Chapter 1 Cells: The Basic Units of Life

• Always carry with 2 hands
• Only use lens paper for cleaning
• Do not force knobs
• Always store covered
• Keep objects clear of desk and cords
Eyepiece
Body Tube
Revolving Nosepiece
Objective Lens
Stage
Clips
Diaphragm
Light
Always carry a microscope with one hand holding the arm and one hand under the base.
Arm
Stage
Coarse Focus
Fine Focus
Base
• Place the Slide on the
Microscope
• Use Stage Clips
• Click Nosepiece to the lowest
(shortest) setting
• Look into the Eyepiece
• Use the Coarse Focus
What’s my power?
To calculate the power of magnification, multiply the power of the ocular lens by the power of the objective.
What are the powers of magnification for each of the objectives we have on our microscopes?
Comparing Powers of Magnification
We can see better details with higher the powers of magnification, but we cannot see as much of the image.
Which of these images would be viewed at a higher power of magnification?
Chapter
1
Cells:
The
Basic
Units of
Life
Sections 1-3
Pages 2-27
Cells and the Cell Theory
• Robert Hooke in 1665 built a microscope
• Looked at cork from trees and saw tiny
“boxes”, he called them cells (little rooms)
• Hooke spent most time looking at plants and fungi because they we easy to see since the had cell walls
Finding Cells in other Organisms
• Anton van Leeuwenhoek in 1673 built a microscope
• He examined pond scum and saw small organisms in the water
• Named the organisms animalcules “little animals”
• Today we call these “little animals” protists
Finding Cells in other Organisms
• Leeuwenhoek also examined animal blood
• Noticed differences in the shape of animal blood cells (humans had round/flat cells while fish, birds and frogs were oval)
• 1 st person to see bacteria
• Discovered yeast to make bread dough rise are single cell organisms
Cell Theory…200 years later
• Schwann wrote the first two parts of the cell theory (1839)
1. All organisms are made of one or more cells.
2. The cell is the basic unit of all living things.
• Virchow added the third part of theory (1858)
3. All cells come from existing cells.
Cell Size
• Most cells are very small because if a cell’s volume gets too large, the cell’s surface area will not be able to take in enough nutrients or get rid of wastes fast enough to keep cells alive.
• Use the surface area-to
–volume ratio=
Surface area/volume
Example: page 6
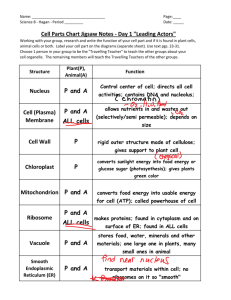
Parts of a cell-Cell Membrane
• All cells are surrounded by a cell membrane
• Protective layer and acts as a barrier
• Controls materials that go in and out of cell
Inside the Cell- Cytoplasm
Organelles
• Organelles are structures within a cell that perform specific functions for the cell
Two Kinds of Cells
Prokaryotes
• Has cell membrane, organelles, cytoplasm, and
DNA
• NO NUCLEUS
• 2 types: eubacteria and archaebacteria
Eukaryotic
• Has cell membrane, organelles, cytoplasm, and
DNA
• HAS A NUCLEUS
Genetic Material
• All cells contain DNA
(deoxyribonucleic acid)
• DNA carries information to make new cells and controls the activities of a cell
• In some cells, DNA is enclosed in the nucleus
• The nucleus is a membrane bound organelle that contains the cell’s DNA and that has a role in process such as growth, metabolism and reproduction.
(eukaryotic cells only)
Eubacteria
• Most common prokaryote
• Called bacteria
• No nucleus, has DNA
• Contain ribosomes
• Strong web like cell wall
• Bacteria can be in water, soil and living on or inside you!
Archaebacteria
• Called Archaea
• Similar to bacteria except have different ribosomes
• Three types:
1. heat loving
2. salt loving
3. methane making
Eukaryotic Cells and Eukaryotes
• Larger than prokaryotic cells
• Have a nucleus and membrane bound organelles
• Multicellular (many cells) like animals and plants
Cell Wall
• Some eukaryotic cells have cell wall
• Cell Wall: rigid structure that gives support to a cell
• Plants and algae have a cell wall which is made of cellulose (complex sugar humans cant digest…FIBER)
Cell Wall in a Plant Cell
• Cell wall
– Protect and support the enclosed substances
(protoplasm)
– Resist entry of excess water into the cell
– Give shape to the cell
Cell Wall in a Plant Cell
• Cell wall
– Fungi (yeast and mushrooms)
– Chitin
– Large empty spaces present between cellulose fibers
freely permeable
Cell Membrane
• All cells have cell membrane, outermost structure in cells that lack a cell wall
• Protective barrier
• Contains proteins, lipids and phospholipids (fat and cholesterol)
• Lipids are a group of compounds that do not dissolve in water
Cell Membrane
• Phospholipids- a lipid that contains a phosphorus.
• Lipids are water fearing or hydrophobic
• The lipid ends of the phospholipids are the inner part of the cell membrane
• The phosphorus ends are water loving or hydrophilic
• The phosphorus ends form the outer part of the cell membrane
Cell Membrane’s 2 Main Functions
• Encloses the cell and separates and protects the cell’s contents from the cell’s environment
• It also controls the movement of materials into and out of the cell
Cytoskeleton
• A web of proteins in the cytoplasm
• Acts as muscle and a skeleton (support and structure)
• Can help cell move
• Made of 3 types of proteins (one is a hollow tube, the other two are long and stringy)
Nucleus
• Large organelle in eukaryotic cells
• Contains cell’s DNA or genetic material
• DNA contains information on how to make a cell’s protein
• Covered by two membranes
• Materials pass through this double membrane through pores
• Most cells have a nucleolus in the center of the nucleus (which stores materials that will be used to make ribosomes)
Ribosomes
• Organelles that make proteins
• Smallest of organelles
• Float freely or are attached to other organelles
• Proteins are made within the ribosomes
• Proteins are made of amino acids (20 of them)
• All cells need protein to live
Proteins - Structure
• Proteins made up of small molecules called amino acids
• There are 20 common amino acids
• How the amino acids combine and their order determine the type of protein made
Proteins - Function
• Much of the structure of a cell is made of protein, including the organelles inside.
• Proteins can be enzymes
• Enzymes are a type of protein that speeds up a chemical reaction
Nucleic Acids
• These are very long organic molecules made of Carbon, Oxygen,
Hydrogen, Nitrogen and
Phosphorus.
• Two kinds: RNA and
DNA
• DNA- genetic material
• RNA- protein synthesis
Endoplasmic Reticulum
• A system of folded membranes in which proteins, lipids and other materials are made.
• Internal delivery system of the cell
• Rough ER: covered in ribosomes, makes proteins
• Smooth ER: makes lipids and breaks down toxic materials
Mitochondria (Mitochondrion)
• POWER SOURCE of cell
• Breaks down sugar for energy
• Covered by two membranes
• Have their own DNA
• Can divide within a cell
• Most eukaryotic cells have mitochondria
Mitochondria
• Energy released by mitochondria is stored in a substance called
ATP (adenosine
triphosphate)
• ATP is used to do
“work”
• ATP made at several places in a cell but most made in the mitochondria
Chloroplasts
• Animal cells can not make their own food but plants and algae can using the chloroplasts
• Photosynthesis
(sun+CO
2
+H
2
O=sugar+O
2
) sugar made helps make ATP in mitochondria
• Chloroplasts have two membranes and their own
DNA
• Green in color because of chlorophyll (green pigment) inside
Golgi Complex
• Processes, Packages and
Distributes proteins
• Named after discoverer
(Camillo Golgi)
• Looks like ER
• Creates “bubble” or a vesicle (small sac) that transports materials within the cell
Cellular Digestion
• Lysosomes: responsible for digestion
1. They destroy worn out or damages organelles
2. Get rid of waste materials
3. Protect cell wall from invaders
Vacuoles
• Large vesicle
• In plant and fungal cells
• Some act like lysosomes
• Some store water
Different kinds of plant cells
Onion Epidermal Cells root hair
Root Hair Cell
Guard Cells
Different kinds of animal cells
white blood cell
Amoeba red blood cell cheek cells sperm nerve cell muscle cell
Paramecium
Similarities between plant cells and animal cells
Both have a cell membrane surrounding the cytoplasm
Both have a nucleus
Both contain mitochondria
Differences between plant cells and animal cells
Animal cells Plant cells
Relatively smaller in size
Irregular shape
Relatively larger in size
Regular shape
No cell wall Cell wall present
Differences between plant cells and animal cells
Animal cells Plant cells
Vacuole small or absent Large central vacuole
Glycogen granules as food store
Nucleus at the centre
Starch granules as food store
Nucleus near cell wall
Benefits of Being Multicellular
• Larger Size: larger than a single celled organism. Larger have less predators and have more choices of prey.
• Longer Life: Not limited to any single cell.
• Specialization: More efficient since each cell has a job.
Cells Working Together
Tissue- group of cells working together to perform a specific job
Animals have 4 types of tissue:
1. Nerve tissue
2. Muscle tissue
3. Connective tissue
4. Protective tissue
Plants have 3 types of tissue:
1. Transport tissue- moves water and nutrients through plant
2. Protective tissue- covers the plant, retain water and protects from damage
3. Ground tissue- where photosynthesis takes place
Organ
• Different tissues group together to carry out specialized functions
– Heart : consists of muscles, nervous tissue and blood vessels
– Leaf : consists of epidermis, mesophyll and vascular tissue
The Structures of a Leaf
Chloroplast
Palisade Mesophyll Cell
Spongy Mesophyll Cell
Air Space
Stoma
The Structures of a Heart
System
• Several organs and tissues work together to carry out a particular set of functions in a coordinated way
– Human : digestive, respiratory, excretory, circulatory and reproductive systems
– Plant : root and shoot systems
Level of Organization
cells (e.g. muscle cells, nerve cells)
tissues (e.g. muscle, epithelium) organs (e.g. heart, lungs, stomach)
systems (e.g. circulatory system)
organisms (e.g. man)
Structure and Function’s relationship
• Structure: arrangement of parts in an organism
• Function: the job each part does within
• Example-
Alveoli function-contain and exchange gases
Alveoli structure- enables them to perform a function
Cell Fun!!!!
• http://crescentok.com/staff/jaskew/isr/biology/comic/page1.htm
• http://www.sheppardsoftware.com/health/anatomy/cell/index.htm
• http://www.biology4kids.com/files/cell_main.html
• http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/begin/cells/
• http://www.biologycorner.com/bio1/diffusion.html
• http://www.cellsalive.com/
• http://biology.clc.uc.edu/courses/bio104/cellresp.htm
• http://www.eurekascience.com/index.htm
• http://www.johnkyrk.com/CellIndex.html
• http://www.ibiblio.org/virtualcell/index.htm
• http://www.biology.arizona.edu/cell_bio/tutorials/pev/page2.html
Pro and Eu
• http://www.harcourtschool.com/activity/cell/cell.html
• http://www.courses.fas.harvard.edu/~biotext/animations/TRANSLATE20b.swf
• http://www.wisc-online.com/objects/ViewObject.aspx?ID=AP1302 protein synthesis
• http://www.brookscole.com/chemistry_d/templates/student_resources/shared_resources/animati ons/protein_synthesis/protein_synthesis.html
• http://www.wiley.com/college/boyer/0470003790/animations/replication/replication.htm
• http://www.nobelprize.org/educational/medicine/2001/
Plants
• http://www2.estrellamountain.edu/faculty/fa rabee/biobk/BioBookPLANTANAT.html
• http://www.softschools.com/science/plants/fl ower_anatomy.jsp
• http://www.amnh.org/learn/biodiversity_cou nts/ident_help/Parts_Plants/parts_of_flower.
htm
• http://www.phschool.com/science/biology_pl ace/biocoach/photosynth/leaf.html