PLANTS
Plants Characteristics
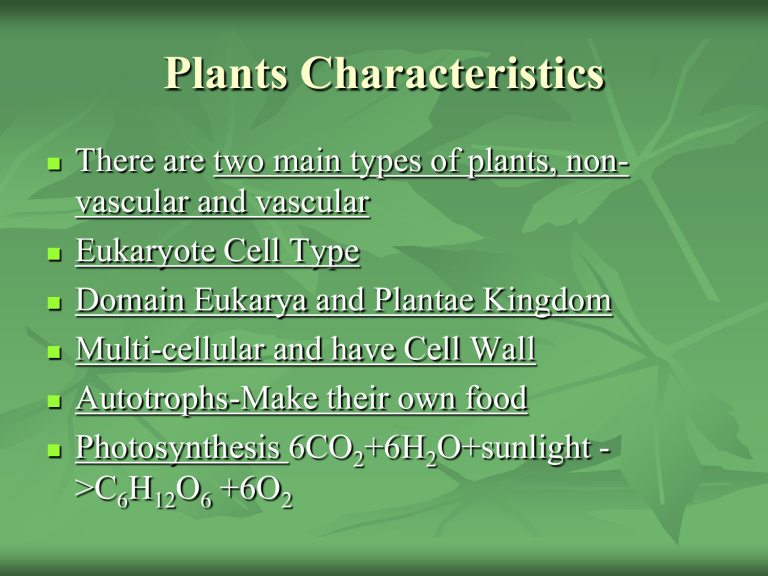
There are two main types of plants, nonvascular and vascular
Eukaryote Cell Type
Domain Eukarya and Plantae Kingdom
Multi-cellular and have Cell Wall
Autotrophs-Make their own food
Photosynthesis 6CO
2
+6H
2
O+sunlight -
>C
6
H
12
O
6
+6O
2
Non vascular plants
Do not have vascular tissue to carry the nutrients and water throughout the plant
They must live in water or moist surroundings
They are usually small and grow close to the ground
No Roots
Ex. Mosses, hornworts and liverworts are examples of nonvascular plants
Nonvascular Plants
Includes mosses (Bryophyta), liverworts
(Hepatophyta), and hornworts (Antherophyta)
Liverworts copyright cmassengale
Hornworts
3
Vascular plants
Vascular tissue is small tubes inside the plant that transport food and water through the plant
two types of vascular tissue: phloem and xylem
Xylem moves water
Phloem moves nutrients (aka Food) produced by photosynthesis down from the leaves to the rest of the plant
copyright cmassengale 5
Seed-Producing Vascular Plants
Includes two groups –
Gymnosperms and Angiosperms
Gymnosperms have naked seeds in cones
Angiosperms have flowers that produce seeds copyright cmassengale 6
Gymnosperms
The oldest living plant –
Bristle cone pine
The tallest living plant – Sequoia or redwood copyright cmassengale
Cycad
Ginkgo
7
Examples of vascular plants: sequoia tree (Sequoiadendron giganteum)
Gymnosperms (Naked Seed)
Plants that do not have flowers are called
Gymnosperms
Conifers, ginkgos and cycads are examples of
Gymnosperms
Plants that have flowers are called
Angiosperms
Angiosperm
Angiosperms
Flowering plants
Seeds are formed when an egg or ovule is fertilized by pollen in the ovary
Ovary is within a flower
Flower contains the male (stamen) and/or female (ovaries) parts of the plant
Fruits are frequently produced from these ripened ovaries (help disperse seeds) copyright cmassengale 11
Flowers have male and female parts
The male part is called the stamen
The stamen is made of the anther and the filament
The anther produces pollen
Fertilization and Importance
Pollen is sometimes spread by birds, bats, insects or wind
All living things on Earth are dependent on plants for their existence.
We depend on them for food and for oxygen
Angiosperms
Subdivided into two groups –
Monocots and Dicots
Monocots have a single seed cotyledon
Dicots have two seed cotyledons
Parts of the Seed copyright cmassengale 14
Monocots and Dicots
copyright cmassengale 15
Plant Adaptations
Tropism
= a plant’s growth response toward or away from a stimulus.
* Positive tropism is when it grows toward a stimulus.
* Negative is when it grows away from it.
* Stimuli can be light, touch, and even gravity.
- Touch (thigmotropism)
[vines coil around anything they touch.]
- Light (phototropism)
[leaves, stems, etc, grow toward light.]
- Gravity (geotropism)
(Positive) roots grow toward gravity’s pull
(Negative) stems grow away from its pull
16
Thigmotropism
Phototropism copyright cmassengale
Geotropism
17
http://www.youtube.com/ watch?v=pCFstSMvAMI
video copyright cmassengale 18
LAB ACTIVITY: Celery
Lab
copyright cmassengale 19
Review Plant Parts Online
Activity
copyright cmassengale 20
Bee
Hummingbird
All living things on Earth are dependent on plants for their existence.
We depend on them for food and for oxygen
Plants
All plants are multicellular
All plants are eukaryotes
All plants have a cell wall
All plants are autotrophs
They produce energy through the process called photosynthesis
The formula for photosynthesis is:
Plant Characteristics
Multicellular eukaryotes
Autotrophic (photosynthesis)
Surrounded by cell walls containing cellulose
(polysaccharide)
Store reserve food as amylose (starch) copyright cmassengale 27
Parts of The Plant
Roots
Leaves
Stem
Flower
Seed
Plants have three main organs
Leaves
The leaves function is to capture sunlight and perform photosynthesis
Stems
The stems function is to support the plant and provide a place through which water and nutrients move
Roots
The roots anchor the plant to the soil and absorb water and nutrients from the soil
Root Functions
Roots have 4 primary functions
Absorption of water and nutrients
performed by root hairs
Transportation of water and nutrients to stem
Anchor plant to maintain stability
Store food and water
Important Functions of
Leaves
Photosynthesis
Process that plants use to produce their food
6CO
2
+ 6H
2
O C
6
H
12
O
6
+ 6O
2
Transpiration
Loss of water and exchange of carbon dioxide
Functions of the Stem
Transport water and nutrients from roots to leaves
Supports leaves, fruit, and flowers
Food storage
Plant
Divisions
copyright cmassengale 36
Nonvascular Plants
Do not have vascular tissue for support or conduction of
Sporophyte stage materials
Require a constantly moist environment
Gametophyte
Stage
Moss Gametophytes &
Sporophytes copyright cmassengale 37
Nonvascular Plants
Plants can’t grow as tall
Cells must be in direct contact with moisture
Materials move by diffusion cell-tocell
Sperm must swim to egg through water droplets copyright cmassengale 38
Plant Divisions
Plants are divided into two groups
Based on the presence or absence of an internal transport system for water and dissolved materials
Called Vascular
System
Vascular
Bundles copyright cmassengale 39
Vascular System
Xylem tissue carries water and minerals upward from the roots
Phloem tissue carries sugars made by photosynthesis from the leaves to where they will be stored or used copyright cmassengale 40
Examples of vascular plants
Coconut palm (Cocos nucifera)
Conifers
Giant sequoia
Gingko
copyright cmassengale 43
copyright cmassengale 44
The female part is called the pistil
It is made of the stigma, style and the ovary
Inside the ovary are ovules which when fertilized, will mature into seeds
Plant Uses
copyright cmassengale 47
Why We Can’t do Without
Plants!
Produce oxygen for the atmosphere
Produce lumber for building
Provide homes and food for many organisms
Prevent erosion
Used for food copyright cmassengale 48
More Reasons We Can’t do
Without Plants!
Produce wood pulp for paper products
Source of many medicines
Ornamental and shade for yards
Fibers such as cotton for fabric
Dyes copyright cmassengale 49
Plant Adaptations to Land
Problems:
Need minerals
Gravity
Increase in Height for Light
Adaptations for Drier environment
Reproduction
Solutions:
Roots absorb H
2
O & minerals
Lignin & cellulose in cell walls
Vascular Transport System
Waxy cuticle & stomata with guard cells
Pollen containing sperm copyright cmassengale 50
EXIT TICKET
copyright cmassengale 51











