Document 9827052
advertisement

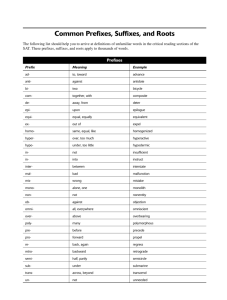
Medical Terminology Health Science 1 Objectives Identify basic medical abbreviations selected from a standard list Define prefixes, suffixes and word roots selected from a list of words Spell and pronounce medical terms correctly Define, pronounce, and spell all the key terms Abbreviations Shortened forms of words, usually just letters Can be used by themselves or several abbreviations combined to give orders or directions. Common Ex. : AM which means morning, and PM which means afternoon or evening BR c BRP, FFl qh, VS qid Which means “bed rest with bathroom privileges, force fluids every hour, vital signs four times a day” Abbreviations Much easier using abbreviations than writing out the corresponding details For Example: NPO 8 pm, To Lab for CBC, BUN, and FBS “Nothing by mouth after 8:00 in the evening, to the laboratory for a complete blood count, blood urea nitrogen, and fasting blood sugar Abbreviations Different abbreviations may be used in different facilities and in different parts of the Responsibility of the health care worker to learn the meanings of the abbreviations used in the agencies where they are employed Notice no periods are used P.M. vs PM Abbreviations Best ways to learn Abbreviations: Make flash cards Use index cards Write Abbreviation on one side – meaning on the opposite side Interpreting Word Parts By breaking a word into parts, it is sometimes possible to figure out their meanings. Prefix: a syllable or word placed at the beginning of a word Suffix: a syllable or word placed at the end of a word Word Roots: main words or parts to which prefixes and suffixes can be added Interpreting Word Parts Prefix Usually serves to further define the word root Suffix Usually describes what is happening to the word root Ex. Pseudoappendicities Pseudo (prefix) means false Appendix (word root) Itis (suffix) means inflimmation of Interpreting Word Parts When prefixes, word roots and suffixes are joined together, vowels are frequently added: Common example: a, e, I, ia, io, o and u The vowels are not used if the word root or suffix begins with a vowel Ex: encephal means brain. When its combined with itis, meaning inflammation, there is NO vowel for encephalitis When combined with gram, meaning tracing or record, the vowel “o” is added for encephalogram Interpreting Word Parts Hepat means liver. When it is combined with itis, the vowel is NOT used for hepatitis Inflammation of the liver When it is combined with megaly, meaning enlarged, the vowel “o” is added for hepatomegaly Means Enlarged Liver Interpreting Word Parts Best way to learn prefixes, suffixes and word roots: Flash cards!!!! Write prefixes, suffixes, and word roots from the list on each card (SPELLED CORRECTLY) Put definitions on the back Then combine: PERI + Cardi/o + Ectomy = Pericardiectomy Peri (surrounding) cardi/o (heart) ectomy (surgical removal) Pericardiectomy = surgical removal of a portion of the membrane surrounding the heart Summary Medical abbreviations and terminology are used in all health care occupations and facilities. In order to communicate effectively, health care workers must be familiar with common abbreviations and terminology. Medical terminology consists of the use of prefixes, suffixes, and word roots to create words. It would be impossible to memorize the meaning of every word. By learning common prefixes, suffixes, and word roots, however, a health care worker can break a word into parts to figure out the meaning.