Centrally planned economy
advertisement

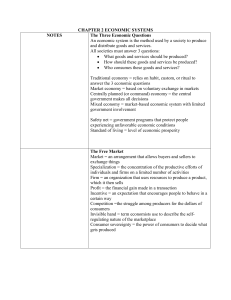
Take out Spiral Notebook . Week: Economic Systems Day 1 What will we learn today? Standard 12.1.5 The role of market economy in political and personal liberty. Standard 12.2.3 Explain the roles of property rights, competition, and profit in a market economy. Directions: Answer the following question in your Spiral. You need to write a one paragraph response. There should be no talking during the Bellwork. Are human beings selfish? Or are they caring? What do you think? Explain. 1 CHAPTER 2 JIGSAW Do Silent Reading First Group1= 3 Economic Questions & what should be produced pg 23 Group2= How should goods & services be produced pg 23 Group3= Who consumes goods and service pg 24 Group4= Economic Efficiency pg 25 Group5= Economic Freedom pg 25 Group6= Economic Security & Predictability pg 25 Group7= Economic Equity pg 26 Group8= Economic Growth and Innovation pg 26 Group9= Economies and Values pg 26 Economic System All societies have an economic system or a way of providing for the wants and needs of their people. $ Economic System -function is to produce and distribute goods and services to consumers Economic Systems Countries must answer 3 key economic questions: what should be produced, how should it be produced and who will consume these goods and services. Economic Systems How a society answers these questions depends on how much it values economic goals of efficiency, freedom, security, equity and growth. $1. What goods or services should be produced? How much resources should we devote to national defense? Education? Public health? $2. How should they be produced? Should we have coal/oil/nuclear power? Should teachers have 20 kids in a room or 50? $3. Who consumes the goods and services? How will society distribute income? Who will drive the Lexus? Who will take the bus? 6 Traditional economy: Relies on habit or custom. Little innovation. Similar to family system. Boys follow dad’s footsteps, girls follow mom. Examples: Hunting, farming. Low standard of living. Market economy: Decisions made by individuals based on exchange, trade. (aka free markets, capitalism) $ Centrally planned economy: (aka command economy) Government decides everything. Example: communism. Mixed economy: Market-based economy where government plays a limited role. This is the United States. 7 Traditional Economy Allocation of scarce resources, and nearly all other economic activity, stems from ritual, habit or custom. Individuals are not free to make own decisions. Ex. Australian aborigines Advantage: everyone knows the role they play Disadvantage: discourages new ideas Command Economy A central authority (government) makes most of the decisions. People have little if any influence over production. Ex. North Korea, Cuba and former Soviet Union. Advantage: can change direction drastically in a short time. Ex. farming to industrial Disadvantage: Not designed to meet the wants of consumers (Everyone gets only 1 In and Out burger. Market Economy People and firms make decisions based on what best suits their interest. Ex. USA, Canada and Great Britain Advantage: overtime it can makes changes in demand. Ex. Fast food to health food Disadvantage: does not always provide for basic needs of people. Ex. Homeless people Checking for understanding-C4U Give one example of: Traditional economy Market economy Command economy Mixed economy I will call on students for a response! Chapter 2 Sec 2 Market: An arrangement that allows buyers and sellers to exchange things. $ Markets exist because it allows people to buy what they need to consume and sell goods and services they produce. Specialization: The concentration of the productive efforts of individuals and firms on a limited number of activities. Example: a mechanic specialized in fixing Japanese cars. Or: assembly line e 12 The Free Market Free market is an economic system where people do what’s best for them for personal gain. Consumers have an interest in looking for lower prices. Producers engage in a competition for consumers money. 14 Household: A person or group of people living in the same residence. Firm: Business; an organization that uses resources to produce a product Factor market: Market in which firms purchase the factors of production (land, labor, capital) from households 15 Profit: The financial gain made in a transaction Product market: The market in which household purchase the goods and services that firms produce. Adam Smith: Wrote The Wealth of Nations in 1776. Father of economics. Said people are selfish, but that is okay because it works. Adam Smith called the relationship between self interest and competition the invisible hand. $ Said government should stay out of economy (laissez faire = hands off) Government should only be involved with education, health care and transportation. 16 However,$ Free Market Economy does need some Government intervention to provide for things that the market place does not address. Example: national defense, roads and highways, education, and health care Self-interest: $ The motivating force behind the freemarket. One’s own personal gain. Incentive: The hope of reward or the fear of punishment that encourages people to act in a certain way. Example: recycling. Buy things on sale. Employee of the month. Sports championships. Getting an F 17 18 Competition: The struggle among producers for the dollars of consumers. This helps control firm’s selfishness. $ Purpose is to act as a regulating force in the marketplace Without competition a business can monopolize a product or service Example: PS3 lowers price, Xbox does the same within a week. 19 Why is the free market system good? 1) It works. Producers make what consumers want, when they want it. Prices are pretty good. 2) Freedom. Work where you want, buy what you want, make what you want. 3) Growth is encouraged because innovation is encouraged. 4) Wide variety of things get made because consumers decide what gets made. Consumer sovereignty: The power of consumers to decide what gets produced. 20 C4U Why do markets exist? Is competition good for consumers or business? What motivates the Free Market? Centrally Planned Economies Chapter 2 Sec 3 In command economies the government controls the factors of production and answers 3 economic questions of what, how and for whom to produce for all of society. Idea is that the government makes all the choices that will benefit or is best for the whole society, not just a few individuals Command economies often associated with socialism, communism and authoritarianism. Centrally Planned Economy Socialism- belief that democratic means should be used to distribute wealth evenly through a society Communism- belief that government leaders should distribute wealth evenly through a society. Authoritarianism (Fascism)- requiring strict obedience to an authority, such as a dictator. No individual freedoms. Centrally Planned Economy Problems Poor Quality of Goods= workers don’t care, as long as they produce what they are told to produce Shortages of Goods and Services= need products are not made Diminishing Production = workers don’t care, they don’t get raises for producing more; no incentives Performance always falls short of ideals that the system is built Can’t meet the needs of consumers needs and wants: Government decides what is produced, not consumers The system does not reward innovation, is not flexible, and sacrifices individual freedoms for the “good” of whole society Chapter 2 Phocabulary Key Terms Pg 46 Remember Word and definition on the right and picture or illustration on the left,( same as Cornell Notes ) • Create a brochure that illustrates and defines The Free Market Economy (left) and the Centrally Planned Economy (right). • Free Market Economy – pg. 28 – 32 • Write definition (pg. 28 – 32) on the inside flaps. • Why is this economy good? • What isn’t good about this economy? •The Centrally Planned Economy – pg. 34 - 38 • Write definition (pg. 34 – 38) on the inside flaps. • Why is this economy good? • What isn’t good about this economy? IMPORTANT: Put everything in your own words! Make it eye-catching. Must be in color. 26