507 Digital Media Production - Lecture 3
advertisement

Info + Web Tech Course
Digital Media
Production
Anselm Spoerri PhD (MIT)
SC&I @ Rutgers University
aspoerri@rutgers.edu
anselm.spoerri@gmail.com
Digital Media Production
© Anselm Spoerri
Lecture 3 – Overview
XHTML Elements Recap
– Hierarchy of Tags
– Block and Inline Elements
– div | id | class
Cascading Style Sheet = CSS
– Formatting Rules
– Inline | Internal | External
specification of CSS rules
CSS Demo
CSS Navigation using Lists
Testing & Debugging Web Pages
Check Easy Stuff First
Lectures – Week 3 Content
http://comminfo.rutgers.edu/~aspoerri/Teaching/DMPOnline/Lectures.html#week3
Digital Media Production
© Anselm Spoerri
Recap & New – Web Basics: HTML Elements & Tags
HTML is made up of elements
<tag>Content</tag>
(read as: open tag, content, close tag)
Three major elements needed on HTML page
<html> - container for all of our HTML code
<head> - put data for browser and other machines
<body> - put content to show to the user
Block-level elements take up own space vertically
(<p>, <h1>, <h2>, ...)
<div>
page division
Inline-level elements placed inside other elements
(<a>, <img>, <strong>, <em>, …)
Digital Media Production
© Anselm Spoerri
Page Layout – DIVs
Two methods for creating Web Page Layout
‒ Tables (last lecture)
‒ DIVs and CSS (this lecture)
Structure Your Pages
URL
‒ Divide logical sections of document into div elements
pageContent
<div>
header
<div> header content </div>
navigation
<div> navigation content </div>
main content
<div> main content </div>
footer
<div> footer content </div>
</div>
Produces “linear / natural flow” of divs
Digital Media Production
© Anselm Spoerri
Page Structure – Hierarchy & Naming Elements
Body of (X)HTML document encloses Content of Web page.
Breaking up Page into Divisions (DIV)
Creating a Line Break: <br />
Hierarchical Structure of Web pages
‒
Elements contained inside another element (latter = parent, former = child)
Naming Elements
‒ id="name"
can be applied only once unique
#idName {…}
‒ class="name"
.className {…}
define CSS rule
can be applied many times
define CSS rule
Useful with div (content blocks) and span (inline text) elements
Digital Media Production
© Anselm Spoerri
Page Layout – DIVs with IDs
Name div elements with unique IDs
pageContent
<div id="pageContent">
header
<div id="header"> text/images/links </div>
navigation
<div id="navi"> text/images/links </div>
main content
<div id="content"> text/images/links </div>
footer
<div id="footer"> text/images/links </div>
</div>
Digital Media Production
© Anselm Spoerri
CSS
Cascading Style Sheets = CSS
‒ Collection of
Formatting Rules
‒ Control Appearance of web page: blocks and text
‒ Ensure a more Consistent Treatment of Page Layout
and Appearance in Browsers
‒ Separation of Content from Presentation
– Easier to Maintain Appearance since Make Change
in Single Location
– Simpler and Cleaner HTML code shorter loading times
Digital Media Production
© Anselm Spoerri
CSS
(cont.)
Cascading Style Sheets (CSS)
‒ Control Text properties
Specific fonts and font sizes; bold, italics, underlining, and text
shadows; text color and background color; link color and link
underlining; etc.
‒ Control Format & Position of Block-level Elements
Set margins and borders for block-level elements; position them in a
specific location; add background color; float text around them; etc.
‒ Liquid layouts: expand/contract based on Browser width.
‒ Easy to apply Same Layout to Whole Site and only
need to modify external CSS file.
‒ Minus: Not all browsers support CSS the same way.
Digital Media Production
© Anselm Spoerri
CSS
(cont.)
CSS Style Sheet stored
a) External CSS style sheet
(.css file linked to page and using a link or an @import rule in
the head section of a document).
b) Internal (or embedded) CSS style sheet
(included in style tag in head portion of an HTML document).
c) Inline styles
(defined within specific tag instance in HTML document)
Using Inline styles is not recommended.
CSS Rule = Selector and Block of Declarations
Enclosed by {...} brackets and separated by ;
Declaration = Property: Value;
Digital Media Production
© Anselm Spoerri
CSS – General Structure of CSS Rule
Basic syntax for Internal and External CSS:
selector {property1: value1; property2: value 2;}
HTML tag you want to modify
Value you want property to take
Property you want to change
p { text-align: left;
color: black;
font-family: Arial; }
causes
Font to be left-aligned
Font to be Arial and black
Digital Media Production
© Anselm Spoerri
CSS Rules – id and class Rules in Internal Style Sheet
<head>
<style type="text/css">
/*
Comment: pageContent ID and define font to use for page and the top
and left margins as well page width. This pageContent div contains all the
other divs */
#pageContent {
font-family: Verdana, Geneva, sans-serif;
font-size: 12px;
margin-top: 10px;
margin-left: 50px;
width: 500px;
}
/* blue text class */
.blueText {
color:#009;
}
</style>
</head>
Digital Media Production
© Anselm Spoerri
CSS Rules – id and class Rules Applied in <body>
<body>
<div
id="pageContent">
<div id="content">
<h1>Heading1</h1>
<p
class="blueText">Open paragraph</p>
</div>
</div>
</body>
Digital Media Production
© Anselm Spoerri
Location of CSS Style Definition
Inline style
(causes only the tag to have desired properties)
<p style="font-family:Arial; color:blue">Something blue </p>
Internal stylesheet
(specific to a document)
– Causes all tags in document to have property
– <style> tag inside <head> tag of document
<head>
<style type="text/css">
p { font-family:Arial; color:blue;}
</style>
</head>
External stylesheet (can control multiple documents)
– Ensure consistent appearance of website
<head>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="mystyle.css" type="text/css" />
</head>
Digital Media Production
© Anselm Spoerri
CSS – Cascasde of How Rules are Applied
Style Rules “Cascade” from broad to narrow:
– Browser’s Default Behavior
– External Style Sheet
– Internal Style Sheet
– Inline Style
Digital Media Production
© Anselm Spoerri
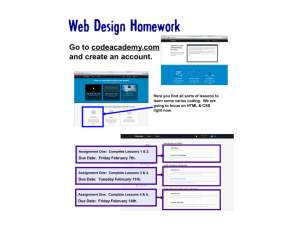
CSS Demo – Step 1
Step 1
‒ Download “startPage.html”
from
http://comminfo.rutgers.edu/~aspoerri/Teaching/DMPOnline/Lectures/Lec3/Steps
‒ Save “startPage” as “page1.html” in folder “week3”
‒ Create nested div structure
pageContent,
header, navi, content, footer
‒ Assign id name to div
Digital Media Production
© Anselm Spoerri
CSS Demo – Step 2
Step 2
‒ Create Internal CSS Style Sheet
<style type="text/css">
‒ Create CSS Rule for id="pageContent"
font-family: Verdana, Geneva, sans-serif;
font-size: 12px;
margin-top: 10px;
margin-left: 50px;
width: 500px;
‒ Create CSS Rule for class="blueText"
color:#009;
Digital Media Production
© Anselm Spoerri
CSS Demo – Step 3
Step 3
‒ Create CSS Rule for id="header"
font-size: 9px;
border-bottom-width: thin;
border-bottom-style: solid;
border-bottom-color: #333;
‒ Create CSS Rule for id="navi"
font-size: 14px;
background-color: #E1E3F7;
padding: 5px;
margin-top: 5px;
Digital Media Production
© Anselm Spoerri
CSS Demo – Step 4
Step 4
‒ Create CSS Rule for id="content"
font-size: 12px;
‒ Apply class="blueText"
<p> tag inside div with id="content"
‒ Create CSS Rule for id="footer"
font-size: 10px;
border-top-width: thin;
border-top-style: solid;
border-top-color: #666;
Digital Media Production
© Anselm Spoerri
CSS – Navigation Bar using Lists and CSS
Navigation = Lists of Links
example
<ul>
<li><a href="home.html">Home</a></li>
<li class="here"><a href=“features.html">Features</a></li>
</ul>
CSS property - display: block; and
Hyperlink States:
Digital Media Production
float: left;
and
clear: both;
a:link | a:visited | a:focus | a:hover | a:active
© Anselm Spoerri
CSS – Navigation Bar using Lists and CSS
(cont.)
Remove Bullets, Eliminate Padding and Margins
#navi ul {
list-style-type: none;
padding: 0px;
margin: 0px;
overflow: hidden; }
Display Link as Block (area of link clickable) and Constrain Width
#navi a {
display: block;
width: 100px; }
Horizontal Navigation
Use floated <li> method for uniform look
#navi li { float: left; }
You are Here Indicator
#navi li.here a { text & background properties }
and want CSS rules for different states of hyperlink
Digital Media Production
© Anselm Spoerri
CSS – Navigation Bar and States of Link Element
Selecting Link Element based on their State
Navigation Structure
Since a link can be in more than one state at a time,
it is important to define rules in following order:
1.
a:link
2.
a:visited
3.
a:focus
4.
a:hover
5.
a:active
LVFHA
a:link, a:visited { color: #FFF; }
a:focus, a:hover, a:active { color: #000; }
#navi a:link, #navi a:visited { color: #FFF; }
#navi a:focus, #navi a:hover, #navi a:active { color: #000; }
Digital Media Production
© Anselm Spoerri
Testing & Debugging Web Pages
•
Before looking for a big problem, check common little problems :)
•
Work incrementally
•
Use process of elimination
(use comments to make code active / inactive).
•
Be careful about
•
In CSS, not sure if the problem is with the property or the selector,
use a very simple declaration (color: red).
Digital Media Production
typos.
© Anselm Spoerri
Check Easy Stuff First - General
•
Refresh browser so that latest file is shown
•
Upload actual file and refresh browser so that latest file is shown
•
Upload file in the correct location
•
Make sure you save file
•
Upload any related files: CSS, images, SWF etc.
•
Make sure
•
Test in multiple browsers
•
Test on different computer than the one used to create the files
spelling of URL = spelling of filename.
Digital Media Production
© Anselm Spoerri
Check Easy Stuff First – HTML & XHTML
HTML
•
Make sure you used correct spelling of tags
•
Be careful about nesting and make sure you have closing tags
•
Use HTML Transitional
XHTML
•
Make sure all attribute value enclosed in straight, not curly, quotes
•
All elements have opening and closing tags
(always put space before / for “ />” closing tag).
• XHTML is case-sensitive.
•
Include # when specifying hexadecimal colors.
Digital Media Production
© Anselm Spoerri
Check Easy Stuff First – CSS
•
Use colon (:) to separate your properties from value (color: red;).
•
Complete each property-value pair with semicolon (;)
•
No spaces between number and their units (16px).
•
Close brackets.
•
Don’t quote values.
•
Use accepted value.
•
Don’t forget closing < /style> tag.
•
Make sure linked (X)HTML document to the proper CSS file(s).
•
Watch the spaces and punctuation between selectors.
Digital Media Production
© Anselm Spoerri
Check Easy Stuff First – Testing Your Page
1. Validate (X)HTML and CSS.
2. Open in Browser
3. Formatting correct?
4. Hyperlinks work & correct?
5. CSS file referenced properly?
6. All images appear?
If not, check the easy stuff first, especially spelling of filenames
and don’t use spaces in filenames and saved as GIF or JPEG.
7. Upload files to server (and set permissions if needed).
8. View pages in different browsers.
9. Still Stuck check for typos and check easy stuff first :)
Digital Media Production
© Anselm Spoerri