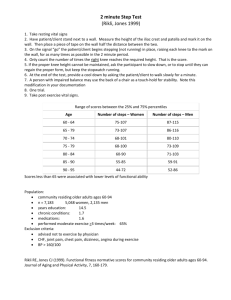
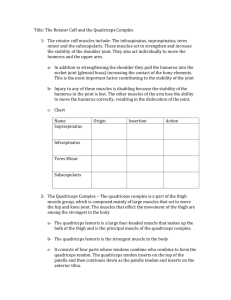
Knee joint
advertisement

Knee joint Vastus Lateralis / Vastus Intermedius / Vastus Medialis / Popliteus Vastus Lateralis Muscle Vastus Lateralis is the most lateral (outside) of the four quadriceps muscles. It is thought to be a major contributor to patella tracking injuries. Origin Outer surface of the greater trochanter of the femur Upper half of the linea aspera Insertion Patella via the quadriceps tendon and then the tibial tuberosity via the patella tendon Actions Knee extension Innervation Femoral nerve Daily uses Cycling Walking up stairs Vastus Intermedius Muscle Vastus Intermedius is located deep to the Rectus Femoris muscle and is part of the quadriceps muscle group. Origin Anterior and lateral surfaces of the shaft of the femur Insertion Patella via the quadriceps tendon and then the tibial tuberosity via the patella tendon Actions Knee extension Innervation Femoral nerve Daily uses Cycling Walking up stairs Vastus Medialis Muscle Vastus Medialis is the most medially located of the quadricep muscles and is thought to be important in stabilizing the knee cap or patella. Origin Intertrochanteric line (between the greater and lesser trochanters of the femur) Medial lip of the linea aspera of the femur Insertion Patella via the quadriceps tendon and then the tibial tuberosity via the patella tendon Actions Knee extension Innervation Femoral nerve Daily uses Cycling Walking up stairs Popliteus Popliteus is a small muscle which is often described as the key of the knee joint. It unlocks the knee joint by rotating the femur at the beginning of knee flexion to allow full knee flexion to occur. Origin Lateral condyle of the femur Insertion Upper posterior surface of the tibia, above the soleal (popliteal) line Actions Knee flexion Internal rotation of the knee when it is flexed Innervation Tibial nerve Daily uses Walking