Immigration, Expansion, and Sectional Conflict 1840-1848
advertisement

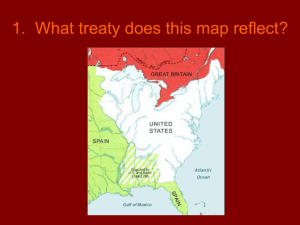
Immigration, Expansion, and Sectional Conflict 1840-1848 Chapter 13 Newcomers and Natives Immigration Statistics 1840-1860 = 4.2 million 1845-1854 = 3 million Largest influx in US history (pop. proportion) Mainly Irish, German ¾ Irish or German Reasons for Expectations Religious freedom Mormons, Quakers Economic opportunity American “Utopia” Reality Embarkation Process difficult Expensive swindlers Farming problems Lacked capital Different that European Farming Reality Lived in cities Worked in factories Patterns Irish Boarded at Liverpool “Coffin” ships No $ for farming Physically weak Clustered in NE, NY, PA, NJ 2 surges 1815s – War of 1812 1845-1850s – Potato Famine Bottom of workforce Mainly factories Domestic servants Conflict Free blacks Whites Norwegians Wisconsin farmers Germans Cotton trade in New Orleans Settled Upper Miss., Ohio River Valley Didn’t support slavery Wide range of social classes/occupations Skilled tradesmen Easily found jobs 25% farmers Culture Common language German unity Lots of voluntary associations Diversity promoted solidarity Economically self-sufficient Resentment Economic success clannishness Unrest in America Anti-Catholicism Irish immigration revived anti- catholic sentiments Nativism Societies American Republicans United Order of Americans Order of Star Spangled Banner (know-nothings) Fed on fear and discontent Scared of “popery” Threats to protestant jobs Irish were hard-drinking and halfcivilized Labor Protest George Henry Evans National Reform Association “Vote yourself a farm” neo-Jeffersonian Answer to “wage-slavery” Appealed only to artisans Labor Unions Irish supported them Commonwealth v. Hunt (1842) Mass. Supreme courts Trade unions not illegal Tensions Ethnic and religious issues Immigrant Politics Immigrants starting to become politically active Supported Democrats Feared for jobs More sympathetic to working class Values of Whigs threatened immigrants Importance of National issues The West and Beyond The Far West American Settlement of Texas Adams-Onis Treaty 1819 to 1835 Oregon still vague 1820- US settlements in Western Trade Trading centers on west coast 1790s-1820s – exchange of goods 1820s- Hudson Bay Company Beaver Trade- Colorado, Utah Santa Fe Trail Trade with Mexico from St. Louis Panic of 1837- needed silver Growing tensions Land/religion Eastern Texas Welcoming Mexico encouraged settlement Protection against Indians Mission had failed Empresarios- Stephen Austin Reversal Closed Texas and forbid slavery More white farmers than Mexicans Concerns Santa Anna Remember the Alamo Texas Revolution 1836 Stephen Austin Santa Anna invades 1835 1836- San Antonio The Alamo 187 die Sam Houston “Remember the Alamo” Lone Star Republic established 1836 American Settlement in Cali, New Mexico, and Oregon Increased immigration American culture, not native Mormons Movement westward Persecution Death of Joseph Smith in Missouri Brigham Young leads Mormons to desert Little persecution Not really inhabited By 1846: 12,000 in Utah Developed irrigation system Annexed to US: 1850 Mormon War:1857 Politics of Expansion Should US annex Texas? 1840-42: main issue still economy Whig Ascendency William Henry Harrison 1840 Controlled House and Senate Henry Clay’s American System Repealed Independent Treasury Protective tariffs Tyler dashes hopes of Whigs Disaster for Whigs Vetoed: National bank- 1841 Banking bill Postponing of tariff reduction Expansion Maine 1842 Daniel Webster Webster-Ashburton Treaty Texas Issue of Slavery 1843 Propaganda campaign for annexation of Texas 1844 President Tyler, John C. Calhoun send treaty to congress for annexation o Defeated in Senate o 1845 Congress approves joint resolution to admit Texas as a state Election of 1844 Nominees Democrats Martin Van Buren Opposed slavery Whigs Henry Clay Proslavery, proannexation The “Dark Horse” James K. Polk, Tennessee “fifty-four forty or fight!” Appealed to westerners and southerners Results Polk wins electoral VERY close popular vote Quickly confirms expansionism with inaugural address Manifest Destiny John O’ Sullivan Invoked God, divine mission Superiority of white culture Called on Americans to resist foreign powers limiting out destiny Pushed by: Nationalism Population increase Rapid economic development Technological advances Reform ideals Solutions To agricultural issues Preserve identity, values Anti-factories Jefferson’s worries void Polk and Oregon US claimed based on: Discovery of Columbia River Lewis and Clark expedition Fur trade established by Astor Oregon Fever Threats British Claim- Sir Francis Drake 1579 “All or nothing” 49th parallel Negotiations Come discontent Ratification 1846, Senate Pushed by war in Mexico Oregon Trail Overland Trails -4 month journey -Donner party, 1846 -1841 wagon trains begin -Difficult travel -Increased cooperation -1843 over 1,000 Mexican- American War Origins Failure of Mexico to pay $2 million in debt Animosity Mexican fears of US domination 1845 Senate ratifies Annexation Polk’s actions Supports Texans claims to Rio Grande River Moved Troops to Corpus Christi, under Zachary Taylor Wants California War Negotiations John Slidell Government too weak Santa Anna troops attack Polk declares war Opposition John C. Calhoun, Whigs War of 1812, “patriots” Expectations Mexico would win Army 4X larger than US army US didn’t expect Mexicans to fight Mexican-American War Leaders Zachary “old rough and ready” Taylor Buena Vista victory, 1847 Col. Stephen Kearny New Mexico, California Gen. Winfield Scott Took over for Taylor Vera Cruz, Mexico City victories, 1847 John D. Sloat New Mexico, California John C. Fremont California rebellion Bear-flag Republic, 1846 Success Mexico City 1847 Led by Scott Heroes: Robert E. Lee Ulysses S. Grant Advantages Santa Anna’s mistakes Superior artillery, military organization Treaty of Guadalupe-Hidalgo 1848 Mexico paid $15 million Ratified 1848, senate Opposition: Whigs, Democrats Problems on the horizon Sectional conflict Polk restored Independent Treasury Jacksonian policies Tariff of 1846 Slashes duties Vetoes Rivers and Harbors Bill 1846 Slavery debate Wilmot Proviso 1847 No slavery in new territories Defeated in senate (passed house 2X) Proviso’s Problems Brings up discussion of slavery again Free-Labor party emerges Calhoun questions constitutionality of prohibiting slavery in new territories Northerners defend by quoting Land Ordinance of 1787 and Missouri Compromise Manifest Destiny to the South Ostend Manifesto Polk offered to buy Cuba from Spain for $100 million dollars Spain refused 1852- secret treaty to buy Spain Too much anger in US, Northerners think “pro-slavery” Walker Expedition William Walker led group into Baja California in 1853 unsuccessful Tried to take Nicaragua 1855 Recognized by US Clayton-Bulwer Treaty 1850 Ambition to build canal in Central America Treaty b/w Great Britain and U.S. Neither nation would take exclusive control of canal and route in Central America Gadsden Purchase 1853 Southwest Arizona, New Mexico border Land for railroad $10 million dollars Election of 1848 Problems for the Whigs: Polk’s Policies successful Independent treasury Low tarrifs Problem’s for Democrats Wilmot Proviso Nominees Democrats Lewis Cass “Squatter Sovereignty” Whigs Zachary Taylor War hero with no platform Southern slaveholder Major Issue Slavery Barnburners- NY “Conscience” Whigs Free Soil Party Free trade, free labor, free speech, free men Nominate Martin Van Buren Outcome Taylor victorious Free Soil party has strong grass-roots showing Sends message to Democrats and Whigs Gold Rush 1848 John Marshall discovers Gold in Sierra Nevada mts. 9 days before Treaty of GuadalupeHidalgo Technological Developments Hydraulic mining operations Consequences Population of California 1848: 15,000 1852: 250,000 Culture clash Diverse mix of cultures, people Chinese discrimination Slavery Should California allow it? Violence Committees of vigilance Crowding, disease, fire, rowdiness Gold Rush 1849