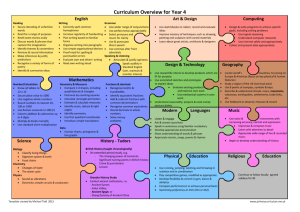
File - Ms. Sanchez Class 151
advertisement
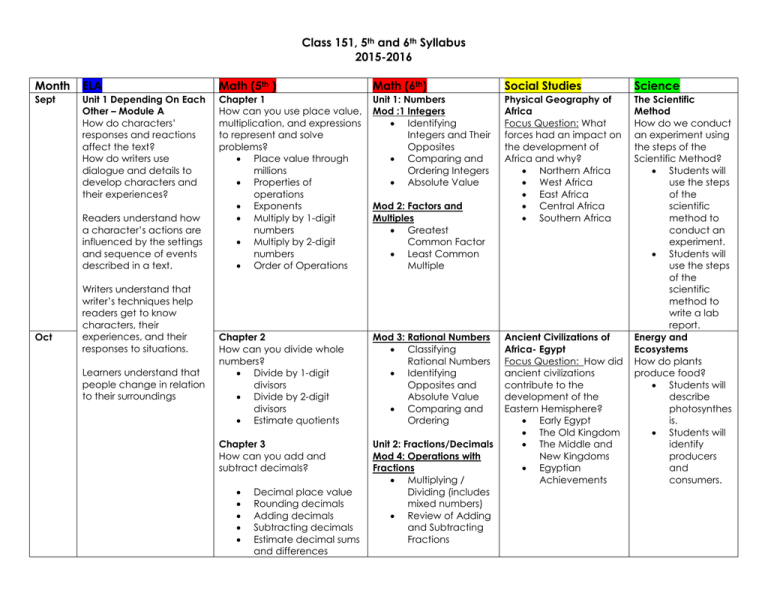
Class 151, 5th and 6th Syllabus 2015-2016 Month ELA Math (5th ) Math (6th) Social Studies Science Sept Unit 1 Depending On Each Other – Module A How do characters’ responses and reactions affect the text? How do writers use dialogue and details to develop characters and their experiences? Chapter 1 How can you use place value, multiplication, and expressions to represent and solve problems? Place value through millions Properties of operations Exponents Multiply by 1-digit numbers Multiply by 2-digit numbers Order of Operations Unit 1: Numbers Mod :1 Integers Identifying Integers and Their Opposites Comparing and Ordering Integers Absolute Value Physical Geography of Africa Focus Question: What forces had an impact on the development of Africa and why? Northern Africa West Africa East Africa Central Africa Southern Africa Chapter 2 How can you divide whole numbers? Divide by 1-digit divisors Divide by 2-digit divisors Estimate quotients Mod 3: Rational Numbers Classifying Rational Numbers Identifying Opposites and Absolute Value Comparing and Ordering Chapter 3 How can you add and subtract decimals? Unit 2: Fractions/Decimals Mod 4: Operations with Fractions Multiplying / Dividing (includes mixed numbers) Review of Adding and Subtracting Fractions The Scientific Method How do we conduct an experiment using the steps of the Scientific Method? Students will use the steps of the scientific method to conduct an experiment. Students will use the steps of the scientific method to write a lab report. Energy and Ecosystems How do plants produce food? Students will describe photosynthes is. Students will identify producers and consumers. Readers understand how a character’s actions are influenced by the settings and sequence of events described in a text. Oct Writers understand that writer’s techniques help readers get to know characters, their experiences, and their responses to situations. Learners understand that people change in relation to their surroundings Decimal place value Rounding decimals Adding decimals Subtracting decimals Estimate decimal sums and differences Mod 2: Factors and Multiples Greatest Common Factor Least Common Multiple Ancient Civilizations of Africa- Egypt Focus Question: How did ancient civilizations contribute to the development of the Eastern Hemisphere? Early Egypt The Old Kingdom The Middle and New Kingdoms Egyptian Achievements Nov/ Dec Depending On Each Other – Module B How do readers identify relationships and interactions in texts? How do writers group information logically, with supporting visuals? Readers understand relationships or interactions between two or more individuals, concepts or events based on specific information from texts. Chapter 4 How can you solve decimal multiplication problems? Multiply decimals and whole numbers Multiply decimals Chapter 5 How can you solve decimal division problems? Estimate quotients Divide decimals by whole numbers Divide decimals Writers understand how to develop a topic with facts, definitions, concrete details, quotations, or other domain-specific information/examples related to the topic. Mod 5: Operations with Decimals Dividing Whole Numbers Adding and Subtracting Decimals Multiplying Decimals Dividing Decimals Applying Operations with Rational Numbers Unit 3: Proportionality: Rations and Rates Mod 6: Representing Rations and Rates Ratios Rates Using Ratios and Rates to Solve Problems Ancient Civilizations of Africa- Trading Kingdoms Focus Question: How did ancient civilizations contribute to the development of the Eastern Hemisphere? Ancient Kush Later Kush Empire of Ghana Mali and Songhai Historical and Artistic Traditions of Western Africa Mod 7: Applying Ratios and Rates Ratios, Rates, Tables and Graphs Solving Problems with Proportions Converting within Measurement Systems Growth and Development of Africa Focus Question: What forces had an impact on the development of Africa and why? Contact with Other Cultures European Colonization Learners understand that people, animals and all living things live in interactive ways and impact one another. Jan Unit 2 Finding Courage – Module A How does the inclusion of visual elements in text contribute to meaning, tone, and perspective? How is theme revealed through details of the text? Readers understand that Chapter 6 How can you add and subtract fractions with unlike denominators? Estimate fraction Common denominators Equivalent fractions Add fractions with unlike denominators Energy and Ecosystems How is energy passed through an ecosystem? How do organisms compete and survive in an ecosystem? Students will understand how food chains and food webs are related. Students will know the roles of producers, consumers, and decomposer s in ecosystems. Students will explain how populations interact. Students will describe plant and animal adaptations. Ecosystems and Change How do ecosystems change over time? How do people affect ecosystems? Students will describe how changing the theme of a text can be determined by analyzing the author’s use of details/description, point of view, voice, imagery, and mood/tone. Writers understand that opinions are supported with evidence from a variety of resources, through analysis, reflection, and research. Learners understand that people respond to inequality and injustice with a variety of tactics. Feb/ March Finding Courage – Module B How does understanding the relationships among individuals and historical events help readers understand text? Why is it important for writers to incorporate multiple points of view when writing to explain? Readers understand that authors support main ideas with key details, providing reasons and Subtract fractions with unlike denominators Add and subtract mixed numbers Subtracting with renaming Chapter 7 How do you multiply fractions? Fractional part of a group Multiply fractions and whole numbers Multiply fractions Multiply mixed numbers Chapter 8 What strategies can you use to solve division problems involving fractions? Divide fractions and whole numbers Chapter 10 What strategies can you use to compare and convert measurements? Customary length Customary capacity Customary weight Metric measures Elapsed time Mod 8: Percents Understanding Percents Percents, Fractions, and Decimals Solving Percent Problems Unit 4: Equivalent Expressions Mod 9: Generating Equivalent Numerical Expressions Exponents Prime Factorization Order of Operations Mod 10: Generating Equivalent Algebraic Expressions Modeling and Writing Expressions Evaluating Imperialism in Africa Revolution and Freedom Africa Since Independence Physical Geography of South and East Asia Focus Question: What forces had an impact on the development of Asia and why? The Indian Subcontinent China, Mongolia, and Taiwan Japan and the Koreas Southeast Asia ecosystems affect the organisms living there. Students will describe the difference between primary and secondary succession. Students will explain how changes can cause extinction. Students will explain how people’s actions can affect the environment. Students will identify ways to protect the environment. The Rock Cycle What are minerals? How do rocks form? Students will classify minerals based on their properties. Students will identify different mineral properties. Students will identify evidence to explain the relationships between individuals, ideas, and concepts within a text. Writers understand that informative/explanatory texts examine a topic and convey ideas and information by drawing upon evidence from both literary and informational texts to support analysis, reflection, and research. Code X: Unit 5: Equations and Inequalities Mod 11:Equations and Relationships Writing Equations to Represent Situations Addition and Subtraction Equations Writing Equations from Tables Writing Inequalities Learners understand that large-scale movements are produced by a unique confluence of leadership and events. April Expressions Generating Equivalent Expressions Chapter 11 How do unit cubes help you build solid figures and understand the volume of a rectangular prism? Polygons Triangles Quadrilaterals Mod 12: Relationships in Two Variables Graphing on the Coordinate Plane Independent and Dependent Variables in Tables and Graphs Writing Equations from Tables Representing Algebraic Relationships in Tables and Graphs Unit 6: Relationships in Geometry Mod 13:Area and Polygons Area of Quadrilaterals Area of Triangles Solving Area properties of rocks. Students will understand how rocks form. Changes to Earth’s Surface How do movements of the crust change Earth? Students will understand the layers of the Earth. Students will describe how movements of the Earth’s crust can change Earth’s surface. Students will describe the causes of earthquakes, volcanoes, and mountains. Ancient Civilizations of Asia- India Focus Question: How did ancient civilizations contribute to the development of the Eastern Hemisphere? Early Indian Food and Nutrition What are the six basic nutrients? What are the food groups? What are calories? Students will name the six May Three-Dimensional figures Volume of rectangular prisms Volume of composed figures Chapter 9 How can you use line plots, coordinate grids, and patterns to help you graph and interpret data? Line plots Coordinate grid Line graph Numerical patterns Equations Area of Polygons Mod 14: Distance and Area in the Coordinate Plane Distance in the Coordinate Plane Polygons in the Coordinate Plane Mod 15: Surface Area and Volume of Solids Nets and Surface Area Volume of Rectangular Prisms Solving Volume Equations Civilizations Origins of Hinduism Origins of Buddhism Indian Empires Indian Achievements Ancient Civilizations of Asia- China Focus Question: How did ancient civilizations contribute to the development of the Eastern Hemisphere? Early China The Han Dynasty The Sui, Tang, and Song Dynasties Confucianism and Government The Yuan and Ming Dynasties basic nutrients. Students will name food sources for certain nutrients. Students will classify foods into the five main food groups. Students will identify their own caloric needs. Human Body Systems How does the body digest food? How does the body take in air? Students will identify the parts of the digestive system. Students will explain the sequence of food through the body. Students will identify the parts of the respiratory system. Students will explain the sequence of air through the body. June Getting Ready for Sixth Grade Portfolio Review Unit 7: Measurement and Data Mod 16: Displaying, Analyzing, and Summarizing Data Measures of Center Mean Absolute Deviation Box Plots Dot Plots and Data Distribution Histograms Final Unit: Getting Ready for 7th Grade Growth and Development of South and East Asia Focus Question: What forces had an impact on the development of Asia and why? Contact Across Cultures Interaction with the West New Political Movements Asia at War A New Asia Water Cycle What is the water cycle? Why is the water cycle important to society? Students will explain how the water cycle works. Students will explain the importance of the water cycle.