Cosi_Background and Context
advertisement

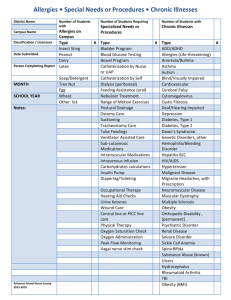
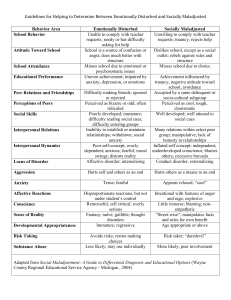
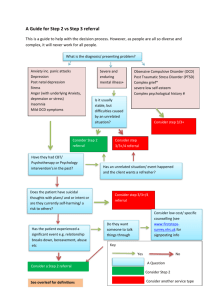
There is the world beyond the stage… and the world that materialises upon it. Così is a play written by Louis Nowra and is set in Melbourne in the early 1970s. Melbourne – 1971 (slide 3) FLINDERS STREET ST KILDA ERROL STREET Anti-Vietnam War Protests (slide 5) • America declared open Involvement in the War in 1964 • In 1965 American men were drafted into the Army. This increased from 3,000 to 33,000 a month. People began to protest by ripping up or burning draft papers. • The world was convinced that America would ‘win’ the war quickly, but when casualty numbers rose, so too did the opposition to the war. • Anti-war sentiment began to gain further support with the Hippy slogan “Make Love Not War” At 18 you were eligible for conscription. You had to be 21 at that time to vote. Australia joined America’s War • This was the first war to be broadcast on television, and the world could witness the horror of warfare, napalm and the execution of civilians including the elderly and children • Many believed that the Americans had no right to be in Vietnam, and by the same token, neither did Australia. Women’s Rights Movements (slide 9) • Women were paid less money to do the same job as a man • In the 1960s women were paid only 59% of what a man was paid • Women rallied against the restrictions and rules that had been placed upon them for years, with many burning bras and refusing to shave body hair, as they felt that these things were symbols of the male repression of females. Psychiatric Institutions/Hospitals for the Insane/Asylums (Slide 10) • Psychiatric institutions were first established in Australia in the mid 1800s. • Many patients were institutionalised for life. • They experienced a variety of illnesses including post-natal depression, schizophrenia, epilepsy, bipolar disorder and dementia. Treatment of the mentally ill • Many people were placed in asylums because there were not effective treatments for mental disorders or illnesses available. • Asylums were generally not pleasant places as they were often more like prisons than hospitals. Cosi is based on the Mont Park Asylum here in Melbourne which closed in the late 1990s. Mental Illnesses in the play (slide 12) • • • • • The next five slides will give a brief description of the following mental illnesses: Manic depression Pyromania Obsessive-compulsive disorder Drug addiction Catatonia Manic depression (Bipolar disorder) A condition in which people experience abnormally elevated (manic) and abnormally depressed states for periods of time in a way that interferes with functioning. • Manic episode = a distinct period of an elevated (extremely happy) mood. People commonly experience an increase in energy and a decreased need for sleep. Attention span is low, judgment may become impaired, and sufferers may go on spending sprees or engage in behaviour that is quite abnormal for them. People may feel out of control or unstoppable, or as if they have been "chosen" and are "on a special mission" or have other delusional ideas. • Depressive episode = persistent feelings of sadness, anxiety, guilt, anger, isolation, or hopelessness, disturbances in sleep and appetite and many others. Pyromania • An impulse control disorder. • An impulse to deliberately start fires to relieve tension or for gratification or relief. Obsessive-compulsive disorder • An anxiety disorder characterised by obsessive thoughts and compulsive actions. • Obsession: Unwanted, intrusive thoughts that cause fear, anxiety, worry and uneasiness. • Compulsion: A repeated behaviour that is engaged in to relieve the anxiety caused by the obsessions. For example: A person has obsessions about germs so repeatedly washes their hands to relieve the anxiety associated with germs. Drug addiction (Substance abuse/dependence) • The overindulgence in and dependence on a drug or other chemical. • Leads to effects that are detrimental to the individual's physical and mental health, or the welfare of others Treatments for mental illness (slide 17) Electroshock therapy (electroconvulsive therapy): Patients are given muscle relaxants and anaesthetic. Electrodes are connected to the temples and an electric current is shot through the brain, causing a seizure. This is only used for severe cases of depression where other medications and treatments have not worked. In the timeframe of Cosi, this therapy was very painful, as patients were not always given anaesthetic and higher levels of electricity were used. Treatments for mental illnesses continued... • Lobotomies: an operation in which the connections between the frontal lobes and rest of the brain are severed, causing ‘mental dullness’ – often a lowering of inhibitions, lack of cognitive processing, and sometimes even an inability to function independently. • Lobotomies were used to treat many different types of mental illnesses, including anxiety, depression and schizophrenia. The procedure was also performed on people who were considered extremely emotional, difficult to handle or simply "moody." Treatments for mental illnesses continued... • Lithium salts: Used medically as a mood stabilising drug. Particularly for disorders such as bipolar disorder, mania and depression. Australian psychiatrist John Cade first used them in treating mania in institutionalised patients in 1949. This opened the door for other medications to be developed to treat mental illness. • In Così, the character of Zac is addicted to lithium. The style of Così The style of Così includes characteristics of the following types of play: 1.Black humour 2.Farce Style: Black humour (slide 21) • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=neCY4hh1wJg Style: Black humour Examples: • South Park • Family Guy • Robot Chicken • Futurama • Monty Python Style: Farce (Slide 23) • Unlikely, extravagant, and improbable situations, disguise and mistaken identity and verbal humour of varying degrees of sophistication. • A fast-paced plot whose speed usually increases, culminating in an ending which often involves an elaborate chase scene. • Physical humour and the use of deliberate absurdity or nonsense. • Many farces move at a frantic pace toward the climax, in which the initial problem is resolved one way or another, often through a twist of the plot. • Generally, there is a happy ending. A play is a performance! Not just a text to be read. (slide 24) • Nowra intended this text to be seen by an audience, not to be read like a novel. • Unlike a novel, meaning is created in a different way in a play. Read the passage on the next slide from a novel. In groups of 3, you must attempt to ‘perform’ this scene, and maintain and generate the same feeling and meaning produced by the original text. Remember to consider: - Tone of voice - Dialogue - Volume - Positioning on stage - Height - Movement/gesture These elements will influence the way the audience will perceive/understand your scene, characters, and overall message. As the teacher entered the room, the atmosphere suddenly changed. Every head turned towards the door; Mr. Smith was the most feared teacher in the school. Now watch part of the trailer for Inside Out