Course 3 Chapter 6 Lesson5
advertisement

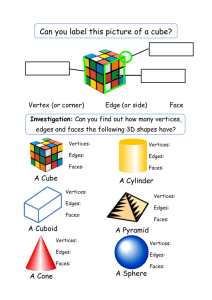
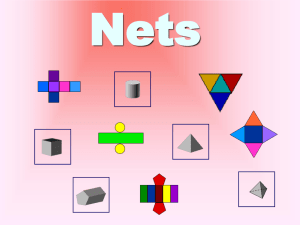
Lesson 1.8 – Space Geometry Homework: Lesson 1.8/1-27 Chapter 1 Test Friday 10/18 Space Geometry • Learn to draw three-dimensional figures. • Identify the parts of three-dimensional figures. • Visualize and identify nets of threedimensional figures. Vertex Edge Face • Three-dimensional figures have faces, edges, and vertices. • A face is a polygon or circle • an edge is a segment, where two faces meet • a vertex is a point, where three or more edges meet Prisms • A prism is – a 3D solid – with two congruent polygon bases • that lie in parallel planes – Lateral faces are rectangles (faces connecting the bases) • The bases can be any polygon shape • The name of the prism is based on the name of the bases. – the prism shown is a triangular prism • The bases are triangles and the lateral faces are rectangles Vertices (points) 6 Edges (lines) 9 Faces (planes) The base has 3 sides. 5 The base has 5 sides. Vertices (points) 10 Edges (lines) 15 Faces (planes) 7 By D. Fisher Pyramid • A pyramid is – – – – a three-dimensional solid with one polygonal base lateral sides are triangles the main vertex is where the lateral sides meet • Names of pyramids depending on the shape off the base • This is a rectangular pyramid. The base has 4 sides. Vertices (points) 5 Edges (lines) 8 Faces (planes) 5 The base has 6 sides. Vertices (points) 7 Edges (lines) 12 Faces (planes) 7 Cylinder • A cylinder is a 3D solid • 2 bases are congruent circles. – The bases are congruent, parallel circles • The smooth lateral face is a rectangle H r Cone • A cone has one circular base • The smooth lateral face is part of a circle, less than a semicircle, called a sector • The cone has one vertex, at the top H r Sphere • Sphere is the set of all points in space a radius distance from the center of the sphere. • A mathematical word for “ball.” • A sphere has a radius and diameter, just like a circle does. • The size of the sphere is measured by its radius r Sketching 3D Objects With your isometric dot paper, sketch the drawing below. Make your box 3 units wide, 2 units high, and 5 units long. After you have sketched the box, try other figures like a cube or pyramid. Example 1 Try This: Use isometric dot paper to sketch a rectangular box that is 4 units long, 2 units deep, and 3 units tall. • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • Example 1 Step 1: Lightly draw the edges of the bottom face. It will look like a parallelogram. 2 units by 4 units • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • Example 1 Continued Step 2: Lightly draw the vertical line segments from the vertices of the base. 3 units high • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • Example 1 Continued Step 3: Lightly draw the top face by connecting the vertical lines to form a parallelogram. 2 units by 4 units • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • Example 1 Continued Step 4: Darken the lines. Use solid lines for the edges that are visible and dashed lines for the edges that are hidden. • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • Drawing a Rectangular Box Use isometric dot paper to sketch a rectangular box that is 5 units long, 3 units deep, and 2 units tall. • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • Nets A net of a geometric solid is a two-dimensional (planar) figure that can be folded into a geometric solid. Here are a few examples of nets of cubes: However, not every figure of six squares can be folded into a cube. Here are some figures that are not nets of cubes: