Thunderstorm Formation ppt.
advertisement

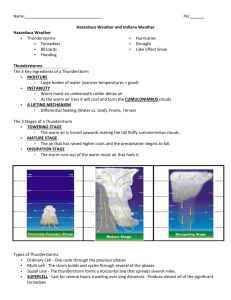
Chapter 10 Thunderstorms Mid-latitude cyclone: counter-clockwise circulation around a low-pressure center Where are thunderstorms located? Along the warm front or the cold front? Tornado over Kansas - May 2004 Thunderstorms… • Form in conjunction with MLC, but can also form on their own. • Generate lightning and thunder, wind gusts and hail • Can cover a small area (single cloud) or a large area; cluster of clouds • Have strong up and down (not spiraling counter clockwise) movement of gusty, variable winds • Forms in unstable air. Thunderstorm Scavenger Hunt 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. What are some other names/types of thunderstorms? Where are thunderstorms most common on Earth? During what time of day/season are thunderstorms most active? What three ‘ingredients’ are needed to form a thunderstorm? What is the size and duration of a thunderstorm? What are the warning signs that a thunderstorm is approaching? What is the #1 thunderstorm killer? What are “super-cells”, how big are they? What is a microburst? What are three stages of thunderstorm development? What is a mesocyclone? According to the National Weather Service (NWS), when is a severe thunderstorm watch or warning issued? Compare… Pg. 287- Air Mass thunderstorm Frontal thunderstorm Formation Size Air Mass Thunderstorms • Air near surface is warmed during the day. • Warm air rises and condenses to form cumulous clouds in the afternoon. • Scattered, isolated. • Most moisture evaporates but eventually it accumulates into taller clouds. Forms along a Cold Front 8 Or…along a Warm Front Unstable air mass 9 Orographic lifting over mountains Forms when air converges, is forced up, cools adiabatically, form clouds These tend to be brief, short-lived storms with moderately heavy downpours. 11 3 Stages of Development of a Thunderstorm Pg. 288 Stage 1 Cloud continues to grow as long as there is a supply of warm, moist air. Updraft occurs. http://www.youtube.com/watc h?v=DualOU_gBn0 13 Bergeron Process Ice crystals collect water molecules and grow larger while cloud droplets evaporate and get smaller. Stage 2 • Mature stage 15 Stage 3 16 Developing Cumulonimbus FairWeather Cumulus Well-Developed Cumulonimbus Severe Thunderstorm Development along a Cold Front 19 Roll Cloud http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QHHUfb7olQ0 ??????????? • Where in the U.S. do thunderstorms occur most frequently? • How many are occurring at any given time world-wide? Average Number of Thunderstorm Days Atmospheric Hazard Flash Floods - Number One Thunderstorm Killer Bell work 1. T or F? A mature stage thunderstorm cloud can be as high as the mesosphere. 2. Severe thunderstorms form along (cold, warm) fronts. 3. Which can have the higher wind speeds – hurricanes or tornadoes? 4. T or F? Thunderstorms have vertical air movement while tornadoes have spiral air movement. 5. Does an updraft cause a “up-dog” ? Supercell Thunderstorm Supercell: A single, very large (65,000 ft. high) massive cloud 12-30- miles in diameter, Lasts for many hours Cluster of Supercell Thunderstorms Temperature Inversion enhances formation of severe thunderstorms: dense, cold layer above prevents warm, moist air from rising. Surface air heats up, and finally erupts upward, producing an unusually large cumulus cloud Mammatus Sky Text book Questions pg. 315 1. 2. 4. 5. 6. Microburst Strong DOWNDRAFTS Beneath the thunderstorm Small 2.5 miles across Cold dense, sinking air Last 2-5 minutes Also called wind shears http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fjFTH3s6BlM