provide opportunities to make choices o Type of task o Order of task o Type of reinforcer o Peers o Materials o Level of assistance Sample Interventions o Attention - Give positive attention before the disruption occurs Meet at door & verbally greet Use diminishing quota: question cards, paper clips, rubber bands Positively reinforce student when replacement behavior is exhibited. Remind student of expected behaviors prior to beginning activity (Pre-corrects) Organize transitions Escape Encourage positive self-talk Teach procedures for becoming “Unstuck” Create opportunities for individual instruction & reinforcement Make reasonable academic expectations Divide academic assignments into smaller chunks Opportunities to escape the setting but continue the work o Self-Stimulation Verbal or visual cue to stop behavior Schedule self-stimulation time Self-monitoring or behavior checklists Remove stimulating object for specified period Teach replacement behavior o Power/ Control Develop cues Allow student to save face Respect student’s personal space Give redirection and walk away Give student choices in activities/assignments Find ways in the classroom/school that the student can have some power and control Use respectful tone of voice when working with student Reinforce approximations of the appropriate behavior. What you see may not be perfect, but it is getting closer to desired behavior. Antecedent teaching procedures such as cues, prompts, assistance, collaborative activities & modeling Errorless teaching procedures such as guiding responses so student is successful – not about right or wrong, it’s about participation Teach the student an appropriate way to request: o Assistance o Breaks from tasks o An end to the activity o Alternatives to activities or tasks Develop the relationship – it’s never just about the technique, it’s always about the relationship o Step 3 – Rewards and Reinforcements Types of reinforcements: o Tangible o Intrinsic o Activity o Social Determine your type of reinforcers Step 4 – Consequences An agreed upon procedure for responding to problem behaviors Consistent across environments Reduces the likelihood that someone will inadvertently reinforce the problem behavior Spells out for the teacher and the student what will happen when the “old” behavior occurs, while learning the new one. Is “one size fits all” fair? What do we do to make the child successful? Fair consequences are the ones that change behavior. Clear, concise, enforceable, related to the behavior – Using consequences implies that the student knows what to do instead. Consequence Procedures: o Positive Practice - Following an episode of noncompliance, you deny the student the reinforcer until they have positive practice. o Extinction - A decrease in a behavior through the removal of the reinforcer. A reinforcer that normally follows a behavior is no longer given, and as a result the behavior decreases. o Redirection - Restate or reword the direction and walk away. o Time-out – An interruption of a student’s unacceptable behavior by removal from the scene o Response cost - A "toll" or "fine" imposed in response to the student's display of inappropriate behavior. o Restitution - An appropriate payback for inappropriate behavior. It requires the student to lesson the negative impact of their behavior. Punishment, inappropriately applied, never teaches a student a new behavior. It creates: o Resentment o Revenge o Rebellion o Retreat