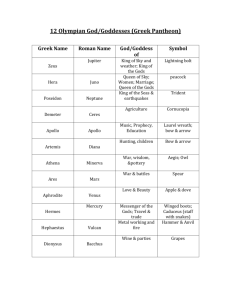
Gods and spirits
advertisement

Introduction Ghosts, ancestors, and vampires used to be human But gods and spirits are supernatural beings that may not have human origins Gods tend to have individual personalities and names and spirits are more less powerful and more localized Gods and Spirits Spirits can be individual (spirit guide, ancestor, shaman’s helper) or communal Gods tend to live in specific location outside of the earth while spirits live in the human world and interact with humans Can offer protection or punishment Offerings, rituals, sacrifices are meant to appease them The site of these rituals are at shrines Example: Vision Quest In Native American cultures, the vision quest is an individualistic ritual in which a person finds his or her spirit guide through ASC The Ojibwa tribe has a boy at puberty sit on a tall platform and fast until he has a vision This vision guide shows what path his life will take A successful vision ushers him in to adulthood The berdache were given their position in this way or in a dream Example: Jinn Islamic In the Qur’an, there are three types of beings: humans (clay), angels (light), and jinns (fire) Can have human or animal form, or be invisible They have lives (born, marry, die) Can have special relationship with a human and can have special powers, but they can also be troublemakers The genie in Aladdin is a jinn Example: Sudan Spirit possession Type of jinn called a zar, who causes illness and is associated with blood and fertility Through spirit possession it can enter a woman’s body Women in this culture are very anxious about their fertility because it determines their place in society Problems with fertility are blamed in zar and rituals help draw them out of those possessed Angels and Demons These appear in Christianity, Judaism, and Islam They are mediators between God and humans Angels come not from the Bible but from Saint Dionysus, who had a hierarchy of angels Angels and Demons Angels and Demons While angels are good beings that help God, demons are evil beings that are associated with the devil Involved in temptation and human evil 68% of Americans in 2007 said they believe that angels and demons are real According to the Bible, Satan was once an angel who fell from Heaven Between 15th-17th centuries demonology was extremely popular Incubus and succubus were male and female demons that have sex with humans while they sleep Angels and Demons Exorcism This is a Christian practice in which religious specialists cure a demonic possession In the Catholic Church, the priest is told to be skeptical and look for other causes of behavior (mental illness) Exorcisms are rare and have become part of pop culture from the 1970s The Exorcist movies Gods Gods are more powerful than spirits Control nature Wind, rain, fertility… In cultures there can be one god up to more than 1000 gods Gods They are anthropomorphic and take on human form and personalities They can be influenced by offerings and sacrifices Behavior of humans is controlled by commandments from the god(s) Types of Gods The gods in a religious system is called a pantheon, which usually has a hierarchy with a supreme god at the top Specialized gods are attribute gods who control that specific thing Creator gods create the physical earth and living things on it Otiose gods are not directly involved in humans’ lives and therefore rituals are rarely performed to them Gods and Society Gods serve important role in society Take on social statuses such as mother, father, sister, son, etc. We relate to them and learn from their actions They model correct human behavior Gods and Society They also show status in the community Status can be ascribed (given based on family) or achieved (given based on achievement) Gods help people understand their place in society and can also help people accept their current status and work hard for a better afterlife or new life Goddesses Some scholars say that early human religions focused on fertility and therefore focused on goddess worship Early statues can Venus figures show exaggerated fertility As monotheism took hold, goddess worship declined Goddesses: Example Ishtar (Near East) Worldview: nature represented violent relationships between gods Ishtar had power over fate Sexuality and marriage were symbolic of her Connected to fertility of land Goddesses: Example Isis (Egypt) “Great Mother” and “Queen of Heaven” Represented family, motherhood Originally associated with royalty, she later was associated with nature 300 BCE began the Isis mystery religion (secret rites) Goddesses: Example Kali (Hindu) Associated with creativity and nature “Black One,” fierce, blood-thirsty But not evil: she is creation and destruction Represents transformation Goddesses: Example Mary (Catholic) Medieval periods she was set above saints and second to God “Queen of Heaven” Bore the son of God Protector and sustainer Monotheism Most religions in the world and through history were polytheistic Three major world religions are monotheistic: Judaism, Christianity, and Islam All believe in one God who is omnipotent (allpowerful), omniscient (all-knowing), and omnibenevolent (all-good) Judaism Believes the Jews have been chosen by God as having a special relationship with him This may have developed from a polytheistic religion Some say the many different names for God in the Hebrew Bible are actually names of different gods Moses made a covenant with God through the Ten Commandments The commandment “though shalt not worship false idols” or “though shalt not have other gods before me” may also point to polytheism Judaism God is very anthropomorphic but can also appear in non-human form (burning bush) He is often cruel and violent and also forgiving and compassionate God is seen as a subjective and private path for the individual to discover Christianity Branched out of Judaism People were expecting a human Messiah Jesus never claimed to be divine and it was not until the Council of Nicea in the 4th century that he was voted as divine and was God in a human form Jesus is mediator between God and humans and will lead people back to God Therefore, he is salvation Christianity Idea of the Trinity God (Father, creator), Jesus (Son, also God), Holy Ghost (spirit of God after Jesus’ death) The concept of the Trinity causes problems for some Christians because it seems polytheistic Islam Centered on prophet Mohammad, in Mecca (also location of Kaaba, a mysterious, huge cubed shrine said to have been built by Abraham and Ishmael) Allah (God) is identical to Jewish and Christian God Islam sought to restore authentic monotheism, which the other two religions had strayed from Mohammad is the way to do this Islam Mohammad was given the word of God to recite from an angel and this became the Qur’an People are encouraged to look for signs of God’s goodness and power in the world Humans can find peace by surrendering completely to God Atheism Historically this meant not accepting the current conception or religious practice of God Scientific developments in the 17th-18th centuries led people to question how the world worked and how their religious beliefs did not seem to be valid to explain this Many atheists also do not condemn the idea of God, only the idea of a cruel, punishing God or the horrible things people do in the name of religion Many people identify as agnostic, which says the existence of God is unprovable HW #4 Select two events connected to religion (next slide) and discuss how fundamentalist religious beliefs can be dangerous. Give details and examples. Select three of the religious views presented in lecture and identify common themes they share. How would seeing similarities in religions help make the world a more peaceful place? HW #4 The Holocaust September 11th/Suicide bombers The Crusades Bombing of abortion clinics Spanish Inquisition