Political Culture 1
advertisement

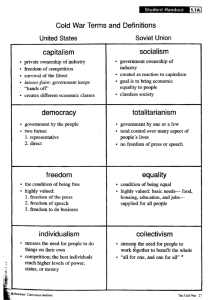
POLITICAL CULTURE CH 4 POLITICAL CULTURE 1 Bell Ringer Which one could you live without? Why? • Majority rule/ Minority Rights • Equality • Private Property • Individual Freedoms • Compromise • Limited Government Please get out your Unit 1 test – MC & FRQ Unit 1 Test Review Today we will … Objectives Define political culture. List some of the dominant aspects of political culture in the U.S. and identify influences. List the sources of our political attitudes. Compare & contrast economic systems – AP6. Agenda Unit 1 Test Review American Political Culture – slide notes Comparing Across Countries – pair/share data analysis Political/Economic Ideologies - movie Political Culture Political Culture is the underlying set of values and beliefs about politics & economic life System of meaning for interpreting politics among a given population What do citizens think about: Beliefs about authority Groups vs. individuals Liberty vs. security Necessary level of legitimacy The role/ independence of the political community Why is it necessary to study more than a country’s institutions? American Political Culture “Shared” set of values and beliefs 5 elements of the American view of our political system: Liberty Equality Democracy Civic Duty Individual Responsibility Sources of American Political Culture History: people came to US for 2 reasons 1. 2. Distrust of rulers/ authority Religion American Revolution Constitution Adversarial culture Federalists v Democratic Republicans Legitimized role of opposition party American Political Culture Majority rule/ Minority Rights Equality Private Property Individual Freedoms Compromise Limited Government Shared Set of Values Alexis de Toqueville Wrote Democracy in America – profound analysis of our political culture Tocqueville’s reasons why democracy would take root: Abundant and fertile soil Vast territory to acquire land and make a living No feudal aristocracy No Low hereditary/ Aristocracy taxes Few legal restraints Role of Religion America is the most religious industrialized country Avg. American compared to avg. European: 1. 2. 3. Believe in God Pray on a daily basis Acknowledge clear standards of right and wrong Religious people in the US: 1. 2. Donate more $ to charities vs. secular folks More likely to give $ and donate time to non-religious organizations than secular folks Religion & Politics Both liberals (Civil Rights movement) & conservatives (Moral Majority, Christian Coalition) have used the pulpit Beliefs about the Economic System Generally Americans: Are more willing to tolerate economic inequality than political inequality. Favor equality of opportunity rather than equality of results. Support common sense regulations and competition in the marketplace. Willing to help those “truly” in need. Economic individualism & personal responsibility Check for Understanding How do we know that Americans share beliefs? How can we explain the existence in our society of behavior that is obviously in conflict with these beliefs? Political Tolerance In order for democracy to work, citizens must have a political culture that allows the discussion of ideas & the selection of leaders in an atmosphere reasonably free of oppression. Culture War The Culture War Class consciousness: middle/lower class ideas vs. those of the upper class We generally believe the same things in America “Ballot not Bullets” So we end up fighting over moral issues Orthodox- belief that morality & religions ought to be of decisive importance, more than liberty Evangelicals & many Protestants - “Religious Right” Progressive – belief that importance of personal freedom > morality “Secular Left” Check for Understanding Which most accurately describes the orthodox view? A. B. C. D. Morality is more important than self-expression, and the rules vary with circumstances. Personal freedom is more important than tradition, and morality is based on unchanging rules from God. Morality is more important than self-expression and is based on unchanging rules from god Personal freedom is more important than tradition and the rules for morality vary with circumstances. Trust in Government Trust in the Federal Gov. 1958-2008 Check for Understanding What are some general observations you can make about American’s trust in government? What are the national trends from the mid-1990s to the present regarding mistrust of the government? Trust in Government “American Malaise” - Jimmy Carter, Watergate, Vietnam People distrust the people in power, but not so much the form of government Trust was only high in the 1950’s/ 1960’s Civil Society Collection of private, voluntary groups that – independent of the gov. & commercial market – make human cooperation easier & provide ways of holding the gov. accountable Political Efficacy Internal: participation External: how government responds Polls show most Americans think that politics and government is too complicated for them to understand. Government cannot really respond to them People are not more “alienated” - they are more realistic Comparing Across Countries External Efficacy Table 4.2 Patriotism Table 4.3 Equality of Results vs Equality of Opportunity Table 4.4 Table 4.5 Religion Table 4.6 Table 4.7 Think/Pair/Share How does America compare to other countries? (generalization) Specific example(s) that support your generalization Most surprising factoid External Efficacy Patriotism Table 4.3 Equality of Results vs Equality of Opportunity Table 4.2 Table 4.4 Table 4.5 Religion Table 4.6 Table 4.7 Study of Political Culture in 5 Nations Americans had strongest sense of civic duty & civic competence (internal political efficacy) Over 50% of Americans felt one should be “active in the community” Vs. Britain 30%, Germany 20% US trust in government is lower than it once was, but higher than other nations. Americans know there are problems, but want policy changes, not changes in the system. Comparing Economic Systems Sweden favors equality of results over equality of opportunity, believed in giving equal pay and setting a limit on incomes. Closure Explain Equality of Results vs. Equality of Opportunity. How does Religion impact American political culture? Homework: Complete questions for Chapter 5 & prepare for quiz on chapters 4 and 5 Political Ideologies & Economic Systems AP6 Common Political Ideologies Liberalism: Emphasis on political and Economic freedom. Emphasis on public opinion. Socialism: Accepts and promotes free market principles, yet believes that the state should regulate the economy and provide benefits in order to ensure some measure of equality. Communism: Values equality over freedom. Effective resource allocation and economic and social equality. Fascism: The state has the right and responsibility to mold the society and economy & eliminate obstacles (including people) that might weaken them. Devalues individual freedom. Economic Systems Command Economy: Government owns almost all industrial enterprises & retail sales outlets. Production goals set by a central government (party-dominated), values equality, quotas and plans/directs production and distribution. Economic Liberalism: Free markets, freedom of the press, freedom of religion, low or no tariffs on trade. Free-Market Capitalism: Relies on profit motive and competition. Mixed Economies: Market economy w/ significant control from the government. Social Welfare Capitalist System (UK) Socialism Market Economy (China) Europe: team oriented & emphasis on cooperation between management and organized labor. Government = economic safety net. Government subsidies, universal health care, day care, pensions. Gradual infusion of market economy while still retaining state control State Capitalism (Russia) Economic Systems Economic Systems explained by cows Commanding Heights Ch 7 & 8 Chart: Command Socialist Capitalist Communism vs. Capitalism Quotes Read your quotes and use them to describe Communism vs. Capitalism JIGSAW 1. 2. 3. 1. JIG Get with same reading folks to check your description. 2. SAW Get with a different folk to compare quotes, choose 2 quotes to compare and write our your comparison/ summary paragraph. CHECK FOR UNDERSTANDING: ONE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN COMMUNIST IDEOLOGY AND CAPITALIST IDEOLOGY Pew Research - Political Typology Quiz Political Typology Quiz | Pew Research Center for the People and the Press