Study Guide Key Honors
advertisement

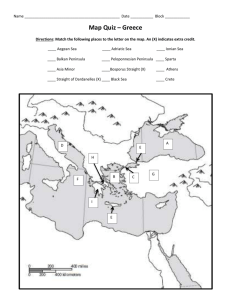
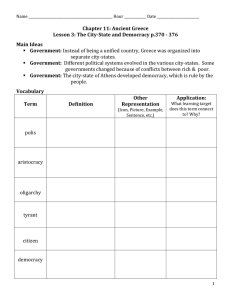
28 January 2016 EQ –What do I know about Greece? • Bellringer – Go over Study Guide • Group challenge – Kahoot • HW – Study for tomorrow’s test. • Study guide, note packet, 8.2 questions Chapter 8 Study Guide Key 7th Grade World History Vocabulary • Aristocrat: Rich landowners in Greece • Dark Age: Nothing was developed; disaster and raids; warfare and disorder; nothing got done during this time. No history • Tyrant: A leader who held power through the use of force. • Polis: The Greek word for a city-state • Classical Age an age marked by great achievements; architecture, inventions, basically everything is stable (government) so people can work on improving society • Citizens: People who had the right to participate in government Democracy • Type of government in which people rule themselves. • Cleisthenes created the first democracy • Government is based on the votes of its free citizens • People were encouraged to speak • “Rule by Many” Oligarchy • A government in which only a few people have power • Rich land owners or aristocrats took power • Common people had little say • “Rule by Few” Tyranny: • When a leader gains power (and holds it) through the use of force • Ancient Tyrants were normally good rulers • Tyrants were able to stay in power because they had strong armies and people supported them. Cleisthenes • Father of Democracy • Developed and created the first democracy. • DID NOT want aristocrats to run the government. Pericles • A leader in Athens during the time of democracy. • Wanted people to participate in the government – and created paying jobs for this (pay for jury duty and some elected officials) • Believed that Athens’ government was superior to other city-states’. Draco • An aristocrat who created very harsh laws after the common Athenians attempted to overthrow the oligarchy (small crimes were punishable by death) Solon • An aristocrat – power in 590s BCE • Reduces the strict laws of Draco to appease the common people of Athens. • Under his laws, all free men become citizens. This to help give some power to the common people of Athens. Peisistratus • The first tyrant of Athens. • Came riding into Athens with “Athena” in 546 BCE. • He was an aristocrat – and the woman probably just a very tall lady from a near-by city-state. Claims to be under her protection – and becomes first tyrant. • He gives loans to farmers/reduces taxes and under him the economy of Athens flourishes. He brings peace and prosperity. • However, when he dies his son Hippias takes over. He follows in his father’s footsteps until his brother is murdered. He then takes out his revenge on everyone – seeing what we consider a tyrant today – very harsh rule. He is eventually overthrown by the aristocrats. Greek’s geography (landforms, climate, etc.) and negatives. (min. 3 each) • • • • • Mountains – Positive & Negative Unpredictable rain fall – Negative No major river – Negative Mild Temperatures - Positive Many peninsulas & Islands – Positive & Negative Minoans • Lived on the Island of Crete • They were excellent ship builders. Lived on the sea basically big in trading; • Destroyed by a volcano and tsunami wave that destroyed the civilization. • Weren’t considered Greek because they didn’t speak it. Mycenaean • Considered the first Greeks • Attacked others and built fortresses around Greece. • They took over Crete when Minoans declined. • Mycenaean society began to fall apart in the 1200’s BC when invaders from Europe swept Greece. Earthquakes also destroyed many cities and Greece slid into the Dark Age. How was the Athenian government ruled prior to democracy? There are three ways – please explain each with as much detail as possible noting key figures when appropriate. Monarchy should be mentioned as the very first. Oligarchy & Tyranny should be fully explained here. Key figures such as Draco, Pericles, Cleisthenes, Solon & Peisistratus should be discussed. How was the form of democracy in ancient Greece different from our current democratic government? • • • • Representative vs. Direct People able to vote – women – foreigners – military service Way in which leaders were elected – vote vs. lottery Levels of government – 1 vs. 3 (due to size)