Covalent Bonds and Compounds
advertisement
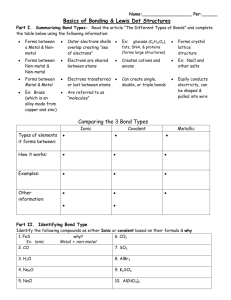
Covalent Bonds and Compounds Molecules Three Kinds of Bonds 1. 2. 3. Non-metal to non-metal metal to non-metal metal to metal Covalent Ionic Metallic Why do atoms bond? To achieve stability Stability is achieved when octet rule is satisfied Bonds and Electronegativity Electrons are transferred between atoms when the difference in electronegativity between the atoms is quite high. The amount of transfer depends on the electronegativity difference. Bonds and Electronegativity The number 1.67 seems to be the magic number.(Note:1.67 rounds to 1.7) If the electronegativity difference is less than 1.67, the bond is more covalent than ionic. If the electronegativity difference is greater than 1.67, the bond is more ionic than covalent. Pg. 263 Figure 9-15 Electronegativity Difference Covalent < 1.67 However – 0 -.3 is non-polar covalent . 3 – 1.67 polar covalent There are 7 instances of perfectly covalent bonds (electronegativity difference = 0) H2, N2, O2, F2, Cl2, Br2, I2 Practice problems 22 Pg. 266 What is a covalent bond? Bond that results from the sharing of electons between nonmetals Type of bonding found in majority of known compounds Molecule – formed when two or more atoms bond covalently ***Ex. of molecules – carbohydrates, proteins, fats, DNA, wool, cotton, and synthetic fibers found in clothes you wear all consist of molecules Lewis structures Use electron dot diagrams or Lewis dot diagrams to show how electrons are arranged in molecules Ex. HBr Pg. 244 practice problems 19 use different colors for different atoms Covalent bonds Lewis structures Single covalent bonds – single pair of electrons shared Double covalent bond - sharing of two pairs of electrons Triple bond – sharing of 3 pairs of electrons Nomenclature (naming) Covalent bonds are generally between two non-metals. CO - Carbon monoxide CO2 - Carbon dioxide Prefixes 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 - - - Mon(o) Di Tri Tetr(a) Pent(a) Hex(a) Hept(a) Oct Non Nitrogen and oxygen (five molecules) N2O NO N2O3 NO2 N2O5 - Dinitrogen monoxide Nitrogen monoxide Dinitrogen trioxide Nitrogen dioxide Dinitrogen pentoxide Metallic Bonds Bonding in metals is due to delocalized electrons. These often exist in what is called a sea of electrons. Sea of “delocalized” electrons Metal atoms Metallic Bonds This explains many of the properties of metals: Malleable Ductile Conducts electricity well Alloys Two Metals (and sometimes other substances) bonded (mixed) together. Alloys Two Metals (and sometimes other substances) bonded (mixed) together. Alloys Two Metals (and sometimes other substances) bonded (mixed) together. Alloys Two Metals (and sometimes other substances) bonded (mixed) together.