The Progressive Era
advertisement

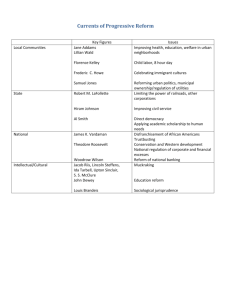
The Progressive Era 1900-1920 Progressivism • Progressivism- aimed to return control of the government to the people, restore economic opportunities, and correct injustices in American life. • Progressivism was a response to the problems about by the industrialization, urbanization, and immigration of the Gilded Age. Main Goals of Progressive Reform • Most Progressives saw dangers in the rising power of Big Business, violence with labor, concentration of wealth, political machines, unrest of the poor, moral decay, racism, and discrimination. • Wanted to improve society and quality of life. • Wanted to put government back into the hands of the people. • Wanted to end abuse of power and social injustice. • Wanted to regulate business and expand democracy. State Reform • Robert M. La Folletteprogressive reform governor of Wisconsin and later Senator who worked to drive business from government. • Efforts to limit child labor and working hours. • Reforming elections: • Initiative- legislature from the people on the ballot. • Referendum- vote on an initiative. • Recall- voters could force politicians to face another election before end of their term. Enabled removal of public officials. Constitutional Amendments • 16th AmendmentIncome tax collected on individuals and businesses to make up for revenue lost on reduced tariffs. • 17th Amendmentallowed for the direct election of Senators Women in Public Life Women began to work outside of the home usually out of economic necessity. They also joined clubs, went to college, and led reform movements such as the National Association of Colored Women (NACW) and the National American Woman Suffrage Association (NAWSA). • Susan B. Anthony was a leading proponent of women’s suffrage, the right to vote. Another leader of this movement who worked closely with Anthony was Elizabeth Cady Stanton. Muckrakers • Journalists who exposed the evils, inequities and injustices in government, business, and society • Ida M. Tarbell- The History of the Standard Oil Company • Lincoln Steffens- The Shame of the Cities and The Struggle for SelfGovernment. • Upton Sinclair- The Jungle exposed the unsanitary conditions of the meat packing industry. It led to the Meat Inspection Act of 1906. Three Progressive Presidents • Theodore Roosevelt 1901-1909 • William Howard Taft 1909-1913 • Woodrow Wilson 1913-1921 Theodore “Teddy” Roosevelt • Square Deal- Govt. is to serve all people. • Elkins Act (1903)Stopped RR rebates and increased power of ICC. • Hepburn Act (1906)fixed RR rates and increased power of ICC. • Trust Busting • Northern Securities Case of 1904 (Morgan) • Duke Tobacco • Swift Meat-Packing • Standard Oil Trust (Rockefeller) • Consumer Protection • Pure Food and Drug Act (1906) • Meat Inspection Act (1906) • Conservation • Increased use of Forest Reserve Act 1891 • Newlands Reclamation Act 1902 • Creation of national Conservation Commission 1908 • Antiquities Act • New Nationalism (1912)- a radical program of reform calling for more govt. regulation . Big Business needed Big Govt. as an equalizer. William Howard Taft • Continuation of Square Deal • Mann-Elkins Act 1910increased powers of ICC to freeze rates of RR, telephones, etc. • Continuation of trustbusting • U.S. Steel • Split in the Republican Party • Payne- Aldrich Tariff 1908 • Pinchot-Ballinger Affair 1910- dispute over private development of lands in Alaska, nonforested lands. • Speaker Joe Cannon dispute. • • • • • • • Conservation Bureau of Mines Set aside federal oil lands Labor Federal Children’s Bureau Department of Labor 8 hour workday for govt. workers Woodrow Wilson • New Freedom- emphasized economic morality by trying to bring back conditions of free and fair competition; opposed all trusts; advocated smaller govt. and smaller business and an end to corruption • Trust-Busting • Clayton Anti-Trust Act 1914exempted unions • Federal Trade Commission (FTC) 1914- monitored unfair trade practices of corporations. • Tariff Reduction • • 16th Amendment- Income tax • • Underwood-Simmons Tariff 1913 (possible due to 16th Amendment). • • Bank Reform • • Federal Reserve Act 1914established fed. Banking system. • • Conservation • • National Park Service • Social Reform Keating-Owens Act 1916- Child labor law later ruled unconstitutional 10 Hour Act 1910- women labor law 18th Amendment 1919Prohibition Expansion of Democracy 17th Amendment 1913- People vote for U.S. Senators 19th Amendment 1920Women’s Suffrage