PPT
advertisement
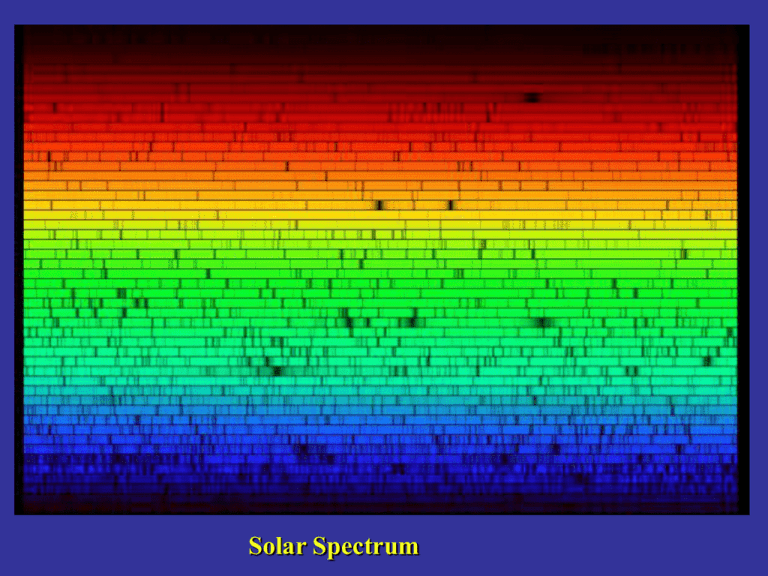
Solar Spectrum Bit of Administration …. • c = 3 x 108 m/sec = 3 x 105 km/sec • Reading – BSNV pp. 153 - 168 The Physics of Light • Doppler Shift The Physics of Light • Doppler Shift • Source moving toward observer or observer moving toward source Shorter Wavelength Higher Frequency Blueshift • Source moving away from observer or observer moving away from source Longer Wavelength Lower Frequency Redshift The Physics of Light • Doppler Shift • Source across (perpendicular to) observer’s line of sight Same Wavelength as emitted Same Frequency as emitted No Shift Doppler Shift only provides measure of radial velocity, or speed along the line of sight The Physics of Light • Doppler Shift rest vradial c vrad = radial velocity of light source or observer (+=> away from each other) = change (shift) in wavelength = observed - rest rest = rest wavelength c = 3 x 105 km/sec ConcepTest! When Mars is in the middle of its retrograde loop, you expect it to show A. B. C. D. A large redshift No Doppler shift A large blue shift Depends on where it is in its orbit The Physics of Light • Light as a Particle = Photons • Photon - A Discrete Unit of Light Energy • Planck’s Law E photon h c h h = Planck’s Constant = 6.626 x 10-34 joule sec = wavelength in m, c = 3 x108 m/sec The Physics of Light • Light as a Particle = Photons • Planck’s Law Small wavelength Large frequency Large energy Large wavelength Small frequency Small energy The Physics of Light • Spectroscopy and Atomic Physics • Types of Spectra Continuous - No spectral lines Absorption - Dark lines superimposed on continuous spectrum Emission - Isolated bright lines The Physics of Light • Spectroscopy and Atomic Physics • Kirchoff’s Laws 1. An opaque object emits a continuous spectrum. 2. An opaque object viewed through a cooler gas will produce an absorption spectrum. 3. A gas viewed against an empty background produces an emission spectrum The Physics of Light • Spectroscopy and Atomic Physics • Kirchoff’s Laws The Physics of Light • Spectroscopy • Temperature - a measure of the speeds of particles Room Temperature 300 oK The Physics of Light • Spectroscopy • Thermal Radiation - Any opaque object that has a temperature above 0 oK emits light The Physics of Light • Spectroscopy • Thermal Radiation The Physics of Light • Spectroscopy • Thermal Radiation The Physics of Light • Spectroscopy • Thermal Radiation • Wien Law max max 3x10 T max in nm T in oK 6 • Spectroscopy The Physics of Light • Thermal Radiation • Wien Law • Stefan-Boltzmann Law Eflux energy emitted from square meter in one second E flux T 4 Stefan-Boltzmann constant The Physics of Light • Spectroscopy and Atomic Physics • Kirchoff’s Laws The Physics of Light • Spectroscopy and Atomic Physics • Quantum Mechanics - Electron can only be in certain specific orbits <=> can only have certain specific energies e Quantum Numbers Hydrogen Atom The Physics of Light • Spectroscopy and Atomic Physics • Quantum Mechanics - Electron energy changes can only have certain values corresponding to energy changes between orbits ==> only certain energies of photons can be absorbed or emitted The Physics of Light • Spectroscopy and Atomic Physics White light Photons/sec • Shine “white” light onto hydrogen atom Wavelength The Physics of Light • Spectroscopy and Atomic Physics Photons/sec • Only photons with energy equal to energy difference between orbits 2 and 3 are absorbed. This energy corresponds to a wavelength of 660 nm. 660 nm Wavelength The Physics of Light • Spectroscopy and Atomic Physics Photons/sec • Photons with energy equal to energy difference between orbits 2 and 3 are emitted. These photons are emitted in all directions. 660 nm Wavelength The Physics of Light • Spectroscopy and Atomic Physics • Kirchoff’s Laws The Physics of Light • Spectroscopy and Atomic Physics • Energy Level Diagrams Ground State