Supporting Evidence for Evolution
advertisement

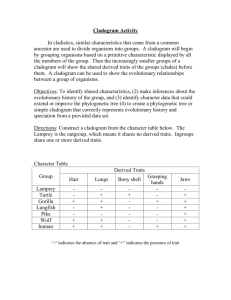
Supporting Evidence for Evolution Evolution evidence does not make sense unless there is an awareness of differences between living organisms process of organizing and classifying organisms into certain groups by their differences is called taxonomy Taxonomy comes from a root Greek word meaning “order” or “arrangement” Taxonomic Classification: biological classification classification; placing of similar objects into similar groups Biological classification organizes all living organisms Structure, DNA, cell type, complexity, etc. History of Classification developed by Swedish scientist Carolus Linnaeus in the 18th century Designed to have a universal naming system binomial nomenclatureorganism's scientific name is comprised of a combination of two terms: genus and species scientific name for humans- Homo sapiens Reason for universal naming system Name this animal Common name: PUMA, MOUNTAIN LION, COUGAR Scientific Name: Felis concolor Classification DOMAIN •Domain is the most broad while species is the most specific •Mnemonic: o dear king phillip came over for good soup Classification Structures, functions and genetics help support the theory of evolution Convergent evolution vs Divergent evolution Homologous Structures Analogous Structures Vestigial Structures Embryology Genetic similarities Atavisms *Other supporting evidence: fossil records, relative/absolute dating Convergent evolution Convergent evolution: unrelated pathways to different species develop similar traits. Similar traits develop due to similar environmental pressures. These traits can be called analogous traits Analogous Traits Different structures with the same function Divergent evolution opposite of convergent evolution related pathways can develop different traits over time: Natural selection, sexual selection, genetic barriers and mutation drive these changes. enough small changes accumulate in closely related but isolated populations, speciation might occur Homologous Traits Same structure but different function characteristics that derive from shared common ancestry Vestigial Structures (vestigial organ) Many organisms possess vestigial structures no apparent function, however; they resemble structures their presumed ancestors had Structures were once important Through evolutionary change the structures became useless Vestigial structure examples Humans-possess a complete set of muscles for wiggling their ears human appendix is believed to be vestigial; it represents the terminal part of the cecum Vestigial Structures Boa constrictors have hip bones and rudimentary hind legs Vestigial Structures Manatees, a type of aquatic mammal, have fingernails on their fins (which evolved from legs) Vestigial Structures Baleen whale, which contains pelvic bones, as other mammal skeletons do, even though such bones serve no known function in the whale. Do Now Questions 1. Which organism has the closest relationship to Panthera leo? How do you know? a. Felis concolor b. Panthera tigris c. Equus caballus d. Canis lupus 2. Which format for scientific name is correct? a. danaus plexippus c. Danaus Plexippus b. Danaus plexippus d. Danaus plexippus Embryology study of embryos formation, development, structure and function An embryo is an organism in its early stages of development Comparative Embryology Comparing stages of early development from very different animals provides evidence for commonality Genetic Similarities (molecular homology) Technology has allowed us to examine the DNA and protein structures/patterns from any organism in existence Comparing different species DNA can undercover similarities and differences How closely related are these organisms? Genetic Similarities protein: hemoglobinWho are humans closest relative using hemoglobin testing? Human Beta Chain 0 Gorilla (greater ape) 1 Gibbon (lesser ape) 2 Rhesus monkey 8 Dog 15 Horse,cow 25 Mouse 27 Gray kangaroo 38 Chicken 45 Frog 67 Lamprey 125 Sea slug 127 Soybean (leghemoglobin) 124 How similar are we when comparing DNA? Another human? ~99.9% A chimpanzee? ~97-98% A mouse? ~90% A fruit fly? ~45% Yeast? ~25% Genetic Similarities Genetic Similarities Humans chromosomes vs. chimpanzees chromosomes Chromosome #2 fused Atavism reappearance of a trait or characteristics in an organism that is typical of an ancestral form (appearing trait has been absent from modern organism for many generations) usually due to mistake in reading DNA Expressing “junk DNA” Atavism can be seen in many different organisms Atavisms Human Atavisms Cladogram A tree-like diagram which shows the evolutionary relationship between organisms Reading and constructing a cladogram vertebrae legs hair Opposable thumbs jellyfish lamprey X salamander X X cat X X X X X X gorilla X cat gorilla salamander lamprey Opposable thum hair jellyfish legs vertebrae time What can a cladogram tell you? •Common ancestor •Closest relative •Distant relative Speciation event Punctuated equilibrium and gradualism Do Now Fill in the chart and create a cladogram. jaws Lizard Tiger Human Salamander Lamprey shark gorilla lungs Amiontic sac hair thumbs bipedal Who is classified as a primate? an animal order (classification) including lemurs, tarsiers, monkeys, apes and human beings Primate Cladogram New fossil evidence! •Oldest primate ancestor was thought to be 60 mya •New primate ancestor foundabsolute dating puts its age at around 85 mya BBC news: http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/science/nature/1935558.stm Earliest primate found thus far (85 myo ) Closer look at an ape cladogram See video** Comparing humans to great apes… Comparing humans to great apes Primate Hand Comparing humans to great apes Genetic comparison: Humans and chimpanzees are ~97% similar in their genetic composition Large difference- # of chromosomes See video** What happened after the speciation event where chimps and humans diverged? •Environmental conditions that lead to chimpanzees: tree-dwellers •Environmental conditions that lead to humans: ground-dwellers The modern human was not always this way… See video** Modern human skull Evolution of humans Evolution of humans Lucy (3.2mya) and Ardi (4.4mya) *Oldest fossils all found in Africa* Species are arranged according to the earliest date of fossils found so far ( a couple of recent discoveries are not shown). The red lines end because fossils have not been found any older for that species. **Note the overlap of time for species** The oldest fossils in the evolution of humans have only been found on the continent of Africa, no where else. •Who is the closest relative to humans? •Is that relative alive today? Specialized Characteristics: •Depth perception (distance of an object) •Binocular vision (using both eyes together) •Social complexity (groups, communication) •Opposable thumbs, grasping fingers •Cranial capacity (size of brain; humans have the largest capacity) •Bipedalism (walking on two feet; strictly a human trait) Why is this picture incorrect? Evolution and the world Can evolution be observed today? YES IT CAN! Some bacteria and viruses evolve at a very fast pace.