Introduction to Engineering Design, Pier Sun Ho
advertisement

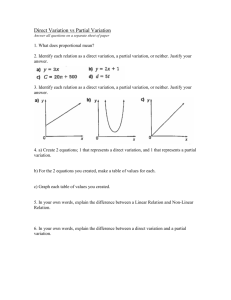
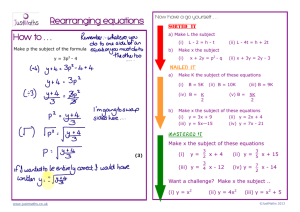
A CADEMY OF E NGINEERING S ESSION Introduction to Engineering Design Integrated Curriculum Pier Sun Ho Rob Atterbury Workshop Objectives and Expectations This workshop is intended to: • Familiarize teacher teams with the integrated curriculum model • Introduce IED and its associated integrated curriculum • Prepare participants for implementing the curriculum • Introduce the participants to a sample culminating engineering project 2 Continuum of Curriculum Integration ELA SCI MATH CTE SOC ARTS FOR LANG Single Subject BASIC Parallel (Paired) Interrelated INTERMEDIATE Conceptual ADVANCED Aug English Biographies Character traits and motivation Numbers Algebra II and functions Biology Scientific method Definitions Geometry Geometric reasoning Law and Justice Sep Oct Nov Dec Short stories Time and sequence Foreshadowing Flashback Universal themes Creative Literary devices writing Imagery, allegory, Interviews symbolism Evaluating credibility Writing persuasive compositions Solving systems of linear equations Solving and graphing quadratics Polynomial functions Cell biology Photosynthesis Cellular respiration Central dogma DNA structure and Meiosis technology Inheritance Protein synthesis Induction vs. deduction Construction of lines, angles, shapes Circles Properties of triangles Congruence Area, and surface Quadrilaterals area Polygons Sectors and segments Codes Criminal investigation Courts Courtroom testimony Ancient legal Sources of law systems Bill of Rights Early laws Amendments Exponential equations Logarithms Cloning Stem cell research Mediation Arbitration Conflict resolution Integrated Curriculum Overview Alg I World Geo Geo IED Bio/ Phys ELA World Hist 5 • Tier I – Introduction to Engineering Design – Principles of Engineering – Digital Electronics • Tier II – – – – Aerospace Engineering Biotechnical Engineering Civil Engineering and Architecture Computer Integrated Manufacturing • Tier III – Engineering Design and Development 6 Introduction to Engineering Design -IEDThe major focus of the IED course is to expose students to design process, research and analysis, teamwork, communication methods, global and human impacts, engineering standards, and technical documentation. Introduction to Engineering Design Unit 1: Introduction to Design Key Concepts: • Design Process • Technical Sketching and Drawing • Measurement and Statistics • Puzzle Cube Introduction to Engineering Design Unit 2: Design Solutions Key Concepts: • Geometric Shapes and Solids • Dimensions and Tolerances • Advanced Modeling Skills • Advanced Designs Introduction to Engineering Design Unit 3: Reverse Engineering Key Concepts: • Visual Analysis • Functional Analysis • Structural Analysis • Product Improvement by Design Introduction to Engineering Design Unit 4: Virtual Design Project Key Concepts: • Engineering Design Ethics • Design Teams Curriculum Overview There are 2 curriculum units for Introduction to Engineering Design • Semester 1: Ship Shape • Semester 2: Reverse Engineering Each unit includes: • Lesson plans for the four academic subject areas and IED • Relevant national standards alignment • Teacher resources (background info, answer keys, rubrics) • Student resources (handouts, worksheets, labs) 12 Workshop Objectives and Expectations This workshop is intended to: • Familiarize teacher teams with the integration of each subject area into the unit • Prepare participants for implementing the curriculum • • • Communicate the intention of the curriculum developers for unit enactment Discuss revisions and planning decisions unique to your site Introduce the participants to a sample culminating engineering project 13 Unit 1 Ship Shape Engineering in the Marine Environment • • • Safely and efficiently move a variety of cargoes across the world’s oceans Effectively project your nation’s economic, political, and military objectives across the seas Protect your nation’s coastline, resources, and waterborne trade • Safely explore and wisely exploit the abundant resources found in the ocean’s depths and in its ice covered areas • Provide better boats and ships for entertainment, sport, and recreational boating Unit Overview • Subunit 1 lessons introduce to ships and ship design and provide some historical context to the importance of naval architecture and marine engineering • Subunit 2 lessons introduce the basic math and science involved in naval architecture and other marine engineering fields • Subunit 3 lessons provide students with the opportunity to apply their knowledge academic knowledge to a design challenge Major Academic Subject Topics and Content • English Language Arts • • • Social Studies • • • Geography—Influence of major waterways on cultures around the world World History—World War II and the invasion of Normandy Science • • • Using figurative language, and writing short stories Technical writing Physical Science/Physics—Density, buoyancy, center of mass Biology—Adaptations in marine animals Mathematics • • Area and volume Simple quadratic equations Subunit 1: High Seas Adventure Lesson and Subject Description Page Lesson 1.1 Lure of the Sea 1-1 Sailing the Wine Dark Sea 1-17 Lost at Sea 1-39 Storming the Beach 1-59 Introduction to Engineering Design Lesson 1.2 English Language Arts Lesson 1.3 English Language Arts Lesson 1.4 World History 18 Early sailing vessels Egyptians and Phoenicians Chinese Junk Tall Ships Container Ships Recreational Boating (Cigarette Boat) Modern Military Fleet Military Transports Air Boats Subunit 1: High Seas Adventure Lesson and Subject Description Page Lesson 1.1 Lure of the Sea 1-1 Sailing the Wine Dark Sea 1-17 Lost at Sea 1-39 Storming the Beach 1-59 Introduction to Engineering Design Lesson 1.2 English Language Arts Lesson 1.3 English Language Arts Lesson 1.4 World History 28 Literature Circles (p 1-35) • Student-directed discussion groups • Each student assigned a different role/perspective during reading and discussion • Possible roles: moderator, psychologist, lexicographer, anthropologist, and many others Life of Pi • Assign roles within your group • Read Chapter 37 • Keep your literature circle role in mind • Discuss your reaction to the reading as a group Subunit 1: High Seas Adventure Lesson and Subject Description Page Lesson 1.1 Lure of the Sea 1-1 Sailing the Wine Dark Sea 1-17 Lost at Sea 1-39 Storming the Beach 1-59 Introduction to Engineering Design Lesson 1.2 English Language Arts Lesson 1.3 English Language Arts Lesson 1.4 World History 31 Setting the Stage • Europe, May 1943 • Allies begin preparations to retake the Europe WWII German Defenses of Coastal France Beach Defenses World War II Engineering Innovations • Higgins Boat • Duplex Drive (DD) Tank • Bobbin Tank • Sherman Flail Tank Subunit 2: Sink or Swim Lesson and Subject Lesson Title Page Lesson 2.1 Denser Sensor 2-1 Archimedes’ Principle 2-15 A Sinking Feeling 2-33 3D Solids 2-49 Cargo Ship Challenge 2-63 Physical Science Chemistry Lesson 2.2 Physical Science Chemistry Lesson 2.3 Biology Lesson 2.4 Geometry Lesson 2.5 Algebra Geometry 36 Float or Founder? Float or Founder? Gravitational Force AKA Weight! 39 Gravitational Force • Weight = mass • accelerationgravity • Fgrav = m • g • • Fgrav = 250 g • 9.8 Fgrav = 2450 m s2 g m s2 40 How about the Buoyant Force? 42 Archimedes’ Principle Buoyant force on the submerged object = Weight of displaced fluid 43 Fbuoyant = Weight Fbuoyant = Weight of displaced fluid = m•g = mfluid • g 44 One Last Substitution: Mass of the Fluid Fbuoyant = mfluid • g Fbuoyant = mfluid • 9.8 Fbuoyant = ( x Vsubmerged ) • 9.8 m s2 m s2 Density () of water = 1 g/cm3 45 Calculating Buoyant Force r • USS Yogurt V= V = • (3.5 cm)2 • 8.6 cm r2 h V ≈ 330 cm3 h Fbuoyant = ( • Vsubmerged) • g • Fbuoyant = ( • Vsubmerged) • 9.8 • g • cm 3 • • Fbuoyant = (1 Fbuoyant = g (1 cm 3 Fbuoyant = 3234 • m s2 Vsubmerged) • 9.8 330cm3) g m s2 • 9.8 m s2 m s2 Will She Float? • Compare the gravitational force and buoyant force acting on the ship Fgrav 2540 g m s2 Fgrav • Seaworthy! ≟ Fbuoyant ≟ 3234 < g m s2 Fbuoyant A Little Trick, Just This Once Fg ≟ Fb mobj • g ≟ • Vsub • g mobj x g ≟ • Vsub x g mobj x g ≟ x Vsub x g 259 g x g < • 330 cm3 x g The submerged volume should equal the total mass! DIY Calculations • 1/10 of this box is above water • The box has a mass of 108 grams • What is the volume of the submerged portion? • What is the volume of the total box? • What possible dimensions might the box have? 49 Subunit 3: Float Your Boat Lesson and Subject Description Page Lesson 3.1 Boats Far and Wide 3-1 Hull Design 3-13 Sea Stories 3-33 Launch Day 3-53 World Geography Lesson 3.2 Introduction to Engineering Design Lesson 3.3 English Language Arts Lesson 3.4 Introduction to Engineering Design 50 Introduction to Design Activity Expectations • • • As a group, design plans for a boat that fulfills the specifications and constraints of the challenge Build a testable model using the materials provided – draw a line at the anticipated waterline Be prepared to: 1. 2. 3. 4. Describe the challenge and constraints Give the dimensions of your boat Defend its design as buoyant Give a brief summary explaining your design decisions 2 possible challenges Speedboat Life Raft • Must have length-to-width ratio of at least 4:1. • Must have capacity for nine people (450 g). • Must have a pointed bow. • • Must have a V-shaped hull. Must have a flat-bottomed hull. • Must minimize use of materials. • Must have a minimum freeboard of 3 cm when loaded. • • Must have load capacity (and seating) for at least two passengers (100 g). Must have a maximum freeboard of 2 cm when loaded. 53 Subunit 3: Float Your Boat Lesson and Subject Description Page Lesson 3.1 Boats Far and Wide 3-1 Hull Design 3-13 Sea Stories 3-33 Launch Day 3-53 World Geography Lesson 3.2 Introduction to Engineering Design Lesson 3.3 English Language Arts Lesson 3.4 Introduction to Engineering Design 54 Unit 2 Reverse Engineering What is Reverse Engineering? • Discover the technological principles of a device, object or system through analysis of its structure, function and operation • Teardown, analyze, copy and/or redesign • Reverse engineering can be done on • • • • • • • Mechanical designs Software Microchips Automotive Consumer products Chemicals Electronics Major Academic Subject Topics and Content • English Language Arts • Writing humorous anecdotes • Writing technical descriptions and instructions • Social Studies • World History—Intelligence gathering during World War II • Science • Physical Science/Physics—Simple machines • Biology—Nature of science • Mathematics • Combinations and permutations Lesson and Subject Lesson Title Lesson 1 Introduction to Reverse Engineering Intro to Engineering Design Lesson 2 Precision Communication English Language Arts Lesson 3 Functional Analysis Intro to Engineering Design Lesson 4 The Design of Everyday Things English Language Arts Lesson 5 Cracking the Enigma World History Lesson 6 The Function of Codes Algebra I Lesson 7 Let Me Count the Ways Algebra I Lesson 8 Science As Reverse Engineering Science Lesson 9 Intro to Engineering Design Product Redesign 58 Implementing Integrated Curriculum • Common Planning Time • Curriculum Mapping and Lesson Discussion IED SEPTEMBER OCTOBER NOVEMBER DECEMBER JANUARY FEBRUARY MARCH APRIL DESIGN PROCESS SKETCHING DRAWING MEASURE MENT BASIC MODELS PUZZLE CUBE GEOMETRIC CONSTRAINTS ADV MODELING ASSEMBLY MODELING FUNCTIONAL ANALYSIS REVERSE ENGIN MENDEL’S LAWS MOLECULAR BIOLOGY BIOTECH ECOLOGY POPULAT’N GENETICS ADAPTATION SPECIATION PHYSIOLOGY HOMEO STASIS INFECTION IMMUNITY SPECTRO SCOPY WEATHER ELECTICITY MAGNETISM ENERGY & WAVES SIMPLE MACHINES CHEMISTRY QUADRATIC FUNCTIONS AND EQUATIONS RATIONAL FUNCTIONS AND EQUATIONS PERSUSIVE WRITING TO KILL A MOCKINGBIRD TIMED ESSAYS TOTALI TARIANISM WW II POST WW II SIMILARITY RIGHT TRIANGLE TRIG CIRCLES CELL BIOLOGY BIO PHYS SCI MEIOSIS FERTILIZATION MEASURING THE UNIVERSE SOLAR SYSTEM HISTORICAL FIGURES FORCES PROPERTIES OF MATTER PLATE TECTONICS REAL NUMBERS SOLVE LINEAR EQUATIONS AND INEQUALITIES GRAPH AND INTERPRET LINEAR EQUATIONS SYSTEMS OF EXPONENTS SOLVING EQUATIONS AND POLY SYSTEMS OF AND NOMIALS EQUATIONS INEQUALITIES AUTO/ BIOGRAPHIES SHORT STORIES THE ODYSSEY ROMEO AND JULIET EXPOSITORY WRITING LITERARY RESPONSES NARRATIVE WRITING HIST WESTERN POLITICAL THOUGH RISE OF DEMOCRATIC IDEALS INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION IMPERIALISM AND COLONIALISM GEOM LINES, ANGLES, CONSTRUC TIONS INDUCTION DEDUCTION PROOFS TRIANGLES QUAD RILATERALS REVIEW ALG I ELA RESEARCH PAPER LITERARY RESPONSES WW I AREA 60 IED SEPTEMBER OCTOBER NOVEMBER DECEMBER JANUARY FEBRUARY MARCH APRIL DESIGN PROCESS SKETCHING DRAWING MEASURE MENT BASIC MODELS PUZZLE CUBE GEOMETRIC CONSTRAINTS ADV MODELING ASSEMBLY MODELING FUNCTIONAL ANALYSIS REVERSE ENGIN MENDEL’S LAWS MOLECULAR BIOLOGY BIOTECH ECOLOGY POPULAT’N GENETICS ADAPTATION SPECIATION PHYSIOLOGY HOMEO STASIS INFECTION IMMUNITY SPECTRO SCOPY WEATHER ELECTICITY MAGNETISM ENERGY & WAVES SIMPLE MACHINES CHEMISTRY QUADRATIC FUNCTIONS AND EQUATIONS RATIONAL FUNCTIONS AND EQUATIONS PERSUSIVE WRITING TO KILL A MOCKINGBIRD TIMED ESSAYS TOTALI TARIANISM WW II POST WW II SIMILARITY RIGHT TRIANGLE TRIG CIRCLES CELL BIOLOGY BIO PHYS SCI MEIOSIS FERTILIZATION MEASURING THE UNIVERSE SOLAR SYSTEM HISTORICAL FIGURES FORCES PROPERTIES OF MATTER PLATE TECTONICS REAL NUMBERS SOLVE LINEAR EQUATIONS AND INEQUALITIES GRAPH AND INTERPRET LINEAR EQUATIONS SYSTEMS OF EXPONENTS SOLVING EQUATIONS AND POLY SYSTEMS OF AND NOMIALS EQUATIONS INEQUALITIES AUTO/ BIOGRAPHIES SHORT STORIES THE ODYSSEY ROMEO AND JULIET EXPOSITORY WRITING LITERARY RESPONSES NARRATIVE WRITING HIST WESTERN POLITICAL THOUGH RISE OF DEMOCRATIC IDEALS INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION IMPERIALISM AND COLONIALISM GEOM LINES, ANGLES, CONSTRUC TIONS INDUCTION DEDUCTION PROOFS TRIANGLES QUAD RILATERALS REVIEW ALG I ELA RESEARCH PAPER LITERARY RESPONSES WW I AREA 61 IED SEPTEMBER OCTOBER NOVEMBER DECEMBER JANUARY FEBRUARY MARCH APRIL DESIGN PROCESS SKETCHING DRAWING MEASURE MENT BASIC MODELS PUZZLE CUBE GEOMETRIC CONSTRAINTS ADV MODELING ASSEMBLY MODELING FUNCTIONAL ANALYSIS REVERSE ENGIN MENDEL’S LAWS MOLECULAR BIOLOGY BIOTECH POPULAT’N GENETICS ADAPTATION SPECIATION ECOLOGY PHYSIOLOGY HOMEO STASIS INFECTION IMMUNITY SPECTRO SCOPY WEATHER ELECTICITY MAGNETISM ENERGY & WAVES SIMPLE MACHINES CHEMISTRY SOLVING SYSTEMS OF EQUATIONS QUADRATIC FUNCTIONS AND EQUATIONS RATIONAL FUNCTIONS AND EQUATIONS CELL BIOLOGY BIO PHYS SCI MEIOSIS FERTILIZATION MEASURING THE UNIVERSE REVIEW ALG I ELA REAL NUMBERS AUTO/ BIOGRAPHIES EXPOSITORY WRITING SOLAR SYSTEM SOLVE LINEAR EQUATIONS AND INEQUALITIES RESEARCH PAPER HIST WESTERN POLITICAL THOUGH RISE OF DEMOCRATIC IDEALS GEOM LINES, ANGLES, CONSTRUC TIONS INDUCTION DEDUCTION PROOFS HISTORICAL FIGURES PLATE TECTONICS FORCES PROPERTIES OF MATTER GRAPH AND INTERPRET LINEAR EQUATIONS SYSTEMS OF EQUATIONS AND INEQUALITIES EXPONENTS AND POLY NOMIALS SHORT STORIES THE ODYSSEY ROMEO AND JULIET LITERARY RESPONSES NARRATIVE WRITING INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION IMPERIALISM AND COLONIALISM TRIANGLES QUAD RILATERALS LITERARY RESPONSES WW I AREA PERSUSIVE TO KILL A WRITING MOCKINGBIRD TIMED ESSAYS TOTALI TARIANISM WW II POST WW II SIMILARITY RIGHT TRIANGLE TRIG CIRCLES 62 IED SEPTEMBER OCTOBER NOVEMBER DECEMBER JANUARY FEBRUARY MARCH APRIL DESIGN PROCESS SKETCHING DRAWING MEASURE MENT BASIC MODELS PUZZLE CUBE GEOMETRIC CONSTRAINTS ADV MODELING ASSEMBLY MODELING FUNCTIONAL ANALYSIS REVERSE ENGIN MENDEL’S LAWS MOLECULAR BIOLOGY BIOTECH POPULAT’N GENETICS ADAPTATION SPECIATION ECOLOGY PHYSIOLOGY HOMEO STASIS INFECTION IMMUNITY SPECTRO SCOPY WEATHER ELECTICITY MAGNETISM ENERGY & WAVES SIMPLE MACHINES CHEMISTRY SOLVING SYSTEMS OF EQUATIONS QUADRATIC FUNCTIONS AND EQUATIONS RATIONAL FUNCTIONS AND EQUATIONS CELL BIOLOGY BIO PHYS SCI MEIOSIS FERTILIZATION MEASURING THE UNIVERSE REVIEW ALG I ELA REAL NUMBERS AUTO/ BIOGRAPHIES EXPOSITORY WRITING SOLAR SYSTEM SOLVE LINEAR EQUATIONS AND INEQUALITIES RESEARCH PAPER HIST WESTERN POLITICAL THOUGH RISE OF DEMOCRATIC IDEALS GEOM LINES, ANGLES, CONSTRUC TIONS INDUCTION DEDUCTION PROOFS HISTORICAL FIGURES PLATE TECTONICS FORCES PROPERTIES OF MATTER GRAPH AND INTERPRET LINEAR EQUATIONS SYSTEMS OF EQUATIONS AND INEQUALITIES EXPONENTS AND POLY NOMIALS SHORT STORIES THE ODYSSEY ROMEO AND JULIET LITERARY RESPONSES NARRATIVE WRITING INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION IMPERIALISM AND COLONIALISM TRIANGLES QUAD RILATERALS LITERARY RESPONSES WW I AREA PERSUSIVE TO KILL A WRITING MOCKINGBIRD TIMED ESSAYS TOTALI TARIANISM WW II POST WW II SIMILARITY RIGHT TRIANGLE TRIG CIRCLES 63 Implementing Integrated Curriculum • Curriculum Mapping and Lesson Discussion • • • Revising lessons: This lesson doesn’t fit my scope and/or standards Removing lessons: We don’t have that subject teacher on our team Adding lessons: My subject isn’t represented in the unit • Common Planning Time! • We don’t have time/structure to fit this into our school year • • Single subject integration Parallel/Paired integration 64 T HANKS FOR A TTENDING ! Download curriculum materials from the NAF curriculum library Contact us with questions and suggestions! Pier Sun Ho psunho@ConnectEdCalifornia.org