Rotational Motion of an Object
advertisement

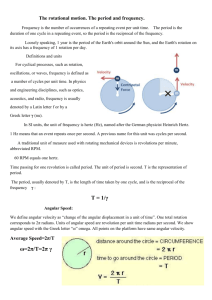
Rotational Motion of an Object Physics Matters: Chapter 7 Rotational Motion • All Spinning Objects • Axis of Rotation • The line about which everything rotates. • Speed of Rotation • Period of rotation • The time of a single complete rotation (T) • Frequency of rotation • The number of cycles completed in a given time (f = hertz) • Period = 1/Frequency or Frequency = 1/Period • T= 1/f f=1/T Spinning • Angular speed Rotational angle Time t • = s/r ( is measured in radians) • For 360 degreed, s = 2r • 3600 = 2 radians • Angular speed = 2f Torque • Tangential force being applied times the perpendicular distance from the axis of rotation • = Ftr Angular Momentum • Moment of inertia • In general, the farther away a mass is from the axis the greater its moment of inertia is. • I = kmr2 Angular Momentum (Cont.) • Momentum of inertia times angular speed • L=I • Conservation of Angular momentum • Direction of Rotation • The right hand rule Center of Gravity Center of Mass "All of science is nothing more than the refinement of everyday thinking." -- Albert Einstein Center of Gravity • Point of an object located at the average position of weight. Center of Mass • The Average position of matter Toppling • Toppling occurs when the center of gravity extends beyond the support base. Stability • Unstable – CG is lowered with displacement • Stable – work must be done to raise the CG • Neutral – displacement neither raises or lowers the CG Objects rotate around their center of gravity. Let’s try some activities!!