1417 Business Law Instructional Guide
advertisement
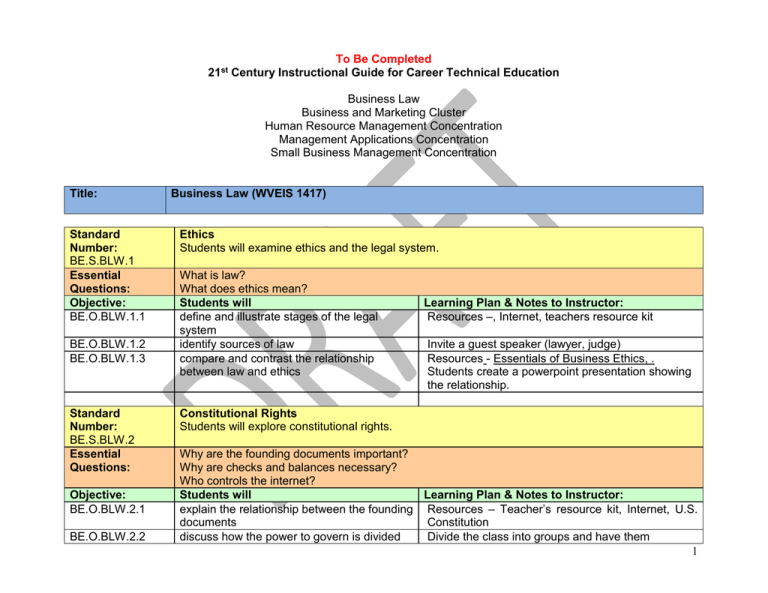
To Be Completed 21st Century Instructional Guide for Career Technical Education Business Law Business and Marketing Cluster Human Resource Management Concentration Management Applications Concentration Small Business Management Concentration Title: Standard Number: BE.S.BLW.1 Essential Questions: Objective: BE.O.BLW.1.1 BE.O.BLW.1.2 BE.O.BLW.1.3 Standard Number: BE.S.BLW.2 Essential Questions: Objective: BE.O.BLW.2.1 BE.O.BLW.2.2 Business Law (WVEIS 1417) Ethics Students will examine ethics and the legal system. What is law? What does ethics mean? Students will define and illustrate stages of the legal system identify sources of law compare and contrast the relationship between law and ethics Learning Plan & Notes to Instructor: Resources –, Internet, teachers resource kit Invite a guest speaker (lawyer, judge) Resources - Essentials of Business Ethics, . Students create a powerpoint presentation showing the relationship. Constitutional Rights Students will explore constitutional rights. Why are the founding documents important? Why are checks and balances necessary? Who controls the internet? Students will Learning Plan & Notes to Instructor: explain the relationship between the founding Resources – Teacher’s resource kit, Internet, U.S. documents Constitution discuss how the power to govern is divided Divide the class into groups and have them 1 BE.O.BLW.2.3 Standard Number: BE.S.BLW.3 Essential Questions: Objective: BE.O.BLW.3.1 BE.O.BLW.3.2 BE.O.BLW.3.3 BE.O.BLW.3.4 BE.O.BLW.3.5 Standard Number: BE.S.BLW.4 Essential Questions: research the history of one of the branches of government. research internet related constitutional issues Use the internet to research and have students create an oral presentation on their findings. Court Systems, Criminal, Civic and Business Law Students will examine the court systems, criminal, civil, and business law. What is the primary difference between the federal court system and a state court system? What is a crime? What is a tort? What remedies are available in a civil suit? Students will Learning Plan & Notes to Instructor: describe the different levels of courts and Have students create a chart that shows WV state their power court system. Compare them and research differences for accuracy. compare and contrast criminal and civil law Have students create a graphic organizer comparing and contrasting criminal and civil law. identify the types of crimes that affect Invite a guest speaker from your local communities business business leaders to speak about business crimes and how they deal with them. distinguish a crime from a tort Have students write the four common elements of a tort on the board, write the definitions for each element. Have students orally match the definitions. recognize the procedures used to try a civil Have students’ role play a civil case. case Contracts Students will explore contracts. What distinquishes a contract from other agreements? Who has contractual capacity in organizations? Why have a statute of frauds? Why is marriage a legal contractual relationship? What is the sole remedy for a minor breach of contract? What is meant by non-assignable rights? How are contracts interpreted? 2 Objective: BE.O.BLW.4.1 Students will identify the elements of a contract BE.O.BLW.4.2 discuss the requirements of an offer and acceptance BE.O.BLW.4.3 identify parties who lack contractual capacity BE.O.BLW.4.4 explain why the statute of frauds is necessary identify the requirements and recognize the forms of consideration BE.O.BLW.4.5 BE.O.BLW.4.6 identify the transfer of contract rights and duties BE.O.BLW.4.7 describe remedies possible for breach of contract recognize the contractual elements of premarital and marital relationships BE.O.BLW.4.8 BE.O.BLW.4.9 Standard Number: BE.S.BLW.5 Essential describe the various ways in which a marriage contract is ended Consumer Law Students will explore consumer law. Learning Plan & Notes to Instructor: Write on the board the six basic elements of a contract. Ask students why each element is so necessary to legally enforce a document. Discuss each one before moving on to the next. Have students summarize in writing, using a computer if possible, the three requirements of a valid offer. On index cards write scenarios that depict enforceable and unenforceable contracts involving minors or others lacking contractual capacity. Divide the class in groups and have each group choose a card. Have them perform a skit based on the situation on their card. Have students list the types of executory contracts that are within the Statute of Frauds. Have students draw up a written contract and then create a scenario with a conflict that involves an exception to the parole evidence rule. Have the other students act as judges to determine which exception will allow the oral statements into evidence. List non-assignable rights and have students point out the difference between assignment and delegation. Books – Basic Contract Law, by Fuller and Eisenberg. Have students write a marriage contract that lists spousal obligations and duties and responsibilities of parenthood. Invite a marriage counselor to speak to the class about typical problems a marriage faces. What makes a sale unique? 3 Questions: Objective: BE.O.BLW.5.1 BE.O.BLW.5.2 BE.O.BLW.5.3 Standard Number: BE.S.BLW.6 Essential Questions: Objective: BE.O.BLW.6.1 BE.O.BLW.6.2 BE.O.BLW.6.3 BE.O.BLW.6.4 Who has the authority to transfer ownership of goods? Who is a consumer? What is the Consumer Product Safety Commision? Students will Learning Plan & Notes to Instructor: identify special rules for sales contracts Request each student to bring in a bill of sale. Identify what features of the transaction are identified on the bill. research what is required for transfer of Create a class chart of the exceptions to the general ownership of goods. rule that only the true owner has the authority to transfer title to goods. discuss consumer protection legislation Have students write a journal entry about how their lives are affected by the Consumer Product Safety Commission, the Food and Drug Administration, and the National Institute of Standards and Technology. Personal and Real Property Law Students will demonstrate legal rules that apply to real and personal property. What is the difference between real and personal property? What is a bailment? What are the rights and limitations associated with the forms of ownership of real property? What protection does a lease offer to the tenant and the landlord? Why have insurance? Why should a person have a will? Students will Learning Plan & Notes to Instructor: distinguish between real and personal Have students work in groups to create a collage property that displays different forms of real and personal property. Students may use any media including pieces of personal property. investigate the ways in which bailments are Define bailments on the board and then have created and ended students brainstorm all of the times they have been in a bailment. evaluate the rights and limitations associated Break students into groups. Have each group with the forms of ownership of real property contact a local real estate agency. Have them find and how they are transferred the costs involved in closing a residential real estate transaction and obtaining a loan. show the kinds of rental relationships that Create two charts on the board. Label one Tenant 4 landlords and tenants may create. BE.O.BLW.6.5 recognize the common types of insurance and when an insurable interest is present BE.O.BLW.6.6 differentiate between dying testate and dying intestate Standard Number: BE.S.BLW.7 Essential Questions: Agency and Employment Law Students will analyze agency employment law. Objective: BE.O.BLW.7.1 BE.O.BLW.7.2 BE.O.BLW.7.3 BE.O.BLW.7.4 and the other Landlord. Under both titles, write rights and duties. Have students copy this chart in their notebooks and augment it as class proceeds. Have students draw a two column chart including the headings Property and Life. Ask students to list the types of property and people in which a person may have insurable interest. Have students collect samples of living wills. Discuss these documents in class and have students draft their own. What is an agency? What are an agency and principal’s duties? How are employment contracts made and terminated? What are the duties of the employer and the employee? How is a union established? Students will Learning Plan & Notes to Instructor: distinguish the scope of agency authority Draw a four column chart on the board to explain the ways agency authority may be created. 1. express authority 2. implied authority 3. apparent authority 4. ratification Have students copy the chart into their notes to augment as discuss progresses. discover the duties of an agent and principal Have student research state or federal statutes that specifically hold a principal liable for violations of public safety or health statutes. research how employment contracts are Have students draft two paragraphs for an employee made and terminated handbook. In one paragraph, create a contract that is terminable at the will of either the employer or employee. In the other paragraph, indicate that the employer cannot fire an employee without good reason. establish the employer and employees duties Have the students compose a list of duties they feel they would owe their employer and their empoyer would owe them. Compare the students’ lists with 5 the law’s expectations. Have students research the origin of the label yellowdog contracts. Have the students find out when this term was first used and during what period in history these contracts were common. BE.O.BLW.7.5 relate the development of labor law to how a union is formed Standard Number: BE.S.BLW.8 Essential Questions: Legal Forms of Business Organization Students will analyze legal forms of business organization. Objective: BE.O.BLW.8.1 BE.O.BLW.8.2 BE.O.BLW.8.3 Standard Number: BE.O.BLW.9 Essential Questions: Objective: What are the roles of general partners and limited partners? What are the three basic business forms? What is a corporation? What are the powers of a corporation? How does a limited partnership or S corporation benefit small business? Students will Learning Plan & Notes to Instructor: recognize the three basic business forms Have students list advantages and disadvantages of and the powers of a partner each form of business. Create a large graphic organizer on the board. Label the organizer Kinds of Partnerships and Partners. Have students come up to the board one at a time to help fill it in. Have students copy the organizer into their notes. determine the powers of a corporation Have students research the history of the corporate form of business. demonstrate the roles of general partners Have students contact WV government for and limited partners information on setting up a limited partnership. Then have students work in groups to write an agreement for two general partners and one limited partner. Borrowing Money and Paying Bills Students will explore negotiable instruments. What is commercial paper? Can we cut down the risks of taking commercial paper? What are the advantages and disadvantages of using electronic funds transfer? What is a secured credit transaction? What five laws prohibit abuses in the credit system? Students will Learning Plan & Notes to Instructor: 6 BE.O.BLW.9.1 recognize the need for commercial paper BE.O.BLW.9.2 distinguish negotiable from non-negotiable instruments BE.O.BLW.9.3 distinguish financial transactions that are electronic funds transfers BE.O.BLW.9.4 assess the importance of secured credit transactions BE.O.BLW.9.5 discuss debtor protection available under the law Standard Number: BE.S.BLW.10 Essential Questions: Participating in the Student Organization Students will participate in a student organization. Objective: BE.O.BLW.10.1 BE.O.BLW.10.2 Make a list on the board of advantages and disadvantages of using commercial paper. Have the students approach various institutions and ask them what types of commercial paper they normally deal with. Have the students form conclusions as to the utility of the various types to different entities. Have students give examples of EFTs. Remind students of the trend of ATM cards replacing the need for traveler’s checks. Recount for the students the history of secured transactions and the unity in procedure achieved by the acceptance of provisions in WV. This process did not occur until the 1950’s and 1960’s. Have students research the Consumer Credit Protection Act and the Truth in Lending Act. Each student should find five facts about each set and share their facts with the class. Definition of EQ: Questions that probe for deeper meaning and set the stage for further questioning foster the development of critical thinking skills and higher order capabilities such as problem-solving and understanding complex systems. A good essential question is the principle component of designing inquiry-based learning. Examples: Considering microorganisms and disease transmission, is clinical facilities safer for patients than home care? Is the output of a system, greater than the sum of its inputs? Is patient care the same for those without insurance as it is for those with insurance? Students will Learning Plan & Notes to Instructor: identify the purposes and goals of the student/professional organization. explain the benefits and responsibilities of participation in student/professional/civic 7 BE.O.BLW.10.3 21st Century Skills Information and Communication Skills: organization as an adult demonstrate leadership skills through participation in student/professional/civic organization activities such as meetings, programs, and projects. Learning Skills & Technology Tools 21C.O.912.1.LS1 Student recognizes information needed for problem solving, can efficiently browse, search and navigate online to access relevant information, evaluates information based on credibility, social, economic, political and/or ethical issues, and presents findings clearly and persuasively using a range of technology tools and media. 21C.O.912.1.LS3 Student creates information using advanced skills of analysis, synthesis and evaluation and shares this information through a variety of oral, written and multimedia communications that target academic, professional and technical audiences and purposes. 21C.O.58.1.TT2 Student increases keyboarding facility and uses mouse and keyboard shortcut techniques and identified assistive technology to improve speed and accuracy. Teaching Strategies Culminating Activity Evidence of Success 8 21C.O.58.1.TT4 21C.O.58.1.TT7 21C.O.58.1.TT9 21C.O.58.1.TT10 Student uses audio, video, pictures, clip art, moviemaker programs, webpage design software, electronic documents, and other files to create and publish electronic products to communicate with various audiences inside and outside the classroom. Student uses advanced features and utilities of presentation software (e.g., design templates, design layouts (fonts/ colors/ backgrounds) animation and graphics, inserting pictures, objects, movies, sound, charts, hyperlinks, and graphs) to create an original product. Student uses telecommunications tools (e.g., email, web pages, blogs, discussion groups, list-servs, etc.) to learn academic content and to gather, share and publish information to various audiences. Student uses Internet browsers, various search engines, book marking features, and advanced search techniques to gather information; student evaluates the information for validity, bias, appropriateness, content and usefulness. 9 Thinking and Reasoning Skills: 21C.O.58.2.LS1 Student engages in a critical thinking process that supports synthesis and conducts evaluations by applying comprehensive criteria. 21C.O.58.2.LS2 Student draws conclusions from a variety of data sources to analyze and interpret systems. Student engages in a problem solving process that divides complex problems into simple parts in order to devise solutions. 21C.O.58.2.LS3 21C.O.912.2.TT2 21C.O.912.2.TT3 Student collaborates with peers, experts and others to contribute to a content-related knowledge base by using technology to compile, synthesize, produce, and disseminate information, models, and other creative works. Student uses multiple electronic sources of information and multiple technology tools and resources tools (e.g., digital cameras, graphing calculators, probes, mp3 players, handheld devices, other emerging technologies, simulations, models, browsers, word processing, authoring tools, spreadsheets, 10 21C.O.912.2.TT4 21C.S.9-12.3 Personal, and Workplace, Skills: 21C.O.912.3.TT5 databases) to collaborate with others, to formulate a hypothesis, to solve problems, make decisions, and present and justify the solutions. Student uses technology tools and multiple media sources to analyze a real-world problem, design and implement a process to assess the information, and chart and evaluate progress toward the solution. The student will exhibit leadership, ethical behavior, respect for others; accept responsibility for personal actions considering the impact on others; take the initiative to plan and execute tasks; and interact productively as a member of a group. Student models ethical behavior relating to security, privacy, computer etiquette, passwords and personal information and demonstrates an understanding of copyright by citing sources of copyrighted materials in papers, projects and multi-media presentations. Student advocates for legal and ethical behaviors among peers, family, and community regarding the use of technology 11 and information. Learning Skills & Technology Tools Entrepreneurship Skills: Culminating Assessment: H.04-06, .18 Teaching Strategies Culminating Activity Evidence of Success .14- Understands concepts and strategies needed for career exploration, entrepreneurial and opportunities, development and growth. Culminating Assessment: Students will participate in a mock trial based on a case that they have researched. Each student will be assigned a specific task related to the trial. The trial will be conducted in an assembly for the high school students to observe. End-Of-Course Technical Skill Test Links and Other Resources Links and Other Resources Related Websites: U.S. Congress on the Internet Pathways to Success http://careertech.k12.wv.us/pathwaystosuccess/ U.S. Department of Labor in the 21st Century http://www.dol.gov/ Advanced Distributed Learning www.adlnet.org America's Career InfoNet www.acinet.org America's Job Bank 12 www.ajb.org America's Service Locator www.servicelocator.org CareerOneStop www.careeronestop.org Employment & Training Administration www.doleta.gov The Job Accommodation Network (JAN) http://www.jan.wvu.edu Monthly Labor Review Online: Labor Force Archives http://www.bls.gov/opub/mlr/indexL.htm#Labor force Occupational Information Network www.doleta.gov/programs/onet Office of Disability Employment Policy www.dol.gov/odep Career Voyages http://www.careervoyages.gov/index.cfm Workforce West Virginia https://www.workforcewv.org/ West Virginia Earn A Degree Graduate Early (EDGE) http://www.wvtechprep.wvnet.edu/edge.htm West Virginia Career and Technical Education http://careertech.k12.wv.us/ Contacts: 13 Contacts: CTE Teachers: See CTE Directory Cluster Coordinator: Name and email OCTI Assistant Executive Director and EOCTST Coordinator: Donna Burge-Tetrick OCTI Executive Director: Gene Coulson 14