Thunderstorms and Severe Weather Read-Along Notes
advertisement

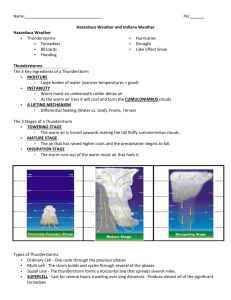
Name: __________________ Date: ______________ Earth Science Mr. Barry Doc. # _______ Class Period _____ Thunderstorms and Severe Weather Read-Along Notes Read sections 13.1 and 13.2 and answer the following questions. How Thunderstorms Form 1. What three conditions must exist for a thunderstorm to form? 2. What limits the growth of thunderstorms? 3. Look at Figure 13-1. What state has the most thunderstorms annually? Air-Mass Thunderstorms 4. Define air-mass thunderstorm: 5. When is an air mass thunderstorm most likely? Why? 6. Define sea-breeze thunderstorm: 7. Look at Figure 13-2. Explain how a sea-breeze thunderstorm forms. Draw a picture that shows the movement of the air. Frontal Thunderstorms 8. Define frontal thunderstorms: 9. How can a frontal thunderstorm form along a cold front? Name: __________________ Date: ______________ Earth Science Mr. Barry Doc. # _______ Class Period _____ 10. How can a frontal thunderstorm form along a warm front? Stages of Development 11. What are the names of the three stages of thunderstorm development? 12. Describe the first stage of formation of a thunderstorm. Draw a picture of the stage (like the one in Figure 13-3). 13. Describe the second stage of formation of a thunderstorm. Draw a picture of the stage (like the one in Figure 13-3). 14. Describe the third stage of formation of a thunderstorm. Draw a picture of the stage (like the one in Figure 13-3). Name: __________________ Date: ______________ Earth Science Mr. Barry Doc. # _______ Class Period _____ Severe Thunderstorms 15. What factors can cause some storms to be more severe than others? 16. Define supercell: 17. How long can supercell storms last? What percent of thunderstorms are considered severe? Lightning 18. How does a lightning bolt form? 19. How hot is a lightning bolt? 20. What is thunder? 21. Read Table 13-1. What do you think is the most important thing to do when thunderstorms approach? 22. What should you do if caught outdoors and there is lightning? The Fury of the Wind 23. Define downburst: 24. What is the difference between a macroburst and a microburst? Hail 25. What is hail? 26. What two characteristics are necessary for hail to form? Name: __________________ Date: ______________ Earth Science Mr. Barry Doc. # _______ Class Period _____ Floods 27. How are floods related to storms? Tornadoes 28. Define tornado: 29. Why is the air in a tornado visible? 30. What can cause a tornado to form? Describe the steps (Figure 13-8). 31. Define Fujita tornado intensity scale: 32. Use Table 13-2 to fill in the following chart. Type of Fujita Scale Percentage Path Tornado of Tornadoes Wind Speed Duration F0 and F1 F2 and F3 F4 and F5 33. When and where do most tornadoes form in the US? 34. Look at Table 13-3. Describe what you would do to protect yourself if a tornado where to come near your house.