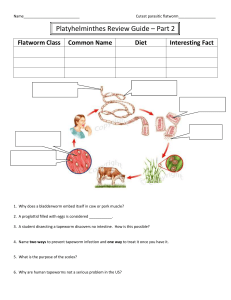
PLATYHELMINTHES LESSON Platyhelminthes (flat worms) Many
advertisement

PLATYHELMINTHES LESSON Platyhelminthes (flat worms) - - - - - Many live in symbiotic relationships as parasites Bilateral body symmetry Mesoderm- a middle layer of cells between the ectoderm and endoderm o This is the first organism that we see this o It gives rise to muscle tissue o These are the first organisms that can actively move using muscles Digestion o only one opening (like Cnidarians) o pharynx- a long tube that extends from the body to capture and tear apart food o undigested food passes out through the mouth Central Nervous System o mass of nerve cells (brain) o ladder-like nerve cord system o “eyes”- nerve bundles that detect light Excretory System o small pores running along sides o flagella that beat to create a current to remove waste called a flame bulb because it looks like it flickers Still no respiratory or circulatory system, so they must be flat so that all cells aren’t far from water to exchange gases with the environment Common Platyhelminthes organisms o tapeworms o marine flatworms often called planarians Name: Platyhelminthes Activity Station 1: Planaria 1. View the flatworm under the microscope under the lowest magnification. Draw the flatworm and label the following parts: eye spots and auricles. 2. Read the article and answer the following questions: a. Is this a parasitic or nonparasitic flatworm? b. What does it primarily feed on? c. Describe the two types of reproduction the planarian uses: Station 2: Schistosoma mansoni 1. View the flatworm under the microscope. Draw what you see. 2. Summarize the life cycle of this organism using simple sentences and bullet points. Station 3: Fasciola hepatica 1. View the flatworm under the microscope. Draw what you see. 2. How do humans become infected with this parasite? 3. What types of animals do these parasites usually inhabit? Station 4: Penis Fencing in Marine Flatworms Read the article and answer the following questions: 1. Explain why the worms are fighting for the right to act as the male. Name: Platyhelminthes Activity Station 1: Planaria 1. View the flatworm under the microscope under the lowest magnification. Draw the flatworm and label the following parts: eye spots and auricles. 2. Read the article and answer the following questions: a. Is this a parasitic or nonparasitic flatworm? b. What does it primarily feed on? c. Describe the two types of reproduction the planarian uses: Station 2: Schistosoma mansoni 1. View the flatworm under the microscope. Draw what you see. 2. Summarize the life cycle of this organism using simple sentences and bullet points. Station 3: Fasciola hepatica 1. View the flatworm under the microscope. Draw what you see. 2. How do humans become infected with this parasite? 3. What types of animals do these parasites usually inhabit? Station 4: Penis Fencing in Marine Flatworms Read the article and answer the following questions: 1. Explain why the worms are fighting for the right to act as the male.