UNIT 1: SOCIAL, ECONOMIC, AND POLITICAL TURNING POINTS
advertisement

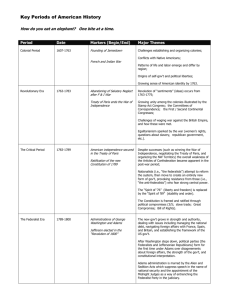
LESSON 1.3: POLITICAL TURNING POINTS This lesson deals with political turning points. What do you think a political turning point is? When an event happens in history involving political decision, that changes the traditional pattern of politics, it's a turning point. Lets look at three examples of political turning points in our nations early history: Shays Rebellion “Revolution” of 1800 Jacksonian Democracy What happened? Shays' Rebellion was an armed uprising that took place in central and western Massachusetts in 1786 and 1787. The rebellion was named after Daniel Shays, a veteran of the American Revolutionary War and one of the rebel leaders. Why? Financial difficulties brought about by a post-war economic depression, a credit squeeze caused by a lack of hard currency, and fiscally harsh government policies instituted in 1785 to solve the state's debt problems. Effects: The Rebellion was crushed, and problems linked to the Articles of Confederation spur consideration of a new Constitution. What happened? The United States Presidential election of 1800 was the 4th presidential election, and is referred to as the "Revolution of 1800," Thomas Jefferson defeated John Adams. Why is this election considered a “Revolution’? The election ushered in a generation of Democratic-Republican Party rule and the eventual demise of the Federalist Party in the First Party System. It was a long, bitter re-match of the 1796 election between the pro-French and pro-decentralization Democratic-Republicans under Jefferson, against incumbent Adams pro-British and pro-centralization Federalists. In other words, neither party had anything in common, and despised one another. To make matters worse the election revealed a flaw in the Constitution regarding presidential elections. Effects: The election of 1800 is the first real transfer of power in our nations history. It proved that, despite strong disagreements among political parties, power can be transferred peacefully and the democratic process would overcome political rivalry. Furthermore, the 12th Amendment was added to the United States Constitution, stipulating that electors make a discrete choice between their selections for president and vicepresident. What is Jacksonian Democracy? Jacksonian democracy is the political movement toward greater democracy for the common white man symbolized by American politician Andrew Jackson and his supporters. Jackson's policies followed the era of Jeffersonian democracy which dominated the previous political era. Why is this a big deal? Andrew Jackson is the first president to come from a modest, common background. As a result, he despised the aristocracy, and the“career politician” . During his presidency, Andrew Jackson and his supporters would move to forge a more democratic nation in which even common men could take part in the political process. Effects of Jacksonian Democracy: Jackson fulfilled his promise of broadening the influence of the citizenry in government. Jacksonian policies included ending the bank of the United States, expanding westward, and removing American Indians from the Southeast. Jackson was denounced as a tyrant by opponents on both ends of the political spectrum. This led to the rise of the Whig Party. List as many political turning points that you can think of in our nations history, both in early and modern history. Brainstorm with a partner and be prepared to present your list to the class. Choosing Washington as first president Election of 1860 and 1864 (Lincoln) 19th amendment (Women vote) WW1 New Deal WW2 Berlin airlift and cold war Brown vs. Board of Education 1968 = losing Vietnam, political turmoil, election End of the Cold War Election of 1980 = Reagan Revolution Election of 2000 (Gore vs. GW Bush) 9/11 attacks Election of 2008 (Obama vs. McCain) http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Timeline_o f_United_States_history Choose 5 turning points for each category: Economic Political Social Military Respond in your Journal to the following: What did you learn today about political turning points? How is Shays Rebellion, Revolution of 1800, and Jacksonian Democracy examples of political turning points?