cells
advertisement

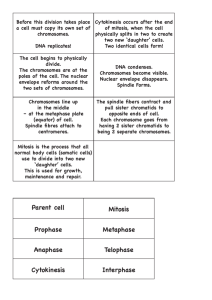
CHAPTER 10 THE CELL CYCLE http://www.biology.arizona.edu/cell_bio/activities/cell_cycle/graphics/cell_cycle_animation.gif CELL GROWTH A LIVING THING GROWS BECAUSE IT PRODUCES MORE AND MORE CELLS http://student.ccbcmd.edu/courses/bio141/lecguide/unit6/genetics/DNA/DNArep/images/interphase1_pc.jpg CELL GROWTH SURFACE AREA OF A CELL DETERMINES HOW LARGE IT CAN GROW –Surface area is critical for passage of food, oxygen, and water entering and leaving the cell *** to solve the problem of getting too large, the CELL DIVIDES http://www.mesoblast.com/images/images-mesoblast_cell_division_still.jpg RATES OF CELL GROWTH CELLS CAN GROW AT ASTONISHING RATES UNDER IDEAL CONDITIONS, BUT REAL CONDITIONS ARE FAR FROM IDEAL CONTROLS ON CELL GROWTH Depends on function http://biounder.kaist.ac.kr/~shy821/images/skin 2stem_630x.jpg •Depends on food, crowding, conditions in surrounding area. •If injury occurs (cells will grow rapidly at the site) http://www.burn-recovery.org/images/burn-classification.jpg •Consequences of uncontrolled cell growth are severe. http://www.upmccancercenters.com/images/prostate/image7_sm.gif •Cancer cells have lost their ability to control their growth rate. Breast cancer cells http://ashoutinthestreet.files.wordpress.com/2009/06/breas tcancercells.jpg Definitions CELL DIVISION - The process whereby the cell divides into 2 daughter cells http://3.bp.blogspot.com/_7XmD8w1yTeY/R4Cy_XjD NjI/AAAAAAAAABk/P7fx2NiM-zM/s320/cytokin.gif MITOSIS – process by which the nucleus of a cell is divided into 2 nuclei; occurs in somatic (body) cells; produces diploid Diploid vs. Haploid Diploid – a cell that contains both sets of homologous chromosomes (two sets); represented by the symbol 2N – Found in somatic or body cells (ex. Skin, digestive tract) – Example : Humans – 2N = 46 Haploid – a cell that contains only a single set of chromosomes (one set); represented by the symbol N or 1N – Found in gametes or sex cells – sperm & egg – Example: Humans – N = 23 CHROMOSOMES – Structures in the cell that contain the genetic information that is passed on from one generation of cells to the next http://www.stanford.edu/group/pandegroup/folding/education/GAH/chromosomes.jpg CHROMATIN – The material of which chromosomes are made http://www.all-science-fairprojects.com/science_fair_projects_encyclopedia/upload/7/79/Chromatin_c hromosome.png CHROMOSOMES THE CELLS OF EVERY ORGANISM CONTAIN A SPECIFIC NUMBER OF CHROMOSOMES http://2.bp.blogspot.com/_7XmD8w1yTeY/R4Cm2HjDNZI/AAAAAAAAAAU/1vRUnLLuwFg/s320/chromosome_chromatid_split.jpg HUMANS HAVE 23 PAIR OR 46 CHROMOSOMES http://openlearn.open.ac.uk/file.php/2355/M150_2_014i.jpg THE CELL CYCLE Interphase --> MADE UP OF 3 PARTS – preparing to divide http://www.sciencecentric.com/images/news/mitosis_300_364.jpg Mitosis --> MADE UP OF 4 PARTS the division of the nucleus Cytokinesis --> MADE UP OF 1 PART division of the cytoplasm http://www.biologyreference.com/images/biol_01_img0100.jpg INTERPHASE A. GAP 1 (G1) Cellular growth and development takes place B.DNA SYNTHESIS (S) DNA is replicated C. GAP 2 (G2) Organelles Synthesis of PHASES OF MITOSIS PHASES OF MITOSIS A. PROPHASE –Centrioles separate from each other and move to the poles –Nuclear Envelope breaks down and Nucleolus disappears –CHROMATIN COILS UP AND BECOMES VISIBLE AS CHROMOSOMES –Chromosomes become attached to the Spindle Fibers at the centromere B. METAPHASE Chromosomes line up across the equator (middle) of CENTRIOLES the cell SPINDLE FIBERS CHROMOSOME C. ANAPHASE CENTROMERES SPLIT CAUSING THE CENTER CHROMATIDS TO SEPARATE, BECOMING INDIVIDUAL CHROMOSOMES Continue to move in 2 groups near the poles D. TELOPHASE Opposite of Prophase –Chromosomes uncoil into a tangle of chromatin Nuclear Envelope reforms around chromatin Nucleolus becomes CYTOKINESIS Division of the cytoplasm into the 2 daughter SHORTCUT TO REMEMBER THE CELL CYCLE I nterphase I P rophase Passed M etaphase Math A naphase At T elophase Tom C ytokinesis Clark Animation of Mitosis http://www.loci.wisc.edu/outreach/biocli ps/CDBio.html http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VlN7 K1-9QB0