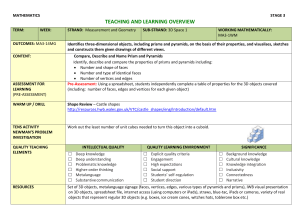
Two and Three Dimensional Figures

Advanced Geometry
Inductive Reasoning
Lesson 3
Two- and Three-
Dimensional Figures
Examples
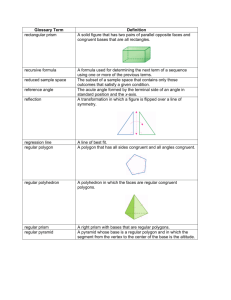
Polygon
NO HOLES
NO CURVES
SIDES
CANNOT
OVERLAP
Named by: all vertices written in consecutive order
Convex extend the sides all extensions lie outside the figure
Concave
“caves in” extend the sides any extension crosses inside the figure
# of sides and angles
7
8
9
10 n
5
6
3
4
Names of Polygons
Name of Polygon triangle quadrilateral pentagon hexagon heptagon octagon nonagon decagon n - gon
Regular Polygon
convex polygon all the sides are congruent and all angles are congruent
Examples: Name each polygon by its number of sides.
Then classify it as convex or concave and regular or irregular.
Pentagon convex regular
Perimeter and Area of a Rectangle
Perimeter – the sum of the lengths of the sides of a polygon
Area – the number of square units needed to cover a surface
ADD ALL SIDES
A
lw
Circumference and Area of a Circle
Circumference – the distance around a circle
C
2
r A
Area
r 2
Example:
Mr. Smith has a circular fence that encloses an area with a diameter of 12 feet. Using the same fence, he wants to create a square fence. What is the maximum side length of the square?
Example:
Find the perimeter of a square with an area of 30 square centimeters.
Example:
Find the circumference of a circle with an area of 36
square units.
Example:
Find the length of each side of the polygon below if its perimeter is 20 units.
Polyhedron
Definition: a solid with all flat surfaces that enclose a single region of space
•All flat surfaces are called faces.
•The line segments where the faces intersect are edges.
•The points where the edges intersect are
vertices.
Prisms
The two bases are parallel AND congruent.
Named by: the shape of the bases
Triangular Prism Rectangular Prism Pentagonal
Prism
A regular prism has bases that are regular polygons.
Pyramids
one base
Named for: the base
Triangular
Pyramid
Rectangular
Pyramid
Hexagonal
Pyramid
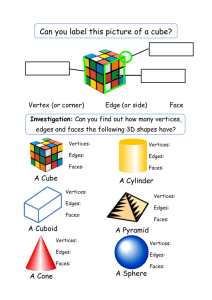
Examples : Identify each solid. Name the bases, faces, edges, and vertices.
This picture is on page 62 in your textbook.
Bases –
Faces –
Edges –
Vertices –
Examples : Identify each solid. Name the bases, faces, edges, and vertices.
This picture is on page 61 in your textbook.
Bases –
Faces –
Edges –
Vertices –
Cylinders Cones
The two bases are congruent, parallel circles.
one circular base
Spheres
NOT polyhedra (polyhedrons)
Examples : Identify each solid. Name the bases, faces, edges, and vertices.
This picture is on page 62 in your textbook.
Bases –
Faces –
Edges –
Vertices –
Examples : Identify each solid. Name the bases, faces, edges, and vertices.
This picture is on page 61 in your textbook.
Bases –
Faces –
Edges –
Vertices –
Height vs. Slant Height
Surface Area and Volume
P
Perimeter of thebase
B
area of the Base l
slant height
Prisms
SA
Ph
2 B
V
Bh
Pyramids
SA
1
2
Pl
B
1
V Bh
3
Surface Area and Volume
Cylinders
SA
2
rh
2
r 2
2 V r h
Cones
SA
rl
r 2
V
1
3
2 r h
Examples: Find the surface area and volume of the square prism.
Examples: Find the surface area and volume of the square pyramid.
This picture is on page 62 in your textbook.
Examples: Find the surface area and volume of the square pyramid.