Document
advertisement

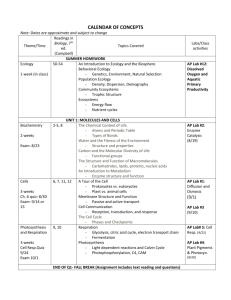
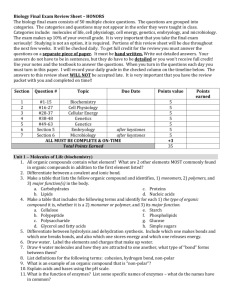
Cells Photosynthesis Respiration Cell Division Molecular Genetics Evolution & Classification Cells Photosynthesis Respiration Cell Division Molecular Genetics Evolution & Classification $100 $100 $100 $100 $100 $100 $200 $200 $200 $200 $200 $200 $300 $300 $300 $300 $300 $300 $400 $400 $400 $400 $400 $400 $500 $500 $500 $500 $500 $500 Cells Storage, breakdown of waste products, hydrolysis of macromolecules, enlargement of vacuole a major mechanism of plant growth $100 Cells What is Function of the central vacuole Back $100 Cells What is DNA that is concentrated around the nucleoid with no membrane separating it. This has a true nucleus bound by a nuclear envelope $200 Cells What is Prokaryotic & eukaryotic Back $200 Cells Used to take cells apart and separate organelles by size and density? $300 Cells What is Ultracentrifuges Back $300 Cells What allows for connection unify in cells and allows cytosol to pass through? $400 Cells What is Connects chemical environment of adjacent cells. Back $400 Cells Food vacuole fuels with plasma membrane. An active hydrolytic enzyme with digestive enzymes in it binds with the lysosome. The hydrolytic enzymes break down the food. $500 Cells What is Phagocytosis Back $500 Photosynthesis 6CO2 + 12H20 + light energy C6H12O6 + 6O2 + 6H20 $100 Photosynthesis What is Chemical equation for photosynthesis Back $100 Photosynthesis Most important to life, band from 380 nm-750 nm wavelength. Can be detected by the human eye $200 Photosynthesis What is Visible light Back $200 Photosynthesis Uses Calvin cycle with an alternative mode of carbon fixation. Has photosynthesis cells, the bundle-sheath and mesophyll. First step carried out by enzyme PEP carboxylase. $300 Photosynthesis What is C4 plant Back $300 Photosynthesis 3-phosphoglycerate receives a phosphate group from ATP becoming 3bisphosphoglycerate electrons from NADPH reduces to G3P. $400 Photosynthesis What is Output is G3P Back $400 Photosynthesis Light enters & strikes pigments, excites P680 to high energy level. Electrons are captured by primary acceptor. Water is split into a hydrogen and an oxygen atom. Electrons are sent down the ETC with APT begin lost. Electrons excite P700 and light enters electrons captured by primary acceptor. Sent down ETC. NADP reductase transfer electrons from FAD to NADP+ 2 electrons required to reduce NADPH $500 Photosynthesis What is Noncyclic Electron flow Back $500 Respiration Process lose electrons oxidation and the other gains electrons reactions $100 Respiration What is Redox reactions Back $100 Respiration Pyruvate is broken down, CO2 is loss NAD+ reduced to NAPH, Coenzyme A is added. What is being made $200 Respiration What is Acetyl CoA Back $200 Respiration The precess glycolysis, the cyturic acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation ETC and chemiosmosis are located where? $300 Respiration What is In the Cytosol and mitochondrion Back $300 Respiration Energy is stored in form of hydrogen ion gradient across a membrane, used to drive the synthesis of ATP $400 Respiration What is Chemiosmosis Back $400 Respiration These two things inhibit and stimulate phosphofructokinase in Glycolysis $500 Respiration What is APT & Citrate inhibits Back $500 Cell Division Haploid cells have this many chromosomes while diploid cells have this many? $100 Cell Division What is N=23 Back 2n=46 $100 Cell Division Caused by independent assortment of chromosomes (meiosis), gametes differ in their combinations of chromosomes merited from parents. This process occurs in meiosis prophase I? $200 Cell Division What is Crossing over Back $200 Cell Division Has complete set of haploid chromosomes composed of 2 sister chromatids. Cytokinesis occurs here, forming haploid daughter cells. Sometimes chromosomes condense & nuclear envelope reform. $300 Cell Division What is Telophase I in meiosis I Back $300 Cell Division This accounts for 90% of cell division. The cell at this stage grows and copies chromosomes. G1, G2 and S phases all occur in this cycle of mitosis $400 Cell Division What is Interphase Back $400 Cell Division Duplicating DNA and getting proteins in the interphase $500 Cell Division What is A cell prepares for cell division Back $500 Molecular Genetics These bonds hold the adenine, thymine, guanine and cytosine together which make up DNA $100 Molecular Genetics What is Hydrogen bonds Back $100 Molecular Genetics Two strands of parental molecule separate and each functions as template for synthesis of new complementary strand, predicted by Watson & Crick $200 Molecular Genetics What is Semiconservative model Back $200 Molecular Genetics When DNA is damaged the segment is cut out by nuclease gap is filled with nucleotides properly paired nucleotides. DNA polymerase and DNA ligase is used to repair & seal the new DNA This process is? $300 Molecular Genetics What is Nucleotide excision repair Back $300 Molecular Genetics Radio activity was used to follow protein and DNA. Bacteriophage-viruses infected bacteria. DNA functions as genetic material. Who did this experiment? $400 Molecular Genetics Who is Hershey & Chase Back $400 Molecular Genetics Can help protect organisms from cancer by limiting number of divisions. Catalyzes lengthening of telomeres in cells, restores original length compensates for shortening during DNA replication $500 Molecular Genetics What is Somatic cells Back $500 Evolution Most common technique based on decay of isotopes has a fixed rate of decay, has a half-life number of years, takes for 50% of sample of decay $100 Evolution What is Radiometric dating Back $100 Evolution Contains little O2, a lot of H2O, CH4, CO, CO2, lighting, volcanic activity, UV, radiation $200 Evolution What is Primitive Earth Back $200 Evolution These classifications contains korarchaeotes, euryarchaeotes, crenarchaeoetes, nanoarchaeotes. Which phylogeny is it? $300 Evolution What is Domain Archaea Back $300 Evolution Symbiotic relationship (+,+)m (+,0), (+,-) $400 Evolution What is Mutualism, Commensalism, Parasitism Back $400 Evolution Plate movements brought the already separated landmass together into a super continent Pangaea over millions of years, the land mass moved apart. How did this happen? $500 Evolution What is Continental drift Back $500 Double Jeopardy!!! Plant Systems Animal Systems Ecology Labs Biotechnology Things we did not cover Plant Systems Animal Systems Ecology Labs Biotechnology Things we didn’t cover $200 $200 $200 $200 $200 $200 $400 $400 $400 $400 $400 $400 $600 $600 $600 $600 $600 $600 $800 $800 $800 $800 $800 $800 $1000 $1000 $1000 $1000 $1000 $1000 Doublel Jeopardy! Plant Systems This is what allows CO2 exchange to occur between surrounding air and photosynthetic cells inside leafs. In CAM plants are closed during the day to reduce dehydration $200 Plant Systems What is Stomata Back $200 Plant Systems Long distance transport occurs through this. Movement of fluid is driven by pressure. Fluids flow through tracheids & vessels of the xylem & phloem $400 Plant Systems What is Bulk flow Back $400 Plant Systems Seeds germinate in branches of tall trees & send numerous roots to ground Snake-like roots wrap around host and objects. Host tree dies eventually due to strangulation & shearling $600 Plant Systems What is Strangling Aerial Roots Back $600 Plant Systems Germinated grain on stigma of carpel, flow down ovary into embryo sac. Sperm & egg meet makes a zygote 2n that develops into an embryo (sporophyte). Seed develops from ovule, fruit develops from ovary. The seed begin to germinate and develops into a mature sporophyte (2n) with flowers $800 Plant Systems What is Angiosperm reproduction Back $800 Plant Systems Sugar moves into tubes where it reduces water potential causes tube to take up water by osmosis. This generates positive pressure forces sap to flow along tubes, pressure relieved by removal of sugar and water $1000 Plant Systems What is Pressure flow Back $1000 Ecology Study of the interactions between organism and environment $200 Ecology What is Ecology Back $200 Ecology This contributes to global distribution of organisms movements of individual away from high population density or area of origin $400 Ecology What is Dispersal Back $400 Ecology Digger wasp use this technique to locate their nest. Fitness of organism is enhance by this. Modification of behavior based on experience. Used for location nest, hazards, food, and mates. $600 Ecology What is Spatial Learning Back $600 Ecology Starts out flat with low death rates from early to middle life and drops steeply as death rates increase in late life. Drops sharply at first with high death rates with young, flattens out when death rates decline with the individual that survive. $800 Ecology What is Curve I - III Back $800 Ecology Located in mid-latitude coastal regions, precipitation seasonal, rainy winters, long dry summers. Collected with shrubs, small trees, diversity of grasses & herbs. Native animals are browsers, deer, goats, diversity of amphibians, birds, & reptiles. Terrestrial Biomes $1000 Ecology What is Chaparral Back $1000 Animal Systems Constant internal milieu, steady state, internal balance $200 Animal Systems What is Homeostasis Back $200 Animal Systems Increased body temperature (exercising or hot environment) thermostat in hypothalamus activates cooling mechanisms, sweat glands, secrete sweat that evaporates cooling body, blood vessels dilate filling with warm blood, heat radiates from skin surface, body temperature decreases $400 Animal Systems What is Maintaining homeostasis Back $400 Animal Systems During hormonal control of digestion there are inhibitors and stimulus. What are they? $600 Animal Systems What is Inhibitor – enterogastrone Stimulus – Gastrin, secretin, Back $600 Animal Systems In small intestine this type of digestion goes from polysaccharides then breaks down pancreatic amylases – next maltose & other disaccharides. $800 Animal Systems What is Carbohydrate digestion Back $800 Animal Systems Reduces heat loss in endotherms, marine mammals & birds. Circulatory adaptation, arrangement of blood vessels $1000 Animal Systems What is Countercurrent heat exchange Back $1000 Labs Topic or theme of lab, date is included on this line $200 Labs What is Title Back $200 Labs This is the place you go to get the information on the lab & to write up the pre-lab $400 Labs What is Lab handout instructions Back $400 Labs These should ALL be included in a lab notebook write up $600 Labs What is Title, pre-lab, overview, personal account, discussion, & conclusion Back $600 Labs These are ways that Mr. Bennett could evaluate us on our labs? $800 Labs What is Lab notebook evaluation, lab report, open lab book quiz Back $800 Labs These are needed in your personal account section of your lab notebook $1000 Labs What is Description: of what you did Hypothesis: independent & dependent variable Data: tables, graphs, calculations Back $1000 Biotechnology Molecules separate nucleic acids or proteins based on size, electrical charge & physical properties $200 Biotechnology What is Gel electrophoresis Back $200 Biotechnology This is a process. Restriction enzyme cuts sugar-phosphate backbone. DNA fragment from a source is added, base pair of DNA ends, causes various combinations DNA ligase seals the deal $400 Biotechnology What is Recombinant DNA Back $400 Biotechnology Matching of genes to traits is called $600 Biotechnology What is Mapping Back $600 Biotechnology Coded material in cells that determines what that cell & its successive cell will become is $800 Biotechnology What is DNA Back $800 Biotechnology PCR can be used to identify an unknown bacterium because $1000 Biotechnology What is RNA primer is specific Back $1000 Things we didn’t cover Results of gene duplication found 10 more than one copy of same gene $200 Things we didn’t cover What is Paralogous genes Back $200 Things we didn’t cover Stranded or cylinders support young parts of plants. Thick primary walls and lack secondary walls. Provide flexible support $400 Things we didn’t cover What is Collenchyma cells Back $400 Things we didn’t cover Most commonly used vector for introducing new genes into plan cells. Integrates a segment of DNA into chromosomal DNA of host cell $600 Things we didn’t cover What is Ti plasmid Back $600 Things we didn’t cover Called descriptive science, describes natural structures to process as accurately as possible through careful obse4rvation and analysis of data $800 Things we didn’t cover What is Discovery science Back $800 Things we didn’t cover Hormone, opposes RAAS, atria of heart release ANF in response to increase blood volume to pressure, inhibits release of rennin and inhibits NaCl reabsorption of collecting ducts $1000 Things we didn’t cover What is Atrial natriuretic factor (ANF) Back $1000 Final Jeopardy!!! Final Jeopardy!!! Chromosomes are made up of this Final Jeopardy!!! What is Chromatin