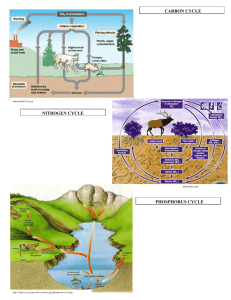
Worksheet All Nutrient Cycles in One Key
advertisement
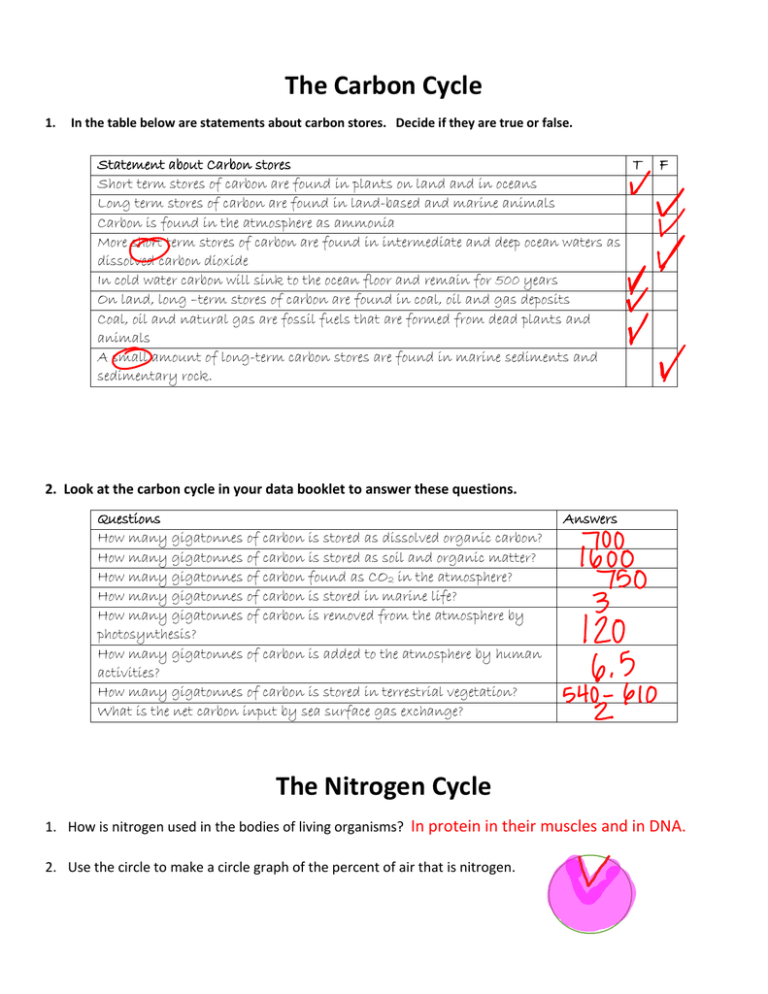
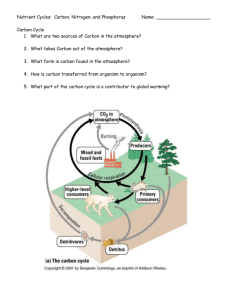
The Carbon Cycle 1. In the table below are statements about carbon stores. Decide if they are true or false. Statement about Carbon stores T Short term stores of carbon are found in plants on land and in oceans Long term stores of carbon are found in land-based and marine animals Carbon is found in the atmosphere as ammonia More short term stores of carbon are found in intermediate and deep ocean waters as dissolved carbon dioxide In cold water carbon will sink to the ocean floor and remain for 500 years On land, long –term stores of carbon are found in coal, oil and gas deposits Coal, oil and natural gas are fossil fuels that are formed from dead plants and animals A small amount of long-term carbon stores are found in marine sediments and sedimentary rock. F 2. Look at the carbon cycle in your data booklet to answer these questions. Questions How many gigatonnes of carbon is stored as dissolved organic carbon? How many gigatonnes of carbon is stored as soil and organic matter? How many gigatonnes of carbon found as CO2 in the atmosphere? How many gigatonnes of carbon is stored in marine life? How many gigatonnes of carbon is removed from the atmosphere by photosynthesis? How many gigatonnes of carbon is added to the atmosphere by human activities? How many gigatonnes of carbon is stored in terrestrial vegetation? What is the net carbon input by sea surface gas exchange? Answers The Nitrogen Cycle 1. How is nitrogen used in the bodies of living organisms? In protein in their muscles and in DNA. 2. Use the circle to make a circle graph of the percent of air that is nitrogen. B. Use the diagram in your data booklet to answer the following questions. 1. Where is most of the nitrogen (N2) on earth found? 2. What is the process that takes nitrogen gas (N2) and converts it into NH4+? 3. Name the process that converts NH4+ into NO2-? 4. What is the form of nitrogen that is taken up by plants? 5. What kinds of bacteria convert nitrogen gas (N2) into NH4+? 6. How does nitrogen get into animals? 7. How does NH4+ and NO2- become dissolved in lakes and rivers? ________________ _atmosphere___ _nitrogen-______ _fixation________ __Nitrification___ __NO3-__________ Nitrogen fixing bacteria _Animals eat plants Leaching and run off Acid precipitation___ How is nitrogen gas converted directly to NO3-? 9. What kinds of bacteria convert NH4+ into NO2-? 10. Name the process that returns NO3- to N2 in the atmosphere. 11. How do humans add to the amount of NH4+ and NO3- in the soil? 12. What kinds of bacteria convert NO3- to N2 in the atmosphere? 13. Which processes add NH3, NO2, NO into the atmosphere? 8. Atmospheric fixation (lightning) Nitrifying bacteria Denitrification___ fertilizer application Denitrifying bacteria Nitrogen oxides _ _from industry___ _decomposers__ (bacteria and fungi) 14. What kinds of organisms return NH4+ into the soil after an animal dies? Phosphorus Cycle 1. 3. How is phosphorus stored? In phosphorus rock and sediment What is weathering and what does it do to phosphorus? Weathering is the breaking down of rock. It releases phosphate into the soil. 4. Look at the Phosphorus Cycle in your Data Booklet and answer the questions in the table below. Questions How many megatonnes of phosphorus are stored in terrestrial organisms? How many megatonnes of phosphorus are found as mineable phosphate rock? How do humans contribute to the phosphate cycle? How many megatonnes of phosphorus are stored as shallow ocean sediments? What kind of bacteria contribute to phosphate in the soil? Answers What is the form of phosphate found in water?